Conclusions
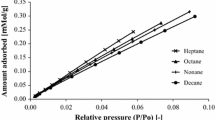
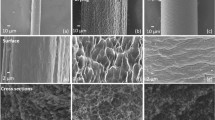
Megalon fibre has a well-developed porous surface (comparable with the pore surface of cotton).
The moisture-retaining characteristics of Megalon, which are a part of the complex of properties which determine the hygienic properties of fibres, are close to the analogous characteristics of cotton fibre.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. F. Kazanskii, R. V. Lutsyk, and V. M. Kazanskii, in: Heat-and Mass-Exchange in Disperse Systems [in Russian], Nauka i Tekhnika, Minsk (1965), pp. 136–141.
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 3, pp. 41–42, May–June, 1983.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khardin, A.P., Zheltobryukov, V.F., Mkrtychev, K.N. et al. Differential water-retaining properties and pore structure of Megalon fibre. Fibre Chem 15, 215–217 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00552807
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00552807