Summary
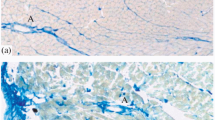
Two types of mast cell can be identified histochemically in the dermis of the rat's external ear. One type is recognized by the binding of concanavalin A (con A) to the cytoplasmic granules (con A-positive cells) while in the other type (con A-negative cells), the granules do not bind con A. The granules in both types are stained metachromatically by toluidine blue.
Antidromic stimulation of the great auricular nerve for 2 min results in an increased proportion of degranulating mast cells in the auricular dermis and both types of cell are affected to an approximately equal extent. In discussion of this observation, it is argued that both the con A-positive and the con A-negative mast cells are probably involved in the mediation of vasodilatation due to axon reflexes in injured skin.
The proportions of degranulating mast cells determined in histological preparations varied with the fixatives (Carnoy and glutaraldehyde-formaldehyde) used, but the increased degranulation due to antidromic nervous stimulation could be detected after either fixation.
Zusammenfassung
In der Rattenhaut des äußeren Ohres können histochemisch zwei Typen von Mastzellen identifiziert werden. Der eine Typ bindet Concanavalin A an cytoplasmatische Granula, während der andere Typ diese Eigenschaft nicht aufweist. Die Granula beider Typen färben sich metachromatisch mittels Toluidin-blau. Durch antidrome Reizung des großen Auriculanervs für 2 min, entwickelt sich eine Degranulation der Mastzellen beider Typen im gleichen Ausmaß. Es wird angenommen, daß beide Mastzelltypen an der Vasodilatation, die durch den Axonreflex provoziert wird, beteiligt sind. Die Ausmaße der Degranulation wechseln mit den verwandten Fixierlösungen, aber die verstärkte Degranulation nach autodromen Nervenreiz ist bei jeder Fixationstechnik nachweisbar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkman, G. L.: The mast cell in normal human bronchus and lung. J. Ultrastruct. Res.23, 115–123 (1968)
Combs, J. W., Lagunoff, D., Benditt, E. P.: Differentiation and proliferation of embryonic mast cells of the rat. J. Cell Biol.25, 577–592 (1965)
Davis, H., Gascho, C., Kiernan, J. A.: The skin in magnesium-deficient rats. Arch. Derm. Res.254, 1–13 (1975)
Etzler, M. E., Branstrator, M. L.: Differential localization of cell surface and secretory components in rat intestinal epithelium. J. Cell Biol.63, 329–343 (1974)
Heap, B. J., Kiernan, J. A.: Histological, histochemical and pharmacological observations on mast cells in the stomach of the rat. J. Anat.115, 315–325 (1973)
Kiernan, J. A.: Degranulation of mast cells following antidromic stimulation of cutaneous nerves. J. Anat.111, 349–350 (1971)
Kiernan, J. A.: The involvement of mast cells in vasodilatation due to axon reflexes in injured skin. Quart. J. exp. Physiol.57, 311–317 (1972)
Kiernan, J. A.: Action of adenosine triphosphate on mast cells in normal and denervated skin. Arch. Derm. Forsch.251, 83–86 (1974)
Kiernan, J. A.: Localization of α-D-glucosyl and α-D-mannosyl groups of mucosubstances with concanavalin A and horseradish peroxidase. Histochemistry44, 39–45 (1975a)
Kiernan, J. A.: A pharmacological and histological investigation of the involvement of mast cells in cutaneous axon reflex vasodilatation. Quart. J. exp. Physiol.60, 123–130 (1975b)
Kiernan, J. A.: Evidence for the involvement of vasoactive constituents of mast cells in axon reflex vasodilatation in the skin of the rat. Arch. Derm. Res.251, 1–8 (1976)
Lampe, M., Kiernan, J. A.: Classification of mast cells in the skin of the rat. Arch. Derm. Res. (Submitted) (1976)
Lewis, T., Grant, R. T.: Vascular reactions of the skin to injury. Part II. The liberation of a histamine-like substance in injured skin; the underlying cause of factitious urticaria and of wheals produced by burning and observations upon the nervous control of certain skin reactions. Heart11, 209–265 (1924)
Nieland, M. L.: Epidermal intercellular staining with fluorescein-conjugated phytohemagglutinins. J. invest. Derm.60, 61–66 (1973)
Riley, J. F.: The relationship of the tissue mast cells to the blood vessels in the rat. J. Path. Bact.65, 461–478 (1953)
Selye, H.: The Mast Cells. Washington: Butterworths 1974
Stoddart, R. W., Kiernan, J. A.: Histochemical detection of the α-D-arbinopyranoside configuration using fluorescent-labelled concanavalin A. Histochemistry33, 87–94 (1973)
Zar, J. H.: Biostatistical analysis. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lampe, M., Kiernan, J.A. Degranulation of dermal mast cells: Effects of fixation and of antidromic nervous impulses on two histochemically identified cell-types. Arch. Derm. Res. 257, 125–129 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558085
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558085