Abstract
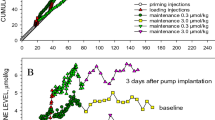
Behavioral hypersensitivity in the rat consisting of increased dopamine-mediated stereotypic behaviors has been found to follow a 10-day course of treatment with the neuroleptic haloperidol as well as with the direct dopamine agonist apomorphine. The daily dose versus response relationship for chronic haloperidol indicates that a threshold daily dose exists and that behaviors increase with increasing daily dose. On the other hand, low rather than high daily doses of chronic apomorphine induce behavioral hypersensitivity and the response decreases with increasing daily dose. Prolonged functional denervation of striatal postsynaptic dopamine receptors by either neuroleptic blockade or autoreceptor stimulation may explain these findings. The results may help elucidate the relative risk of daily neuroleptic dose on tardive dyskinesia development and indicate a possible mechanism for chronic agonist-associated side effects likel-Dopa dyskinesias.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama K, Sato M, Otsuki S (1982) Increased3H-spiperone binding sites in mesolimbic area related to methamphetamine-induced behavioral hypersensitivity. Biol Psychiatry 17:223–231
Burt DR, Creese I, Snyder SH (1977) Antischizophrenic drugs: Chronic treatment elevates dopamine receptor binding in brain. Science 196:326–328
Carlsson A (1975) Receptor-mediated control of dopamine metabolism. In: Usdin E, Bunney WE (eds) Pre- and post-synaptic receptors. Dekker, New York, pp 49–65
Clow A, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1979) Changes in dopamine-mediated behavior during one year's neuroleptic administration. Eur J Pharmacol 57:365–375
Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH (1977) Dopamine receptor binding enhancement accompanies lesion-induced behavioral supersensitivity. Science 197:595–598
Dourish CT, Cooper SJ (1981) Single or repeated administration of small doses of apomorphine on water intake and activity in water-deprived rats. Neuropharmacology 20:257–260
Fray PJ, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Koob GF, Iversen SD (1980) An observational method for quantifying the behavioral effects of dopamine agonists: Contrasting effects ofd-amphetamine and apomorphine. Psychopharmacology 69:253–259
Gunne LM, Häggström JE (1983) Reduction of nigral glutamic acid decarboxylase in rats with neuroleptic-induced oral dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 81:191–194
Hjorth S, Jackson D, Carlsson A, Lindberg P (1981) A behavioural study of the changes in the CNS of mice after sub-chronic treatment with the dopamine autoreceptor agonist 3-PPP. Poster presentation at the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology Annual Meeting, San Juan, 1981
Iversen SD, Howells RB, Hughes RP (1980) Behavioral consequences of long-term treatment with neuroleptic drugs. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 24:305–313
Kane JM, Smith JM (1982) Tardive dyskinesia: Prevalence and risk factors, 1959 to 1979. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:473–481
Kane JM, Struve FA, Weinhold P, Woerner M (1980) Strategy for the study of patients at high risk for tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 137:1265–1267
Kenny M, Leonard BE (1980) The effects of strain differences and emotional status of rats on the behavioural and neurochemical effects of chronic treatment with apomorphine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol 4:161–170
Klawans HL, Carvey P, Goetz CG (1981) Effect of dose, duration and type of neuroleptic in an animal model of tardive dyskinesia. Paper presented at Third World Congress of Biological Psychiatry, Stockholm, 1981
Klawans HL, Carvey P, Hitri A, Nausieda PA, Weiner WJ (1980) Correlation between daily dosage of chlorpromazine and subsequent supersensitivity. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 24:569–572
Klawans HL, Margolin DI (1975) Amphetamine-induced dopaminergic hypersensitivity in guinea pigs. Arch Gen Psychiatry 32:725–732
Muller P, Seeman P (1979) Presynaptic subsensitivity as a possible basis for sensitization by long-term dopamine mimetics. Eur J Pharmacol 55:149–157
Nelson LR, Ellison G (1978) Enhanced stereotypies after repeated injections but not continuous amphetamines. Neuropharmacology 17:1081–1084
Post RM, Rubinow DR, Ballenger JC (1984) Conditioning, sensitization, and kindling: Implications for the course of affective illness. In: Post RM, Ballenger JC (eds) Neurobiology of mood disorders. Williams Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 432–466
Randrup A, Munkvad I (1967) Stereotyped behavior produced by amphetamine in several animal species and man. Psychopharmacologia 11:300–310
Rosengarten H, Schweitzer JW, Friedhoff AJ (1983) Induction of oral dyskinesias in naive rats by D1 stimulation. Life Sci 33:2479–2482
Roth RH (1979) Dopamine autoreceptors: Pharmacology, function and comparison with post-synaptic dopamine receptors. Commun Psychopharmacol 3:429–445
Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Iversen SD (1976)alpha-Flupenthixol-induced hyperactivity by chronic dosing in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 37:169–178
Segal DS, Weinberger SB, Cahill J, McCunney SJ (1980) Multiple daily amphetamine administration: Behavioral and neurochemical alterations. Science 207:904–906
Skirboll LR, Grace AA, Bunney BS (1979) Dopamine auto- and postsynaptic receptors: Electrophysiological evidence for differential sensitivity to dopamine agonists. Science 206:80–82
Strömböm U (1976) Catecholamine receptor agonists: Effects on motor activity and rate of tyrosine hydroxylation in mouse brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 292:167–176
Tarsy D, Baldessarini RJ (1974) Behavioural supersensitivity to apomorphine following chronic treatment with drugs which interfere with the synaptic function of catecholamines. Neuropharmacology 13:927–940
Tarsy D, Baldessarini RJ (1977) The pathophysiologic basis of tardive dyskinesia. Biol Psychiatry 12:431–450
Ungerstedt U (1971) Postsynpatic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxydopamine induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta Physiol Scand (Suppl) 367:69–93
Waddington JL, Cross AJ, Gamble SJ, Bourne RC (1983) Spontaneous orofacial dyskinesia and dopaminergic function in rats after 6 months of neuroleptic treatment. Science 220:530–532
Waddington JL, Gamble SJ (1980) Emergence of apomorphine-induced ‘vacuous chewing’ during 6 months continous treatment with fluphenazine decanoate. Eur J Pharmacol 68:387–388
Wilcox RE, Riffee WH, Chen PC, Hammett S, Smith RV (1980) Behavioral facilitation following chronic administration of N-n-propylnorapomorphine. Psychopharmacology 72:113–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinon, B.J., Merson, D. & Kane, J.M. Effect of daily dose of chronic haloperidol and chronic apomorphine on behavioral hypersensitivity in the rat. Psychopharmacology 84, 347–351 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00555211
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00555211