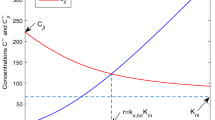
Summary
A constant plasma drug concentration can be achieved and maintained by the intravenous administration of an initial bolus loading dose in conjunction with a constant rate and an exponential intravenous drug infusion. The drug input required to achieve a constant plasma drug concentration is derived without making any assumptions about the nature of drug distribution within the body or elimination from the body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adgey, A.A.J., Geddes, J.J., Webb, S.W., Allen, J.D., James, R.G.G., Zaidi, S.A., Pantridge, J.F.: Acute phase of myocardial infarction. Lancet1971 II, 501–504
Aps, C., Bell, J.A., Jenkins, B.S., Poole-Wilson, P.A., Reynold, F.: Logical approach to lignocaine therapy. Brit. med. J.1976 I, 13–15
Bellet, S., Roman, L., Kostis, J.B., Fleischmann, D.: Intramuscular lidocaine in the therapy of ventricular arrhythmias. Amer. J. Cardiol.27, 291–293
Bennett, M.A., Wilner, J.M., Pentecost, B.L.: Controlled trial of lignocaine in the prophylaxis of ventricular arrhythmias complicating myocardial infaction. Lancet1970 II, 909–911
Bischoff, K.D., Dedrick, R.L., Zahorko, D.S., Longstreth, J.A.: Methotrexate pharmacokinetics. J. pharm. Sci.60, 1128–1133 (1971)
Boundurant, S.: Problems of the pre-hospital phase of acute myocardial infarction. Amer. J. Cardiol.24, 612–161 (1969)
Boyes, R., Adams, M., Duce, B.R.: Oral absorbtion kinetics of lidocaine hydrochloride in dogs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.174, 174–178 (1970)
Darby, S., Bennett, M.A., Cruickshand, J.C., Pentecost, B.L.: Trial of combined intramuscular and intravenous lignocaine in prophylaxis of ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Lancet1972 I, 817–819
Foldes, F.F., Molloy, R., McNall, P.G., Koukal, L.R.: Comparison of the toxicity of intravenously given local anaesthetic agents in man. J. Amer. med. Ass.172, 1493–1498 (1960)
Gianelly, R., von der Groeben, J.O., Spivack, A.P., Harrison, D.C.: Effect of lidocaine on ventricular arrhythmias in patients with coronary heart disease. New Engl. J. Med.277, 1215–1219 (1967)
Jewitt, D.W., Kishon, Y., Thomas, M.: Lignocaine in the management of arrhythmias after acute myocardial infarction. Lancet1968 I, 266–270
Krüger-Thiemer, E.: Continuous intravenous infusion and multicompartment accumulation. Europ. J. Pharmacol4, 317–324 (1968)
McNeilly, R.H., Pemberton, J.: Duration of last attack in 998 fatal cases of coronary artery disease and its relation to possible cardiac resucitation. Brit. med. J.1968 III, 139–142
Price, H.L.: A dynamic concept of the distribution of thiopental in the human body. Anaesthesiology21, 40–45 (1960)
Price, H.L., Kovnat, P.J., Safer, B.S., Conner, E.H., Price, M.L.: The uptake of thiopental by body tissue and its relation to the duration of narcosis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.1, 16–22 (1960)
Rowland, M., Thomson, P.D., Guichard, A.G., Melmon, K.L.: Disposition kinetics of lidocaine in normal subjects. Annals. N.Y. Acad. Sci.179, 383–398 (1971)
Shen, D., Gibaldi, M.: A hypothesis for the rapid attainment and maintenance of lidocaine plasma levels. J. clin. Pharmacol.14, 339–344 (1974)
Spoerel, W.E., Thomas, A., Gerula, G.R.: Continuous epidural analgesia. Experience with mechanical injection devices. Canad. Anaesth. Soc. J.17, 37–51 (1970)
Vaughan, D.P.: Estimation of biological availability after oral drug administration when the drug is eliminated by urinary excretion and metabolism. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.27, 458–461 (1975)
Vaughan, D.P., Beckett, A.H.: An analysis of the inter-subject variation in the metabolism of pentazocine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.26, 789–798 (1974)
Vaughan, D.P., Mallard, D.J.H., Trainor, A., Mitchard, M.: General pharmacokinetic equations for linear mammillary models with drug absorption into peripheral compartments. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.8, 141–148 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaughan, D.P., Tucker, G.T. General derivation of the ideal intravenous drug input required to achieve and maintain a constant plasma drug concentration. Theoretical application to lignocaine therapy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 10, 433–440 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563080
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563080