Summary
In 14 patients with arterial hypertension secondary to chronic renal parenchymal disease and impaired renal function, 24-h ambulatory and casual blood pressure readings plasma, angiotensin II, aldosterone, arginine vasopressin and atrial natriuretic peptide, creatinine clearance, plasma lipids and lipoproteins, and body weight were determined after consecutive 3-week periods on placebo and sustained release verapamil 240 mg/day.
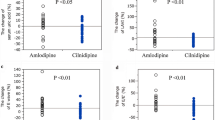
Verapamil reduced the mean 24-h ambulatory blood pressure from 152/104 to 142/97 mm Hg. Blood pressure was significantly reduced during the daytime and the evening, but not at night. Casual blood pressure was also significantly reduced from 176/106 mm Hg to 154/96 mm Hg. No significant changes were found in the hormones, creatinine clearance, plasma lipids and lipoproteins, heart rate or body weight. The atrial natriuretic peptide level was significantly correlated with the calculated creatinine clearance (r=−0.797).
Thus, sustained release verapamil 240 mg as a single daily dose had a moderate hypotensive effect in patients with chronic renal disease without inducing tachycardia, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, or increasing body weight, and without altering renal function and plasma lipids and lipoproteins. The negative correlation between atrial natriuretic peptide and glomerular filtration rate supports the hypothesis that the extracellular volume increases during progression of renal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berglund G, De Faire U, Castenfors J, Andersson G, Hartford M, Liedholm H, Ljungman S, Thulin T, Wikstrand J (1985) Monitoring 24-hour blood pressure in a drug trial. Evaluation of a noninvasive device. Hypertension 5: 688–694
Bock KD, Kreuzenbeck W (1966) Spontaneous blood pressure variations in hypertension: The effect of antihypertensive therapy and correlations with the incidence of complications. In: Gross E (ed) Ciba Symposium-Antihypertensive therapy: Principles and practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Boero R, Quarello F, Guarena C, Piccoli G (1986) Verapamil in arterial hypertension with renal disease. Nephron 44: 80
Bradley JV (1968) Distribution-free statistical tests. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA
Brod J, Bahlmann J, Cachovan M, Pretschner P (1983) Development of hypertension in renal failure. Clin Sci 64: 141–152
Carlson LA, Böttiger LE (1981) Serum triglycerides, to be or not to be a risk factor for ischemic heart disease? Atherosclerosis 39: 287
Churg J (1982) Renal disease. Classification and atlas of glomerular disease. Igahu-Schoen, Tokyo
Edmonds D, Baumgart P, Tenschert W, Vetter W, Vetter H (1985) Verapamil 240 mg — effective blood pressure reduction with a single daily dose? Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax 74: 507–509
Færgeman O, Meinertz H, Hansen JF (1984) Serum lipoproteins after treatment with verapamil for 6 months. Acta Med Scand 681 [Suppl]: 49–51
Gordon T, Castelli WP, Hjortland MC, Kannel WB, Dawber TR (1977) High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. Am J Med 62: 707–713
Grimm RH, Leon AS, Hunninghake DB, Lenz K, Hannan P, Blackburn H (1981) Effects of thiazide diuretics on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in mildly hypertensive patients. Ann Intern Med 94: 7–11
Hull JH, Hak LJ, Koch GG, Wargin WA, Chi SL, Mattocks AM (1981) Influence of range of renal function and liver disease on predictability of creatinine clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29: 516–521
Jürgensen HJ, Meinertz H, Færgeman O (1982) Plasma lipids and lipoproteins in long term beta-adrenergic blockade. Acta Med Scand 211: 449–452
Kappelgaard AM, Nielsen MD, Giese J (1976) Measurement of angiotensin II in human plasma: Technical modifications and practical experience. Clin Chim Acta 67: 299–306
Kerr DNS (1982) The assessment of renal function. Medical Education (International) Ltd.: 1049–1053
Lewis GRJ, Morley KD, Lewis BM (1978) The treatment of hypertension with verapamil. N Z Med J 87: 351
Mann S, Millar Craig MW, Altman DG, Melville DI, Raftery EB (1979) The effects of metoprolol on ambulatory blood pressure. Clin Sci 57: 375S-377S
Møller A, Rasmussen L, Ledet T, Christiansen JS, Christensen CK, Mogensen CE, Hermansen K (1986) Lipoprotein changes during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 46: 471–475
Palma JL, Codina J (1985) Ambulatory monitoring of blood pressure and arrhythmias by noninvasive methods in hypertensive patients treated with metoprolol. Clin Exp Hxypertens 7: 365–369
Pedersen EB, Danielsen H, Spencer ES (1984) Effect of indapamide on renal plasma flow, glomerular filtration rate and arginine vasopressin in plasma in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26: 543–547
Pedersen OL (1978) Does verapamil have a significant antihypertensive effect? Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13: 21
Rascher W, Tulassay T, Lang RE (1985) Atrial natriuretic peptide in plasma of volume-overloaded children with chronic renal failure. Lancet 2: 303–305
Rask-Madsen J, Bruunsgaard A, Munck O, Nielsen MD, Worning H (1974) The significance of bile acids and aldosterone for the electrical hyperpolarization of human rectum in obese patients treated with intestinal by-pass operation. Scand J Gastroenterol 9: 417–426
Rion F, Waeber B, Graf HJ, Jaussi A, Porchet M, Brunner HR (1985) Blood pressure response to antihypertensive therapy: Ambulatory versus office blood pressure readings. J Hypertension 3: 139–143
Robertson GL, Mahr EA, Athar S, Sinna T (1973) Development and clinical application of a new method for the radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Invest 52: 2340–2353
Sørensen SS, Thomson OØ, Danielsen H, Pedersen EB (1985) Effect of verapamil on renal plasma flow, glomerular filtration rate and plasma angiotensin II, aldosterone and arginine vasopressin in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29: 257–261
Thomassen AR, Bagger JP, Nielsen TT, Pedersen EB (1987) Atrial natriuretic peptide during pacing in controls and patients with coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiol 17: 267–276
Walldius G (1984) Effect of verapamil on serum lipoproteins in patients with angina pectoris. Acta Med Scand 681 [Suppl]: 43–48
Wilkins MR, Wood JA, Adu D, Lote CJ, Kendall MJ, Michael J (1986) Change in plasma immunoreactive atrial natriuretic peptide during sequential ultrafiltration and haemodialysis. Clin Sci 71: 157–160
Wilkinson R, Sellars L, Pickering M, Robson V, Kerr DNS (1981) The relative roles of sodium and renin in the hypertension of renal disease. An assessment based on the response to frusemide and propranolol. Clin Nephrol 16: 307–313
Zachariah PK, Sheps SG, Schirger A, Spiekerman RE, O'Brien P, Simpson KK (1986) Verapamil and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in essential hypertension. Am J Cardiol 57: 74D-79D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eiskjær, H., Pedersen, E.B., Rasmussen, L.M. et al. Sustained release verapamil in renal hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33, 549–555 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542485
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542485