Abstract
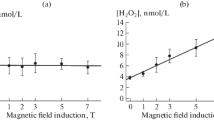
The influence has been detected of weak variable magnetic fields, modulating the geomagnetic field, and of UHF radiation on the tangent of the dielectric losses of water and ice and also on the absorption and fluorescence spectra of aqueous rhodamine 6Zh solutions and albumin. At certain magnetic field frequencies the physical characteristics have extreme values. The long term relaxation of these characteristics after switching off the field (radiation) have been studied along with the mechanism of the effects and their possible role in magnetobiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. N. Dubrov, The Geomagnetic Field and Life [in Russian], Gidrometeoizdat, Moscow (1974), p. 174.
M. V. Goland, “Influence of monochromatic electromagnetic radiation of millimeter range and of low power on biological processes” Biofizika, 31, No. 1, 139–147 (1986).
V. I. Kopanev and A. I. Shakula, “The Influence of a Hypomagnetic Field on Biological Specimens [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1986), p. 158.
W. R. Adey, “Tissue interactions with nonionizing electromagnetic fields” Physiol. Rev., 61, No. 2, 435–514 (1981).
L. P. Semikhina, “Changes of the refractive index of water after magnetic treatment” Kolloid Zh., 43, No. 2, 401–404 (1981).
L. P. Semikhima, V. F. Kiselev and Yu. A. Lyubimov, Changes of Electrical, Dielectric and Thermal Properties of Water and Ice after the Action of Weak Magnetic Fields [in Russian], Preprint No. 22, Moscow University, Moscow (1965), p. 5.
F. R. Chernikov, “Oscillations of light scattering intensities in aqueous solutions of protein” Biofizika, 31, No. 4, 596–600 (1986).
S. V. Zhuravlev, L. V. Levshin, A. M. Saletskii and V. I. Yuzhakov, “The role of energy migration between monomeric molecules of rhodamine pigments in the concentration extinguishing of luminescence” Opt. Spectrosk., 53, No. 2, 245–251 (1982).
V. I. Kvlividze, V. F. Kiselev and A. B. Kurzaev, “Features of the phase transition of water in disperse systems” Biofizika, 20, No. 3, 533–536 (1975).
V. I. Klassen, Magnetization of Aqueous Systems [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1982). p. 296.
V. Ya. Antochenko, The Microscopic Theory of Water in Pores of Membranes [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1983), p. 160.
A. S. Davydov, Solitons in Molecular Systems [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1984), p. 288.
L. D. Kislovskii, “Reactions of biological systems and adequately weak low frequency electromagnetic fields” Probl. Kosm. Biol., 43, 148–160 (1982).
L. N. Novikov, G. V. Sktroitskii and G. I. Solomakho, “The Hanley effect” Usp. Fiz. Nauk., 113, No. 4, 597–625 (1974).
A. V. Kiselev and A. Ch. Mincik, “X-ray investigation of short range order in water and its interface” Acta Crystallogr. A. Suppl., 40, 474–481 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Teoreticheskaya i Éksperimental'naya Khimiya, Vol. 24, No. 3, pp. 330–334, May–June, 1988.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiselev, V.F., Saletskii, A.M. & Semikhina, L.P. Influence of weak magnetic fields and UHF radiation on certain dielectric and optical properties of water and aqueous solutions. Theor Exp Chem 24, 319–323 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00534559
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00534559