Summary
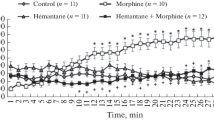
Diazepam, injected into the lateral ventricles reduced the antinociceptive effect of morphine in rats, as measured by the tail-flick method. Specific antagonists of diazepam (Ro 15-1788 and Ro 15-3505) had no effect themselves but prevented inhibition by diazepam of morphine antinociception. Furthermore, the action of diazepam was partially reversed by intracerebroventricular injection of bicuculline or caffeine. These findings support the view that the depressant effect of diazepam on morphine antinociception is specific and GABAergic in nature and that some actions of diazepam are also mediated via the purinergic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaffer FB, De Balbian Werster F, Hall S, Long CJ, D'Encarnacao P (1970) A simple and inexpensive cannula technique for chemical stimulation of the brain. Physiol Behav 5:119–121
Armitage P (1974) Statistical methods in medical research. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London, p 394
Brady LS, Mansbach RS, Skurdal DN, Muldoon SM, Barrett JE (1984) Reversal of the antinociceptive effects of centrally-administered morphine by the benzodiazepine recoptor antagonist Ro 15-1788. Life Sci 35:2593–2600
Campbell RC (1974) Statistics of biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 61
Christmas AJ, Maxwell DR (1970) A comparison of the effects of some benzodiazepines and other drugs on aggressive and exploratory behavior in mice and rats. Neuropharmacology 9:17–29
D'Amour EF, Smith DL (1941) A method for determining loss of pain sensation. J Pharmac Exp Ther 72:74–79
De Feudis FV (1983) Central GABA-ergic system and analgesia. Drug Development Research 3:1–15
Fan SG, Qu ZC, Han JS (1982) GABA: antagonistic effect of electroacupunture analgesia and morphine analgesia in the rat. Life Sci 31:1225–1228
Fennessy MR, Sawynok J (1973) The effect of benzodiazepines on the analgesic effect of morphine and sodium salicylate. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 204:77–85
Gluckman MI (1965) Pharmacology of oxazepam (Serax) a new antianxiety agent. Curr Ther Res 7:721–740
Gupta SK, Gaitonde BB (1964) Analgesic activity of a new quinoline derivative Ro 4-1788. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 8:27–32
Haefely W (1983) Antagonists of benzodiazepines: functional aspects. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) Benzodiazepine recognition ligands: Biochemistry and Pharmacology. Raven Press NY, pp 73–93
Hunkeler W, Mohler H, Pieri I, Pole P, Bonetti EP, Cumin R, Schaffner R, Haefely W (1981) Selective antagonists of benzodiazepine. Nature 290:514–516
Leitner DS, Kelly DD (1984) Potentiation of cold swim stress analgesia in rats by diazepam. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:813–816
Mantegazza P, Parenti M, Tammiso R, Vita P, Zambotti F, Zonta N (1982) Modification of the antinociceptive effect of morphine by centrally administered diazepam and midazolam. Br J Pharmacol 75:569–572
Mantegazza P, Tammiso R, Zambotti F, Zecca L, Zonta N (1984) Purine involvement in morphine antinociception. Br J Pharmacol 83:883–888
Phillis JW, Edstrom JP, Kostopoulos GK, Kirkpatrick JR (1979) Effects of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on synaptic transmission in the cerebral cortex. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 57:1289–1312
Phillis JW, Wu PH (1981) The role of adenosine and its nucleotides in central synaptic transmission. Prog Neurobiol 16:187–239
Pole P, Bonetti EP, Pieri I, Cumin R, Angioi RM, Mohler H, Haefely WE, (1981) Caffeine antagonizes several effects of diazepam. Life Sci 28:2265–2275
Randall LO, Kappell B (1973) Pharmacological activity of some benzodiazepines and their metabolites. In: Garattini S, Mussini E, Randall LO (eds) The benzodiazepines. Raven Press, New York, pp 27–51
Randall LO, Scheckel CL, Pool W (1970) Pharmacology of medazepam and metabolites. Archs Int Pharmacodyn Ther 185:135–148
Romandini S, Samanin R (1984) Muscimol injections in the nucleus raphe dorsalis block the antinociceptive effect of morphine in rats: apparent lack of 5-hydroxytryptamine involvement in muscimol's effect. Br J Pharmacol 81:25–29
Weiss H (1969) Morphine antagonistic effect of chlordiazepoxide (Librium). Experientia 25:381
Yamamoto H, McCain WH, Izumi K, Misawa S, Way EL (1981) Effects of aminoacids, especially taurine and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on analgesia and calcium depletion induced by morphine in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 71:117–184
Zambotti F, Zonta N, Parenti M, Tammiso R, Vicentini L, Conci F, Mantegazza P (1982) Periaqueductal gray matter involvement in muscimol-induced decrease of morphine antinociception. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 318:368–369
Zonta N, Zambotti F, Vicentini L, Tammiso R, Mantegazza P (1981) Effects of some GABA-mimetic drugs on the antinociceptive activity of morphine andβ-endorphin in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 316:231–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by M.P.I. grant.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zambotti, F., Zonta, N., Tammiso, R. et al. Reversal of the effect of centrally-administered diazepam on morphine antinociception by specific (Ro 15-1788 and Ro 15-3505) and non-specific (bicuculline and caffeine) benzodiazepine antagonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 333, 43–46 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569658
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569658