Summary
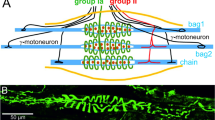
The ultrastructure of the muscle spindles has been studied in human lumbrical muscles. The findings have been compared with the morphology of muscle spindles of rat and sheep examined with light and electron microscopy. The study is based on cross and longitudinal sections of the entire muscle spindle obtained by dissection. The different components of the spindle are described with special reference to the nuclear bag and nuclear chain fibres. These nuclei have been examined in human adult and newborn material and compared to the animal ones. ADN measurements revealed that although there are morphological differences between the two kinds of nuclei in human newborn spindles, the amount of ADN is the same as well in the nuclear bag as in the nuclear chain nuclei. Special attention is also given to the sensory and motor endings in the muscle spindles and to the presence of Pacinian corpuscules in these receptors. Finally two kinds of leptomeric organelles are described in human material.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliographie
Barker, D.: The structure and distribution of muscle receptors. Symposium on Muscle Receptors (Barker, D., edit.). Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press 1962.
Barker, D., Gidumal, J. L.: The morphology of intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 157, 513–528 (1961).
Barker, D., Harker, D., Stacey, M. J., Smith, C. R.: Fusimotor innervation. Excerp. Medic. Internat. Congr. Series No 240 (ISBN 90 219 0173 0).
Barker, D., Stacey, M. J.: Rabbit intrafusal muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 210, 70–72 P. (1970).
Boyd, I. A.: The diameter and distribution of the nuclear bag an nuclear chain muscle fibres in the muscle spindles of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 153, 23–24 (1960).
Cooper, S., Daniel, P. M.: Human muscle spindles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 133, 1–3 (1956).
Cooper, S., Daniel, P. M.: Muscle spindle in man; their morphology in the lumbrical and the deep muscle of the neck. Brain 86, 563–586 (1963).
Goglia, G.: Ricerche ultrastrutturali sopra in fuse neuromuscolari del Gatto, del Coniglio et del Ratto. Act. med. romana. Anno VIII. 7, 53 (1970).
Grüner, J. E.: La structure fine du fuseau neuro-musculaire humain. Rev. neurol. 104, 490–507 (1961).
Johnson, F. A., Sommer, J. R.: A strand of cardiac muscle. Its ultrastructure and the electrophysiological implications of its geometry. J. Cell Biol. 33, 103–128 (1967).
Karlsson, U., Andersson-Cerdergren, E.: Small leptomeric organelles in intrafusal muscle fibers of the frog as revealed by electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 417–426 (1968).
Merillees, N. C.: The fine structure of muscle spindles in the lumbrical muscle of the rat. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 725–742 (1960).
Ovalle, W. K.: Fine structure of rat intrafusal muscle fibers. The equatorial region. J. Cell Biol. 52, 382–396 (1972).
Rumpelt, H. J., Schmalbruch, H.: Zum Verständnis der Morphologie von Muskelspindeln bei Mensch und Ratte. Verh. Anat. Ges. Erg.-Bd. Anat. Anz. 126, 405–410 (1970).
Rumpelt, H. J., Schmalbruch, H.: Zur Morphologie der Bauelemente von Muskelspindeln bei Mensch und Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 102, 601–630 (1969).
Ruska, H., Edwards, G. H.: A new cytoplasmic pattern in striated muscle fibres and its relation to growth. Growth 21, 73–88 (1957).
Thonnes, W., Ruska, H.: Über leptomere Myofibrillen in den Herzmuskelzellen. Z. Zellforsch. 15, 650–670 (1960).
Viragh, S., Challice, C. E.: Variations in filamentous and fibrillar organization and associated sarcolemmal structures in cells of the normal mammalian heart. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 28, 321–334 (1969).
Winckler, G.: L'innervation proprioceptive des muscles extrinsèques du globe oculaire chez l'homme. C. R. Ass. Anat. 848–857 (1956).
Winckler, G.: Les aspects morphologiques de l'innervation des muscles striés. Arch. Biol. (Liège) 75, Suppl. 943–973 (1964).
Winckler, G.: L'innervation des fuseaux neuro-musculaires du masséter chez l'homme. Acta anat. (Basel) 73, Suppl. 436–443 (1969).
Winckler, G., Foroglou, Ch.: Caractéristiques des nuclear bag et des nuclear chain fibres des fuseaux neuro-musculaires. Brain Res. 42, 289–296 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foroglou, C., Winckler, G. Ultrastructure du fuseau neuro-musculaire chez l'homme. Z. Anat. Entwickl. Gesch. 140, 19–37 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00520715
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00520715