Abstract
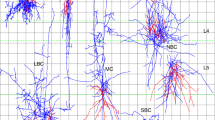
In this paper a modern statistical method is applied to an old cell classification and identification problem in the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus. In a recent computer-based reconstruction study of Golgi-impregnated neurons in the rat, two types of cell with flattened dendritic arbors, flat (F) and less flat (LF), were defined. Both types contributed to the anisotropic and laminar pattern of the nucleus. The classification was based on five morphological features of complete dendritic arbors, two assessed visually and three numerically. With respect to the latter criteria, the two types were classified by preselected cut-off values. The distinction of the two types was supported, among other things, by a prevailing spatial segregation into laminar and interlaminar compartments. The cell sample was too small, however, to validate the classification and segregation definitively. In the present study, the classification is tested by the partial least squares regression method which is independent of the preselected cut-off values, and is able to handle small sample sizes and interdependent variables. In the plots, the F and LF cells are clearly separated into two distinct clusters, strongly supporting the distinction of the two types. The different density of the two clusters shows that the F cells are more homogeneous that the LF cells. The relative importance of the classification criteria is also evaluated. The three-dimensional (3D) inspection and the 3D convex hull-based form factor were found to be the most powerful criteria for identifying the two cell types, while the 2D evaluation of camera lucida drawings, a standard method in neuroanatomy, proved to have the least predictive value.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackstad TW, Karagülle T, Malmierca MS, Osen KK (1993) Computer methods in neuroanatomy: determining mutual orientation of whole dendritic arbors. Comput Biol Med 23:227–250
Karagülle T (1990) A systematic approach to computer-aided 3D reconstruction and analysis of individual neurons. Thesis for the Cand Scient degree, University of Oslo
Malmierca MS (1991) Computer-assisted 3D reconstructions of Golgi-impregnated cells in the rat inferior colliculus. Doctoral Thesis, Universities of Oslo and Salamanca
Malmierca MS, Blackstad TW, Osen KK, Karagülle T, Molowny RL (1993) The central nucleus of the inferior colliculus in rat. A Golgi and computer reconstruction study of neuronal and laminar structure. J Comp Neurol 333:1–27
Martens H, Næs T (1989) Multivariate calibration. Wiley, Chichester
Pearson JC, Norris JR, Phelps CH (1985) Subclassification on neurons in the subthalamic nucleus of the lesser bushbaby (Golago senegalensis): a quantitative Golgi study using principal components analysis. J Comp Neurol 238:323–339
Rowe MH, Stone J (1977) Naming of neurons. Classification and naming of neurons of cat retinal ganglion cells. Brain Behav Evol 14:185–216
Rowell CHF (1989) The taxonomy of invertebrate neurons: a plea for a new field. Trends Neurosci 12:169–174
Seip KL, Sneek M, Snipen L-G (1994) How far do physical factors determine phytoplankton biomass in lakes? Chemometry Intelligent Lab Syst 23:247–258
Tyner CF (1975) The naming of neurons. Applications of taxonomic theory to the study of cellular populations. Brain Behav Evol 12:75–96
Wold S, Esbensen K, Geladi P (1987) Principal component analysis — a tutorial. Chemometry Intelligent Lab Syst 2:37–52
Yelnik J, Percheron G, Francois C, Burnod Y (1983) Principal component analysis: a suitable method for the three-dimensional study of the shape, dimensions and orientation of dendritic arborizations. J Neurosci Methods 9:115–125
Yelnik J, Francois C, Percheron G, Tande D (1991) Morphological taxonomy of the neurons of the primate striatum. J Comp Neurol 313:273–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malmierca, M.S., Seip, K.L. & Osen, K.K. Morphological classification and identification of neurons in the inferior colliculus: a multivariate analysis. Anat Embryol 191, 343–350 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00534687
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00534687