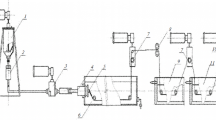
Conclusions
-- The spinning of polyacrylonitrile copolymers into organic baths containing dimethyl sulfoxide and isopropyl alcohol has been investigated. It has been found that the optimum DMSO:IPA ratio in the precipitation bath is 60:40% by wt..
-- It has been discovered that the strength of the spun yarn is higher the lower the jet stretch.
-- The effect of temperature on orientation stretch ratio has been studied. It has been shown that the optimum temperature for heat stretching of PAN yarn lies in the range 155–160°C.
-- The dimethyl sulfoxide content of yarn has been determined by technological transitions. In the final yarn it does not exceed 0.3–1.2% by wt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Japanese Application 61-89328; 61-132631; 61-97477; 60-246821.
Japanese Application 1-298217, 1-306619.
Carbochain Synthetic Fibres, K. E. Perepelkin (ed.) [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1973).
L. N. Matveeva, T. A. Romanova, T. V. Rybina, L. A. Kochorova, V. A. Medvedev, and A. T. Serkov, Khim. Volokna, No. 4, 61–62 (1989).
Additional information
VNIIPV. Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 3, pp. 15–16, May–June, 1991.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanova, T.A., Medvedev, V.A., Kochorova, L.A. et al. Preparation of polyacrylonitrile fibre by spinning into organic baths. Fibre Chem 23, 161–163 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545851
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545851