Summary
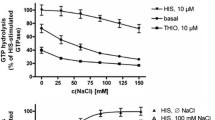
Equilibrium binding isotherms of [3H]diprenorphine in membranes from NG 108-15 cells are consistent with a homogenous population of binding sites. Upon addition of Na+, Mg2+ and GTP, only a 2-fold reduction in affinity with a minor decrease in the number of sites is observed. Dissociation curves of [3H]diprenorphine, however, are clearly biphasic: in the absence of Na+, Mg2+ and GTP, 80% of the bound ligand dissociates slowly with at 1/2 of 100 min, and only 20% rapidly (t 1/2 4.5 min). In the presence of Mg2+, nearly all the binding is found in the slowly dissociating form. Upon the addition of either Na+ or GTP, 20–30% of the binding dissociates more rapidly. The rate constant of the rapidly dissociating form generated by Na+, however, is 2.5 times greater than that induced by the presence of GTP. Thus, the addition of both, Na+ and GTP, converts about 80% of the receptor into a very fast dissociating form (t 1/2 1.7 min).
Exposure of intact cells to pertussis toxin (10 ng/ml) or treatment of membranes with N-ethyl maleimide (500 μM), strongly reduces the proportion of the slowly dissociating component. Following these treatments, the effect of GTP is reduced or abolished, but that of Na+ remains unaffected.
We conclude from these data that the effects of Na+ and GTP are not only distinct in site but also in mechanism of action and that there are three forms of opioid receptors that can be differentiated by their kinetic properties. The slowly dissociating receptor form requires a functional N unit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang K-J, Miller RJ, Cuatrecasas P (1978) Interaction of enkephalin with opiate receptors in intact cultured cells. Mol Pharmacol 14:961–970
Chang K-J, Hazum E, Killian A, Cutrecasas P (1981) Interactions of ligands with morphine and enkephalin receptors are differentially affected by guanine nucleotide. Mol Pharmacol 20:1–7
Childers SR, Snyder SH (1980) Differential regulation by guanine nucleotides of opiate agonist and antagonist receptor interactions. J Neurochem 34:583–593
Childers S (1984) Interaction of opiate receptor binding sites and guanine nucleotide regulatory sites: selective protection from N-ethylmaleimide. J Pharm Exp 230:684–691
Costa T, Aktories K, Schultz G, Wüster M (1983) Pertussis toxin decreases opiate receptor binding and adenylate cyclase inhibition in a neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cell line. Life Sciences 33:219–222
Costa T, Wüster M, Gramsch C, Herz A (1985) Multiple states of opioid receptors may modulate adenylate cyclase in intact neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. Mol Pharmacol 28:146–154
De Léan A, Munson PJ, Rodbard D (1978) Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Phys 235:E97-E102
De Léan A, Stadel JM, Lefkowitz J (1980) A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupledβ-adrenoceptor. J Biol Chem 255:7108–7117
Hamprecht B (1977) Structural electrophysiological, biochemical and pharmacological properties of neuroblastoma x glioma cell hybris in cell culture. Int Rev Cytol 49:99–170
Hsia JA, Moss J, Hewlett EL, Vaughan M (1984) ADP-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase by pertussis tosin. J Biol Chem 259:1086–1090
Koski G, Streaty RA, Klee WA (1982) Modulation of sodium-sensitive GTPase by partial opiate agonists. J Biol Chem 257:14035–14040
Krumins SA, Lutz RA, Costa T, Rodbard D (1986) Interaction of dimeric and monomeric enkephalins with NG 108-15 hybrid cells: A kinetic analysis. Neurochem Res 11 (in press)
Kurose H, Katada T, Amano T, Ui M (1983) Specific uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, of negative signal transduction viaα-adrenergic, cholinergic and opiate receptors in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem 258:4870–4875
Larsen NE, Mullikin-Kilpatrick D, Blume AJ (1981) Two different modifications of the neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid opiate receptors induced by N-ethylmaleimide. Mol Pharmacol 20: 255–262
Law P-Y, Loh HH (1978)3H-Leu5-Enkephalin specific binding to synaptic membrane-comparison with [3H]dihydromorphine and3H-naloxone. Res Comm Chem Path Pharm 21:409–434
Law P-Y, Hom DS, Loh HH (1985) Multiple affinity states of opiate receptor in neuroblastoma x glioma NG 108-15 hybrid cells. J Biol Chem 260:3561–3569
Limbird LE, Speck JL (1983) N-Ethylmaleimide, elevated temperature, and digitonin solubilization eliminate guanine nucleotide but not sodium effects on human plateletα 2-adrenergic receptor — agonist interactions. J Cyc Nucl Prot Phos Res 9:191–201
McMahon KK, Hosey MM (1985) Agonist interactions with Cardiac muscarinic receptors. Effects of Mg2+, guanine nucleotides, and monovalent cations. Mol Pharmacol 28: 400–409
Munson PJ, Rodbard D (1980) Ligand: A versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem 107:220–239
Ott S, Costa T, Wüster M, Hietel B, Herz A (1986) Target size analysis of opioid receptors. No difference between receptor types, but discrimination between two receptor states. FEBS Eur J Biochem 932:1–10
Petersen GL (1983) Determination of total protein. In: Hirs CHW, Timasheff SN (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 91, Enzyme structure. Academic Press, New York, pp 95–119
Pryhuber KG, Roth BL, Coscia CJ (1982) Demonstration of a slowly dissociating form of bovine hippocampal synaptic membrane opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 83:47–53
Sadée W, Pfeiffer A, Herz A (1982) Opiate receptor: Multiple effects of metal ions. J Neurochem 39:659–667
Sharma SK, Nirenberg M, Klee WA (1975) Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:590–594
Smith McM, Harden TK (1984) Modification of receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase in NG 108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma cells by N-ethylmaleimide. J Pharmacol Exper Therap 228:425–433
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ott, S., Costa, T. & Herz, A. Effects of sodium and GTP on the binding kinetics of [3H]diprenorphine in NG 108-15 cell membranes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 334, 444–451 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569384
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569384