Abstract
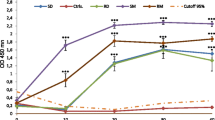
In order to investigate whether the schistosome Trichobilharzia ocellata interferes with defence activities in its snail intermediate host Lymnaea stagnalis, aspects of the immune system of infected snails and of non-infected controls were compared. The elimination of injected live Staphylococcus saprophyticus bacteria starts at a lower rate in infected snails 1 and 5 weeks after exposure to the parasite, but then proceeds faster than in control snails. During the first 3 weeks of infection, when only mother sporocysts are present, the haemocytes of the infected snails have an increased capacity to phagocytose rabbit red blood cells in vitro. From 5 weeks onwards, when mother and daughter sporocysts are present but cercariae are not yet mature, the phagocytic activity decreases to below control level. The number of circulating haemocytes is also higher in infected snails than in controls at this time. Moreover, the cells are larger, have more inclusions and an increased surface area with many long, branched, spiked pseudopods. The development of the parasite is retarded in a subpopulation of snails in which the haemolymph plasma agglutinates erythrocytes with high titres, compared to a subpopulation with low haemagglutinating activity. The haemagglutinating activity in infected snails of the first decreases significantly from 6 weeks onwards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Salam JM, Michelson EH (1980) Biomphalaria glabrata amoebocytes: Effect of Schistosoma mansoni infection on in vitro phagocytosis. J Invertebr Pathol 35:241–248
Abdul-Salam JM, Michelson EH (1983) Schistosoma mansoni: Immunofluorescent detection of its antigen reacting with Biomphalaria glabrata amoebocytes. Exp Parasitol 55:132–137
Acton RT, Weinheimer PF (1974) Hemagglutinins: Primitive receptor molecules operative in invertebrate denfense mechanisms. In: Cooper EL (ed), Contemporary topics in immunobiology 4 Invertebrate immunology. Plenum Press; New York, London, pp 271–282
Bayne CJ (1980) Molluscan immunity: Interactions between the immunogenic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the internal defense system of the snail Helix pomatia. Dev Comp Immunol 4:215–222
Benex J, Tribouley J (1974) Mise en évidence à la surface de la cercaire de Schistosoma mansoni d'antigène possédant le caractère planorbe. CR Acad Sci [D] Paris 279:683–685
Bourns TKR (1963) Larval trematodes parasitizing Lymnaea stagnalis appressa Say in Ontario with emphasis on multiple infections. Can J Zool 41:937–941
Dikkeboom R, Van der Knaap WPW, Meuleman EA, Sminia T (1984) Differences between blood cells of juvenile and adult specimens of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Cell Tissue Res 238:43–47
Granath WO, Yoshino TP (1983) Lysosomal enzyme activities in susceptible and refractory strains of Biomphalaria glabrata during the course of infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Parasitol 69:1018–1026
Jeong KH, Lie KJ, Heyneman D (1980) Leucocytosis in Biomphalaria glabrata sensitized and resensitized to Echinostoma lindoense. J Invertebr Pathol 35:9–13
Jeong KH, Sussman S, Rosen SD, Lie KJ, Heyneman D (1981) Distribution and variation of hemagglutinating activity in the hemolymph of Biomphalaria glabrata. J Invertebr Pathol 38:256–263
Jeong KH, Lie KJ, Heyneman D (1983) The ultrastructure of the amebocyte-producing organ in Biomphalaria glabrata. Dev Comp Immunol 7:217–228
Joky A, Matricon-Gondran M, Benex J (1985) Response of the amoebocyte-producing organ of sensitized Biomphalaria glabrata after exposure to Echinostoma caproni miracidia. J Invertebr Pathol 45:28–33
Kassim OO, Richards CS (1979) Host reactions in Biomphalaria glabrata to Schistosoma mansoni miracidia, involving variations in parasite strains, numbers and sequence of exposures. Int J Parasitol 9:565–570
Klühspies G (1983) Angeborene und erworbene Resistenz von Lymnaea stagnalis und Radix ovata gegen Miracidien-Invasion. Z Parasitenkd 69:591–611
Lie KJ (1982) Swellengrebel lecture. Survival of Schistosoma mansoni and other trematode larvae in the snail Biomphalaria glabrata. A discussion of the interference theory. Trop Geogr Med 34:111–122
Lie KJ, Heyneman D (1976) Studies on resistance in snails. 6. Escape of Echinostoma lindoense sporocysts from encapsulation in the snail heart and subsequent loss of the host's ability to resist infection by the same parasite. J Parasitol 62:298–302
Lie KJ, Lim H-K, Ow-Yang CK (1973) Synergism and antagonism between two trematode species in the snail Lymnaea rubiginosa. Int J Parasitol 3:729–733
Lie KJ, Heyneman D, Yau P (1975) The origin of amebocytes in Biomphalaria glabrata. J Parasitol 61:574–576
Lie KJ, Jeong KH, Heyneman D (1981) Selective interference with granulocyte function induced by Echinostoma paraensei (trematoda) larvae in Biomphalaria glabrata (Mollusca). J Parasitol 67:790–796
Loker ES (1979) Pathology and host responses induced by Schistosomatium douthitti in the freshwater snail Lymnaea catascopium. J Invertebr Pathol 33:265–273
Loker ES, Bayne CJ, Yui MA (1986) Echinostoma paraensei: Hemocytes of Biomphalaria glabrata as targets of echinostome mediated interference with host snail resistance to Schistosoma mansoni. Exp Parasitol 62:149–154
Mellink JJ, Van den Bovenkamp W, Van der Knaap WPW (1986) Parasite products possibly affecting host defences in the schistosome-snail model Trichobilharzia ocellata — Lymnaea stagnalis. Dev Comp Immunol 10:140
Meuleman EA (1972) Host-parasite interrelationships between the freshwater pulmonate Biomphalaria pfeifferi and the trematode Schistosoma mansoni. Neth J Zool 22:355–427
Meuleman EA, Huyer AR, Luub TWJ (1984a) Injection of Lymnaea stagnalis with miracidia of Trichobilharzia ocellata. Z Parasitenkd 70:275–278
Meuleman EA, Huyer AR, Mooy JH (1984b) Maintenance of the life cycle of Trichobilharzia ocellata via the duck Anas platyrhynchos and the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Neth J Zool 34:414–417
Renwrantz L, Schäncke W, Harm H, Erl H, Liebsch H, Gercken J (1981) Discriminative ability and function of the immunobiological recognition system of the snail Helix pomatia. J Comp Physiol 141:477–488
Richards CS (1975) Genetic factors in susceptibility of Biomphalaria glabrata for different strains of Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology 70:231–241
Rondelaud D, Barthe D (1980) Etude descriptive d'une réaction amibocytaire chez Lymnaea truncatula Müller infestée par Fasciola hepatica L. Z Parasitenkd 61:187–196
Rondelaud D, Barthe D (1981) The development of the amoebocyte-producing organ in Lymnaea truncatula Müller infected by Fasciola hepatica L. Z Parasitenkd 65:331–341
Sminia T (1974) Haematopoiesis in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis studied by electron microscopy and autoradiography. Cell Tissue Res 150:443–454
Sminia T (1981) Gastropods. In: Ratcliffe NA, Rowley AF (eds), Invertebrate blood cells. Academic Press; London, New York, pp 191–232
Sminia T, Van der Knaap WPW, Edelenbosch P (1979a) The role of serum factors in phagocytosis of foreign particles by blood cells of the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Dev Comp Immunol 3:37–44
Sminia T, Van der Knaap WPW, Kroese FGM (1979b) Fixed phagocytes in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Cell Tissue Res 196:545–548
Sminia T, Van der Knaap WPW, Van Asselt LA (1983) Blood cell types and blood cell formation in gastropod molluscs. Dev Comp Immunol 7:665–668
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1969) Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. Freeman WH and company, San Francisco
Stumpf JL, Gilbertson DE (1980) Differential leukocytic responses of Biomphalaria glabrata to infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Invertebr Pathol 35:217–218
Sullivan JT, Richards CS (1981) Schistosoma mansoni, NIH- SM-PR-2 strain, in susceptible and nonsusceptible stocks of Biomphalaria glabrata: comparative histology. J Parasitol 67:702–708
Sullivan JT, Cheng TC, Howland KH (1984) Mitotic responses of the anterior pericardial wall of Biomphalaria glabrata (Mollusca) subjected to challenge. J Invertebr Pathol 44:114–116
Van der Knaap WPW, Meuleman EA (1986) Interaction between the immune system of lymnaeid snails and trematode parasites. In: Lackie AM (ed), Immune mechanisms in invertebrate vectors. Symposia of the Zoological Society of London. Oxford University Press; Oxford, pp 179–198
Van der Knaap WPW, Sminia T, Kroese FGM, Dikkeboom R (1981) Elimination of bacteria from the circulation of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Dev Comp Immunol 5:21–32
Van der Knaap WPW, Doderer A, Boerrigter-Barendsen LH, Sminia T (1982a) Some properties of an agglutinin in the haemolymph of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Biol Bull 162:404–412
Van der Knaap WPW, Tensen CP, Kroese FGM, Boerrigter-Barendsen LH (1982b) Adaptive defence reactions against bacteria in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Dev Comp Immunol 6:775–780
Van der Knaap WPW, Boots AMH, Van Asselt LA, Sminia T (1983a) Specificity and memory in increased defence reactions against bacteria in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Dev Comp Immunol 7:435–443
Van der Knaap WPW, Sminia T, Schutte R, Boerrigter-Barendsen LH (1983b) Cytophilic receptors for foreignness and some factors which influence phagocytosis by invertebrate leucocytes: in vitro phagocytosis by amoebocytes of the snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Immunology 48:377–383
Van der Knaap WPW, Boots AMH, Meuleman EA, Sminia T (1985a) Search for shared antigens in the schistosomesnail combination Trichobilharzia ocellata — Lymnaea stagnalis. Z Parsitenkd 71:219–226
Van der Knaap WPW, Meuleman EA, Mellink JJ (1985b) Schistosome-snail immunological compatibility: shared antigens in the model Trichobilharzia ocellata — Lymnaea stagnalis. Dev Comp Immunol 9:172
Yoshino TP, Bayne CJ (1983) Mimicry of snail host antigens by miracidia and primary sporocysts of Schistosoma mansoni. Parasite Immunol 5:317–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Knaap, W.P.W., Meuleman, E.A. & Sminia, T. Alterations in the internal defence system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis induced by infection with the schistosome Trichobilharzia ocellata . Parasitol Res 73, 57–65 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00536337
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00536337