Abstract
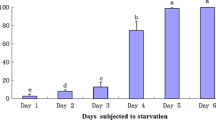
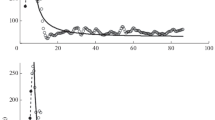
The influence of starvation on respiration (R), dry weight (W), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), and energy content (E; calculated fromC) of spider crab (Hyas araneus L.) larvae was studied in the laboratory. In all larval stages (zoea I and II, megalopa)W increased during postmoult, independent of food, and decreased subsequently. The final reduction inW after continued starvation increased from stage to stage (9, 13, and 20% respectively), but it was always much lower than the decrease inC (44 to 52%),N (42 to 46%),H (50 to 58%), andE (53 to 62%). Individual (R) and weight-specific respiration rates (QO 2) were reduced by 83 to 88%. The time-dependence of these reductions in metabolism and biomass as well as the rates of change in all parameters studied were described with non-linear regression models and differential equations, respectively. Rates and total amounts of energy lost during starvation were independently calculated fromC andR values, and similar results were mostly obtained. Only in the megalopa stage was there a conspicuous difference between the two estimates: higher losses were calculated fromR. This shows that further (biochemical) data are required for a more complete understanding of the energetics of this stage. Estimates of total protein (fromN) and lipid (fromC) suggest that both constituents serve as metabolic substrates during starvation, but most of the energy originates from the breakdown of protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Anger, K. and K. K. C. Nair: Laboratory experiments on the larval development ofHyas araneus (Decapoda, Majidae). Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters.32, 36–54 (1979)
Anger, K. and R. R Dawirs: Influence of starvation on the larval development ofHyas araneus (Decapoda, Majidae). Helgoländer Meeresunters.34, 287–311 (1981)
Anger, K. and R. R. Dawirs: Elemental composition (C, N, H) and energy in growing and starving larvae ofHyas araneus (Decapoda, Majidae). Fish. Bull. U.S.80, 419–433 (1982)
Anger, K., N. Laasch, C. Püschel and F. Schorn: Changes in biomass and chemical composition of spider crab (Hyas araneus) larvae reared in the laboratory. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.12, 91–101 (1983)
Anger, K. and C. C. Jacobi: Respiration and growth ofHyas araneus L. larvae (Decapoda: Majidae) from hatching to metamorphosis. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol.88, 257–270 (1985)
Barclay, M. C., W. Dall and D. M. Smith: Changes in lipid and protein during starvation and the moulting cycle in the tiger prawn,Penaeus esculentus Haswell. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol.68, 229–244 (1983)
Capuzzo, J. M. and B. A. Lancaster: Some physiological and biochemical considerations of larval development in the American lobster,Homarus americanus Milne-Edwards. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol.40, 53–62 (1979)
Conover, R. J. Transformation of organic matter.In: Marine ecology, 4. Dynamics, pp 221–499. Ed by O. Kinne. Chichester, New York, Brisbaine, Toronto: John Wiley & Sons 1978
Dawirs, R. R.: Elemental composition (C, N, H) and energy in the development ofPagurus bernhardus (Decapoda: Paguridae) megalopa. Mar. Biol.64, 117–123 (1981)
Dawirs, R. R.: Respiration, energy balance and development during growth and starvation ofCarcinus maenas L. larvae (Decapoda: Portunidae). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol.69, 105–128 (1983)
Dawirs, R. R.: Respiratory metabolism ofPagurus bernhardus (Decapoda: Paguridae) megalopa. Mar. Biol.83, 219–223 (1984)
Giese, A. C.: Lipids in the economy of marine invertebrates. Physiol. Rev.46, 244–298 (1966)
Gnaiger, E.: Calculation of energetic and biochemical equivalents of respiratory oxygen consumption.In: Polarographic oxygen sensors, pp 337–345. Ed by E. Gnaiger and H. Forstner. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1983
Gnaiger, E. and G. Bitterlich: Proximate biochemical composition and caloric content calculated from elemental CHN analysis: a stoichiometric concept. Oecologia62, 289–298 (1984)
Grasshoff, K.: Methods of sea water analysis, 317 pp. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1976
Hiller-Adams, P. and J. J. Childress: Effects of prolonged starvation on O2 consumption, NH +4 excretion, and chemical composition of the bathypelagic mysidGnathophausia ingens. Mar. Biol.77, 119–127 (1983a)
Hiller-Adams, P. and J. J. Childress: Effects of feeding, feeding history, and food deprivation on respiration and excretion rates of the bathypelagic mysidGnathophausia ingens. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole165, 182–196 (1983b)
Holland, D. L.: Lipid reserves and energy metabolism in the larvae of benthic marine invertebrates.In: Biochemical and biophysical perspectives in marine biology, Vol. 4, pp 85–123. Ed. by D. C. Malins and J. R. Sargent. London: Academic Press 1978
Ikeda, T.: Changes in respiration rate and in composition of organic matter inCalanus cristatus (Crustacea Copepoda) under starvation. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ.21, 280–298 (1971)
Ikeda, T.: Nutritional ecology of marine zooplankton. Mem. Fac. Fish Hokkaido Univ.22, 1–97 (1974)
Ikeda, T.: The effect of laboratory conditions on the extrapolation of experimental measurements to the ecology of marine zooplankton. IV. Changes in respiration and excretion rates of boreal zooplankton species maintained under fed and starved conditions. Mar. Biol.41, 241–252 (1977)
Ikeda, T. and H. R. Skjoldal: The effect of laboratory conditions on the extrapolation of experimental measurements to the ecology of marine zooplankton. VI. Changes in physiological activities and biochemical components ofAcetes sibogae australis andAcartia australis after capture. Mar. Biol.58, 285–293 (1980)
Jacobi, C. C. and K. Anger: Growth and respiration during the larval development ofHyas coarctatus (Decapoda: Majidae). Mar. Biol.87, 173–180 (1985)
Le Borgne, R. P.: Influence of duration of incubation on zooplankton respiration and excretion results. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol.37, 127–137 (1979)
Lemcke, H. W. and W. Lampert: Veränderungen im Gewicht und der chemischen Zusammensetzung vonDaphnia pulex im Hunger. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl.48, 108–113 (1975)
Mayzaud, P.: Respiration and nitrogen excretion of zooplankton. II. Studies of the metabolic characteristics of starved animals. Mar. Biol.21, 19–28 (1973)
Mayzaud, P.: Respiration and nitrogen excretion of zooplankton. IV. The influence of starvation on the metabolism and the biochemical composition of some species. Mar. Biol.37, 47–58 (1976)
McNamara, J. C., G. S. Moreira and P. S. Moreira: Respiratory metabolism ofMacrobrachium olfersii (Wiegmann) zoeae during the moulting cycle from eclosion to first ecdysis. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole159, 692–699 (1980)
Regnault, M.: Respiration and ammonia excretion of the shrimpCrangon crangon L.: metabolic response to prolonged starvation. J. comp. Physiol.141, 549–555 (1981)
Salonen, K., J. Sarvala, I. Hakala and M.-L. Viljanen: The relation of energy and organic carbon in aquatic invertebrates. Limnol. Oceanogr.21, 724–730 (1976)
Sasaki, G. C.: Biochemical changes associated with embryonic and larval development in the American lobster, 458 pp. Thesis, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 1984
Seiring, J. V. and C. C. E. Hopkins: Analyses of starvation-stress on respiration rates, and body weight and composition in the deep-water prawnPandalus borealis from Balsfjorden Northern Norway, measured during mid-summer in a laboratory experiment.In: Marine biology of polar regions and effects of stress on marine organisms, pp 287–298. Ed. by J. S. Gray and M. E. Christiansen. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons 1985
Skjoldal, H. R., U. Bråmstedt, J. Klinken and A. Laing: Changes with time after capture in the metabolic activity of the carnivorous copepodEuchaeta norvegica Boeck. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol.83, 195–210 (1984)
Speck, U. and K. Ulrich: Der Abbau körpereigener Substanzen in dem FlußkrebsOrconectes limosus während des Hungers. Z. vergl. Physiol.63, 410–414 (1969)
Wallace, J. C.: Feeding, starvation and metabolic rate in the shore crabCarcinus maenas. Mar. Biol.20, 277–281 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (An 145/1-1)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anger, K. Changes of respiration and biomass of spider crab (Hyas araneus) larvae during starvation. Mar. Biol. 90, 261–269 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569137
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569137