Summary
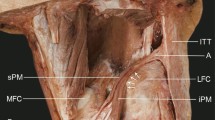
Pain at the site of the tibial insertion of the flexor digitorum longus and the soleus near the middle third of the medial border of the tibia may be encountered in young athletes, who have usually started to run in late adolescence. Heel valgus, abnormal mid-foot pronation and excessive tibial torsion may be seen in association. The symptoms are brought on after excessive training. Radiographs may show cortical thickening at the site of the pain, and a bone scan may demonstrate a mild increase in the uptake of the isotope at this site. The pain appears to be related to a strain of the attachment of the flexor digitorum longus and the aponeurotic insertion of the soleus into the tibia. The pressure in the deep posterior compartment of the tibia is normal. Histological examination of specimens from the flexor digitorum longus may demonstrate ischaemic changes in the muscle. Treatment is based on an understanding of the biomechanics of the foot in running, modification of training methods and the use of suitable orthotics. If these measures fail, partial division of the aponeurotic attachment of soleus and freeing of the insertion of the flexor digitorum longus is usually succesful.
Résumé
Certaines douleurs situées le long du bord interne du tibia à son tiers moyen apparaissent parfois chez les jeunes athlètes venus sur le tard à la course. Améliorées par le repos, elles finissent néanmoins par devenir subintrantes. Le maximum douloureux se situe au niveau de l'insertion tibiale du fléchisseur commun des orteils et du soléaire. Au syndrome douloureux s'associe souvent une accentuation de la pronation tarsienne. Celle-ci s'accompagne parfois d'une valgisation excessive de l'arrière-pied. Des troubles de torsion du membre inférieur font partie de l'ensemble du tableau. L'entraînement intensif et certains exercice's de propulsion sur la pointe des pieds semblent déclencher ces troubles. Les radiographies peuvent montrer des remaniements corticaux moniliformes. Les scintigraphies osseuses au technétate marqué montrent principalement des zones d'hypercaptation longitudinale sur le bord interne du tibia. La douleur serait déclenchée par une surcharge d'utilisation du fléchisseur commun des orteils et par une rupture partielle de l'aponévrose d'insertion tibiale du soléaire. Les mesures de pression de la loge postérieure profonde ne sont pas en faveur d'un syndrome des loges, cependant certaines images histopathologiques suggèrent l'existence de phénomène ischémique. Le traitement orthopédique se fonde sur la compréhension des mécanismes déficients de l'appui au sol lors de la course. Des corrections au niveau des chaussures, des mesures d'entraînement lentement progressif peuvent venir à bout de ces problèmes. Parfois ces douleurs deviennent rebelles à tout traitement conservateur et bénéficient favorablement d'une aponévrotomie associée à une désinsertion partielle du soléaire et du fléchisseur commun des orteils.
Similar content being viewed by others
Références
Brody D (1981) Pathologie du jogging. Clinical Symposia Ciba, Summit
Carter DR, Hayes WC (1977) Compact bone damage. Clin Orthop 127: 265
Daffner RM (1982) Stress fracture in runner. JAMA 247: 1039
D'Ambrosia R (1982) Prevention and treatment of running injuries. SLACK, Thorfare
Davey JR, Rorabeck CM, Fowler PJ (1984) The tibialis posterior compartment. Am J Sports Med 12: 391–197
Devas M (1975) Stress fractures. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh Harlow
Detmer Don E, Sharpe K, Robert L, Forrest M (1985) Chronic compartment syndrome, diagnosis, management and outcomes. Am J Sports Med 13: 162–170
Freeman MAR, Dean MRE, Hanham JWF (1969) The etiologie and preventive of function instability of the foot. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 7: 678–685
Guoping L, Shudong Z, Gang C, Hui C, Anming W (1985) Radiographie and histologie analyses of stress in rabbit tibias. Am J Sports Med 13: 285–294
Jackson DW, Strizak AM (1988) Stress fractures in runners excluding the foot. Symposium of AAOS. Mosby, London, pp 109–122
James SL, Bates BT, Ostering LR (1987) Injuries to runners. Am J Sports Med 6: 40–50
Lacroix P (1949) L'organisation des os. Desoer, Liège
Lelièvre J (1961) Pathologie du pied. Masson, Paris New York Barcelona Milan
Martens M, Backaert M, Vermaut G, Mulier J (1985) Chronic leg pain in athletes due to a recurrent compatment syndrome. Am J Sports Med 12: 148–151
Michael RM, Holder LE (1985) The Soleus syndrome. Am J Sports Med 13: 87–92
Milgrom C, Chisin R, Giladi M, Stein M, Kashtan H, Margulies J (1984) Negative bone scans in impending tibial stress fractures. J Am Sports Med 12: 488–491
Steinmetz M (1984) Le pied, le rachis, la course et la chaussure. Med Sport 58: 37–45
Slocum DB (1967) The shin splint syndrome. Medical aspects and differential diagnosis. Am J Surg 114: 875–881
Wagner J (1983) Blomécanique du cadre tibiopéronier. Cah Enseign SOFCOT 19: 101–114
Walheim J, Andrish J, Bergfeld J (1974) A prospective study on the management of shin splints. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 56: 1700
Wallenstein R, Eriksson E (1982) Is medical lower leg pain (shin splint) a chronic compatment syndrome? Symposium of AAOS. Mosby, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sepulchre, P., Blaimont, P. & Pasteels, J.L. Douleurs tibiales internes chez les coureurs à pied. International Orthopaedics 12, 217–221 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00547166
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00547166