Summary
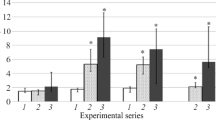
The binding of salicylate, sulphadiazine and phenylbutazone in whole serum of patients with alcohol-induced liver disease has been compared to that of chronic alcoholics with no evidence of liver disease, and normal healthy subjects. Binding of all three drugs was normal in the chronic alcoholic group, but decreased in patients with alcoholic liver disease. In subjects with alcoholic hepatitis, this decrease appeared to be correlated with variations in serum bilirubin and albumin levels. These observations may be of clinical relevance to the distribution of drugs in alcoholic patients with accompanying hepatic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affrime, M., Reidenberg, M. M.: The binding of drugs to plasma from patients with cirrhosis. Pharmacologist15, 207 (1973)
Affrime, M., Reidenberg, M. M.: The protein binding of some drugs in plasma from patients with alcoholic liver disease. Europ. J. Clin. Pharmacol.8, 267–269 (1975)
Dromgoole, S. H.: The binding capacity of albumin and renal disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.191, 318–323 (1974)
Hooper, W. D., Bochner, F., Eadie, M. J., Tyrer, J. H.: Plasma protein binding of diphenylhydantoin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.15, 276–282 (1974)
Hooper, W. D., Dubetz, D. K., Bochner, F., Cotter, L. M., Smith, G. A., Eadie, M. J., Tyrer, J. H.: Plasma protein binding of carbamazepine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.17, 433–440 (1975)
Koch-Weser, J.: Serum drug concentrations as therapeutic guides. New Eng. J. Med.287, 222–231 (1972)
Olsen, G. D., Bennett, W. M., Porter, G. A.: Morphine and phenytoin binding to plasma protein in renal and hepatic failure. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.17, 677–685 (1975)
Powell, L. W., Axelsen, E.: Corticosteroids in liver disease: Studies on the biological conversion of prednisone to prednisolone and plasma protein binding. Gut13, 690–696 (1972)
Reidenberg, M. M.: Effect of disease states on plasma protein binding of drugs. Med. Clin. N. Amer.58, 1103–1109 (1974)
Reidenberg, M. M., Affrime, M.: Influence of disease states on binding of drugs to plasma proteins. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.226, 115–126 (1973)
Thiessen, J. J., Sellers, E. M., Denbeigh, P., Dolman, L.: Plasma protein binding of diazepam and tolbutamide in chronic alcholics. J. Clin. Pharmacol.16, 345–351 (1976)
Wallace, S., Brodie, M. J.: Decreased drug binding in serum from patients with chronic hepatic disease. Europ. J. Clin. Pharmacol.9, 429–432 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brodie, M.J., Boobis, S. The effects of chronic alcohol ingestion and alcoholic liver disease on binding of drugs to serum proteins. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13, 435–438 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566322
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566322