Abstract
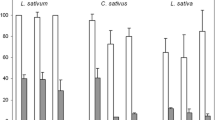
Paper substrate, especially circular filter paper placed inside a Petri dish, has long been used for the plant seed toxicity test (PSTT). Although this method is simple and inexpensive, recent evidence indicates that it gives results that are significantly different from those obtained using a method that does not involve paper, especially when testing metal cations. The study compared PSTT using three methods: filter paper, Growth Pouch-TM, and seed tray. The Growth Pouch-TM is a commercially available device. The seed tray is a newly designed plastic receptacle placed inside a Petri dish. The results of the Growth Pouch-TM method showed no toxic effects on rice for Ag up to 40 mg L−1 and Cd up to 20 mg L−1. Using the seed tray method, IC50 (50% inhibitory effect concentration) values were 0.55 and 1.4 mg L−1 for Ag and Cd, respectively. Although results of filter paper and seed tray methods were nearly identical for NaF, Cr(VI), and phenol, the toxicities of cations Ag and Cd were reduced by using the filter paper method; IC50 values were 22 and 18 mg L−1, respectively. The results clearly indicate that paper substrate is not advisable for PSTT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adema, D.M.M. and Henzen, L.: 1989, ‘A Comparison of Plant Toxicities of Some Industrial Chemicals in Soil Culture and Soilless Cultures’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 18, 219–229.
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Pollution Control Federation: 1989, Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th ed., Washington, DC.
Correll, D.S. and Correll, H.B.: 1972, Aquatic and Wetland Plants of Southwestern United States, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 16030 DNL, Washington, DC.
Gorsuch, J.W., Kringle, R.O. and Robillard, K.A.: 1990, ‘Chemical Effects on Germination and Early Growth of Terrestrial Plants’, ASTM STP 1091, Amer. Soc. Testing & Materials, Philadelphia, PA, pp. 49–58.
Peltier, W.H. and Weber, C.I. (Eds.): 1985, Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents to Freshwater and Marine Organisms, 3rd ed., EPA/600/4-85/013, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH.
Ratsch, H.C. and Johndro, D.: 1986, ‘Comparative Toxicity of Six Test Chemicals to Lettuce Using Two Root Elongation Test Methods’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 6, 267–276.
Swanson, C.P.: 1946, ‘A Simple Bioassay Method for the Determination of Low Concentrations of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid in Aqueous Solution’, Bot. Gaz. 108, 39–44.
Walsh, G.E., Weber, D.E., Simon, T.L., Brashers, L.K. and Moore, J.C.: 1991, ‘Use of Marsh Plants for Toxicity Testing of Water and Sediment’, ASTM STP 1115, Amer. Soc. Testing & Materials, Philadelphia, PA, pp. 341–354.
Walsh, G.E., Weber, D.E., Simon, T.L. and Brashers, L.K.: 1991, ‘Toxicity Tests of Effluents with Marsh Plants in Water and Sediment’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 10, 517–525.
Wang, W.: 1987, ‘Root Elongation Method for Toxicity Testing of Organic and Inorganic Pollutatns’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 6, 409–414.
Wang, W.: 1990, ‘Toxicity Assessment of Pretreated Industrial Effluents Using Higher Plants’, Res. J. Water Poll. Control Fed. 62, 853–860.
Wang, W.: 1991, ‘Literature Review on Higher Plants for Toxicity Testing’, Water, Air, Soil Poll. 59, 381–400.
Wang, W.: 1992, ‘Use of Plants for the Assessment of Environmental Contaminants’, Reviews Environ. Contam. Toxicol., in press.
Wang, W.: forthcoming, ‘Plant Seed Toxicity Test: Effects of Filter Paper on Cadmium Toxicity’.
Wang, W. and Keturi, P.H.: 1990, ‘Comparative Seed Germination Tests Using Ten Plant Species for Toxicity Assessment of Metal Engraving Effluent Sample’, Water, Air, Soil Poll. 52, 369–376.
Wang, W. and Williams, J.M.: 1988, ‘Screening and Biomonitoring of Industrial Effluents Using Phytotoxicity Tests’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 7, 645–652.
Wang, W. and Williams, J.M.: 1990, ‘The Use of Phytotoxicity Tests (Common Duckweed, Cabbage, and Millet) for Determining Effluent Toxicity’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 14, 45–58.
Wong, M.H. and Bradshaw, A.D.: 1982, ‘A Comparison of the Toxicity of Heavy Metals, Using Root Elongation of Rye Grass, Lolium Perenne’, New Phytol. 91, 255–261.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W. Comparative rice seed toxicity tests using filter paper, growth pouch-tm, and seed tray methods. Environ Monit Assess 24, 257–265 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545982
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545982