Abstract
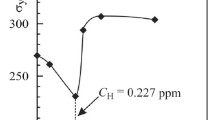
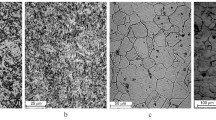
We investigate fatigue crack growth in cast heat-resistant steel pipes of reforming furnaces in a vacuum, in air, and in gaseous hydrogen in the temperature range 20 – 800°C. It is shown that the character and intensity of hydrogen-induced effects depend on temperature and loading amplitude. For the crack resistance threshold, we discovered the phenomenon of temperature inversion of these effects. Namely, the value of ΔK th in hydrogen increases with temperature up to 400°C and then decreases. Under high-amplitude loading, the influence of hydrogen manifests itself only in the acceleration of crack growth. The ambiguity in the influence of hydrogen on the plastic strain resistance of the material at the crack tip is analyzed on the basis of well-known physical concepts of the influence of hydrogen on the processes of generation and displacement of dislocations. The effects discovered in this work are explained by the realization of different fracture mechanisms and different types of hydrogen-induced effects under different conditions. Thus, at low temperatures (up to 400°C) and high ΔK, one observes a decrease in the tearing strength; the case of low temperatures and low ΔK is characterized by the shear fracture mechanism and the strengthening effect of hydrogen; for high temperatures (≥ 400°C) and low ΔK, the shear fracture mechanism is combined with a decrease in the plastic strain resistance under the influence of hydrogen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. M. Nykyforchyn, O. Z. Student, I. D. Skrypnyk, et al., “High-temperature crack-growth resistance of cast steel pipes of reforming furnaces,”Fiz-Khim. Mekh. Mater. 26, No. 2, 68–74 (1990).
O. N. Romaniv, H. M. Nykyforchyn, and B. N. Andrusiv, “Effect of crack closure and evaluation of the cyclic cracking resistance of structural alloys,”Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater. 19, No. 3, 47–61 (1983).
O. M. Romaniv, H. M. Nykyforchyn, O. Z. Student, and I. D. Skrypnyk, “Analysis of high-temperature fatigue crack growth in corrosion-resistant steels on the basis of a two-parameter fracture criterion,”Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater. 26, No. 5, 9–19 (1990).
O. M. Romaniv, S. Ya. Yarema, H. M. Nykyforchyn, et al., “Fatigue and cyclic cracking resistance of structural materials,” in: V. V. Panasyuk (editor),Fracture Mechanics and Strength of Materials. A Handbook [in Russian], Vol. 4 Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1988).
S. Surech, G. F. Zamiski, and R. O. Ritchie, “Oxide-induced crack closure: An explanation for near-threshold corrosion fatigue crack growth behavior,”Metal. Trans. 12A, No. 8, 1435–1443 (1981).
Yu. I. Archakov,Hydrogen Resistance of Steel [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1979).
O. M. Romaniv, G. M. Nykyforchyn, I. D. Skrypnyk, and M. Schaper, “Influence of hydrogen on deformation and torsional fracture of high-strength steel,”Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater. 29, No. 4, 93–101 (1993).
I. A. Clum, “The role of hydrogen in dislocation generation in iron alloys,”Scr. Met, No. 1, 51–58 (1975).
M. M. Shved, “The role of hydrogen in iron and steel embrittlement,”Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater. 17, No. 1, 11–16 (1981).
C. D. Beacuhem, “A new model for hydrogen-assisted cracking (‘hydrogen embrittlement’),”Met. Trans. 3, 437–451 (1972).
F. H. Vitovec, “Effect of high-pressure hydrogen environment on the creep behaviour of steel,” in:Fracture Problems and Solution in the Energy Industry Pergamon Press, Oxford (1982), pp. 107–114.
I. S. Slabkovskii,Influence of Hydrogen on X-Ray Emission Spectra of Iron, Author's Abstract of Candidate Degree Thesis (Physics and Mathematics), L'viv (1971).
Additional information
Karpenko Physicomechanical Institute, Ukrainian Academy of Sciences, L'viv. Translated from Fiziko-Khimicheskaya Mekhanika Materialov, Vol. 30, No, 4, pp. 7–15, July – August, 1994.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nykyforchyn, H.M., Student, O.Z. & Skrypnyk, I.D. Double influence of hydrogen on fatigue crack growth in heat-resistant steels. Mater Sci 30, 403–409 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558831
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558831