Summary
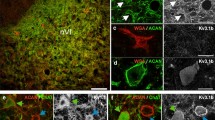
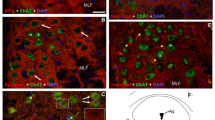
Multiply-innervated fibers from rat superior oblique extraocular muscle were followed in sequential serial sections using histochemistry. Sudan black and adenosine-triphosphase (ATPase) histochemical staining reactions were used to identify these fibers in the muscle's global layer and orbital surface layer. Regional differences in ATPase staining occurred along the length of multiply-innervated fibers from the orbital surface layer. In their middle third where these fibers appear ‘morphologically-fast’ and contain endplatelike endings, they were found to exhibit a dual ATPase activity. In their distal third where they appear ‘morphologically-slow’ and contain simple, superficial endings, they had an alkaline-labile and acid-stabile ATPase activity profile. In contrast, the multiply-innervated fibers of the global layer exhibited a homogeneous ATPase activity, i.e., alkaline-labile and acid-stabile pattern. This histochemical homogeneity parallels their uniform morphologically-slow profile. These fibers contain only multiple superficial endings. It would appear that the histochemical and ultrastructural profile of a fiber is dependent upon the type and location of the motor innervation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davidowitz J, Pachter BR, Phillips G, Breinin GM (1977) Systematic morphological variability along the length of muscle fibers in extraocular muscles of. rabbit. A study in serial sections. 35th Ann Proc of the Electron Microscopy Soc Amer, pp 566–567
Farrell P, Fedde MR (1969) Uniformity of structural characteristics throughout the length f skeletal muscle fibers. Anat Rec 164:219–230
Guth L, Samaha FJ, Albers RW (1970) The neural regulation of some phenotypic differences between the fiber types of mammalian skeletal muscle. Exp Neurol 26:126–140
Hanson J, Lennerstrand G (1977) Contractile and histochemical properties of the inferior oblique muscle in the rat and in the cat. Acta Ophthalmol 55:88–102
Hess A (1970) Veterbrate slow muscle fibers. Physiol Rev 50:40–62
Kucera J (1982) A study of motor nerve terminals on cat nuclear bag, intrafusal muscle fibers using the ChE staining technique. Anat Rec 202:407–418
Kucera J, Dorovini-Zis K (1979) Types of human intrafusal muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve 2:437–451
Kucera J, Dorovini-Zis K, Engel WK (1978) Histochemistry of rat intrafusal muscle fibers and their motor innervation. J Histochem Cytochem 26:973–988
Lennerstrand G (1975) Motor units in eye muscles. In: Lennerstrand G, Bach-y-Rita P (eds) Basic mechanisms of ocular motility and their clinical implications. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 119–143
Lennerstrand G, Nichols KC (1977) Morphology of motor units in cat extraocular muscle. Acta Ophthalmol 55:913–918
Manolides L, Balogannes S (1981) Histological and ultrastructural findings in the vocal muscles of patients suffering from muscular dystrophies. Acta Otorhinolaryngol 230:181–188
Nemeth PM, Pette D, Vrbova G (1980) Malate dehydrogenase homogeneity of single fibers of the motor unit. In: Pette D, (ed) Plasticity of muscle. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin New York, pp 45–57
Pachter BR (1982) Fiber composition of the superior rectus extraocular muscle of the Rhesus macaque. J Morphol 174:237–250
Pachter BR (1983) Rat extraocular muscle. I. Three dimensional cytoarchitecture, component fibre populations and innervation. J Anat 137:143–159
Pachter BR, Colbjornsen C (1983) Rat extraocular muscle. 3. Histochemical fibre types. J Anat 137:161–170
Pachter BR, Davidowitz J, Breinin GM (1976) Light and electron microscopic analysis of mouse extraocular muscle: Morphology, innervation and topographical organization of component fiber populations. Tissue Cell 8:547–560
Schmalbruch H (1967) Fasertypen in der Unterschenkelmuskulatur der Maus. Zellforsch mikrosk Anat 79:64–75
Veggetti A, Mascarello F, Carysene E (1982) A comparative histochemical study of fibre types in middle ear muscles. J Anat 135:333–352
Yellin H (1969) Unique intrafusal and extraocular muscle fibers exhibiting dual actomyosin ATPase activity. Exp Neurol 25:153–163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pachter, B.R. Rat extraocular muscle. Histochemistry 80, 535–538 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00553713
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00553713