Abstract
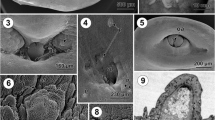
Surface structures of the early third-stage larae were examined by scanning electron microscopy. There were hemispherical head-bulbs at the apical ends. These bulbs could be clearly distinguished from the bodies. The head-bulbs (52 × 29 Μm) had four transverse rows of sharp booklets. The number of booklets in each row was 37, 36, 38, and 43, posteriorly. The larvae possessed a pair of lateral lips in the head-bulb. Each of the lips had two labial papillae and an amphid between the papillae. Small unidentate cuticular spines were present along the entire length of larvae on their transverse striations. The number of these cuticular striations was 175–217. A pair of cervical papillae and an excretory pore were present on the anterior part of the body. Another pair of papillae was detected laterally on the posterior one-third of the body. The shape of the posterior body papillae resembled that of cervical papillae. The cuticular spines were absent around the anus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anantaphruti M, Setasubun P, Daengsvang S, Vajrasthira S (1982) Electron microscopy of the advanced third-stage larvae of Gnathostoma spinigerum. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 13:531–540
Daengsvang S (1972) An experimental study on the life cycle of Gnathostoma hispidum Fedtschenko 1872 in Thailand with special reference to the incidence and some significant morphological characters of the adult and larval stages. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 3:376–389
Golovin OV (1956) The biology of Gnathostoma hispidum. [in Russian] Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 111:242–244
Ishii Y (1971) The world of scanning electron microscope (53). The structure of parasitic helminths: 2. Third-stage larva of Gnathostoma spinigerum. [in Japanese] Igaku no Ayumi 77:A183–184
Koga M, Ishibashi J, Ishii Y, Hasegawa H, Choi DW, Lo TY (1985) Morphology and experimental infections of gnathostome larvae from imported loaches, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. [in Japanese] Jpn J Parasitol 34:361–370
Kondo K, Akao N, Takakura Y, Ohnishi Y, Konishi Y, Yoshimura H (1984) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of larvae and adult worms of Gnathostoma hispidum. [in Japanese] Jpn J Parasitol 33:577–586
Miyazaki I (1952) On the second-stage larvae of three species of Gnathostoma occurring in Japan (Nematoda: Gnathostomidae). [in Japanese] Acta Med (Fukuoka) 22:1433–1441
Morita H, Segawa T, Nishiyama T, Yamada S, Yagi J, Chin I, Shimazu K, Uno T, Araki T, Amano H, Takahashi Y (1984) Gnathostomiasis cases caused by imported loaches, [in Japanese] J Nara Med Assoc 35:607–619
Ratanarapee S, Jesadapatarakul S, Mangkalanond K (1981) Spontaneous exit of a gnathostome through a surgical wound. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 12:376–379
Wang P, Sun Y, Zhao Y (1976) On the development of Gnathostoma hispidum in the intermediate host with special reference to its transmission route in pigs. [in Chinese] Acta Zool Sin 22:45–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koga, M., Ishii, Y., Huang, W.C. et al. Early third-stage larvae of Gnathostoma hispidum in cyclops. Parasitol Res 74, 69–72 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00534935
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00534935