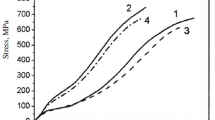
Conclusions
In twisting complex yarns based on CMC, the plasticizing role of water is more noticeable than in twisting viscose yarns.
The dependence of the breaking load of twisted CMC yarns on degree of twist has an extreme character, with a maximum at a twist of 150–200 twists/m.
A number of medico-biological properties of reabsorbable surgical CMC yarns (capillarity, swellability, diameter, elasticity) depend on the degree of twist, a twist of 320–350 twists/m being optimal.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. A. Sarymsakov, U. É. Begaliev, et al., Summaries of Reports at the Fifth All-Union Symposium “Synthetic Polymers for Medical Purposes”, Riga (1981), p. 210.
É. A. Mal'vinov, G. G. Finger, et al., Khim. Volokna, No. 2, 32–33 (1982).
É. A. Mal'vinov, G. G. Finger, et al., Khim. Volokna, No. 2, 40–41 (1984).
O. V. Plotnikov, A. I. Mikhailov, and E. L. Rayavi, Vysokomol. Soed., Ser. A, 19, No. 11, 2528–2537 (1977).
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 5, pp. 43–45, September–October, 1987.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Israilov, S.Y., Sarymsakov, A.A., Turaev, A.S. et al. Carboxymethylated viscose yarns for surgical purposes. Fibre Chem 19, 350–353 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00551566
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00551566