Summary
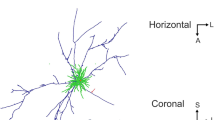
The embryonic cerebral cortex was examined for signs of a columnar organization. In vertical montages extending from the intermediate lamina to the pia, nerve cells arranged in columns are separated by bundles of radial processes. However, sections tangential to the pial surface revealed little evidence for repeating modular units; bundles of radial processes are not regular in outline, and surrounding groups of cells display little symmetry in their distribution.
Tangential processes representing the development of a rudimentary neuropile are present in the marginal lamina and at lower levels of the cortical plate. However, well defined synapses were not seen at this stage of development when proliferation and migration of neuroblasts continues to provide cells to the upper part of the cortical plate. The association of neuroblasts with bundles of radial fibers suggests that these vertical elements serve as preferential pathways for cells migrating to the cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, J.: Autoradiographic investigation of cell proliferation in the brains of rats and cats. Anat. Rec. 145, 573–592 (1963).
Angevine, J. B., Sidman, R. L.: Autoradiographic study of cell migration during histogenesis of cerebral cortex in the mouse. Nature (Lond.) 192, 766–768 (1961).
Berry, M., Rogers, A.: The migration of neuroblasts in developing cerebral cortex. J. Anat. (Lond.) 99, 691–709 (1965).
Bodian, D.: Development of fine structure of spinal cord in monkey fetuses. I. The motoneuron neuropil at the time of onset of reflex activity. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 119, 129–149 (1966).
Bonin, G., von, Mehler, W. R.: On columnar arrangement of nerve cells in cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 27, 1–9 (1971).
Brodmann, K.: Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Großhirnrinde; in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues. Leipzig: J. A. Barth 1909.
Caley, D. W., Maxwell, D. S.: An electron microscopic study of neurons during postnatal development of the rat cerebral cortex. J. comp. Neurol. 133, 17–44 (1968).
Colonnier, M. L.: The structural design of the neocortex. In: Brain and conscious experience, by J. C. Eccles (ed.), p. 1–23. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1966.
Del Cerro, M. P., Snider, R. S.: Studies on the developing cerebellum. Ultrastructure of the growth cones. J. comp. Neurol. 133, 341–362 (1968).
Fujita, S.: Kinetics of cellular proliferation. Exp. Cell Res. 28, 52–60 (1962).
Hicks, S. P., D'amato, C. J.: Cell migrations to the isocortex in the rat. Anat. Rec. 100, 619–634 (1968).
Hubel, D. H., Wiesel, T. N.: Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 106–154 (1962).
Lorente de Nó, R.: Cerebral cortex: architectonics, intra-cortical connections. In: Physiology of the nervous system, by J. F. Fulton, p. 274–301. New York: Oxford University Press 1949.
Meller, K., Breipohl, W., Glees, P.: Synaptic organization of the molecular and the outer granular layer in the motor cortex in the white mouse during postnatal development. A golgi- and electronmicroscopical study. Z. Zellforsch. 92, 217–231 (1968).
Millonig, G.: Further observations on a phosphate buffer for osmium solutions in fixation. Inter. Congr. Elec. Micr. 5, P-8. New York: Academic Press 1962.
Mountcastle, V. B.: Modality and topographic properties of single neurons of cat's somatic sensory cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 20, 408–434 (1957).
Nauta, W. J. H., Karten, H. J.: A general profile of the vertebrate brain, with sidelights on the ancestry of cerebral cortex. In: The neurosciences, by Francis O. Schmitt (ed.), p. 7–26. New York: Rockefeller University Press 1970.
Noback, C., Purpura, D. P.: Postnatal ontogenesis of neurons in cat neocortex. J. comp. Neurol. 117, 291–307 (1961).
Rakic, P.: Guidance of neurons migrating to the fetal monkey neocortex. Brain Res. 33, 471–476 (1971).
Ramón y Cajal, S.: Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés, vol. II. Paris: Maloine Tr. by Azoulay (1909).
Schwartz, I. R., Pappas, C. D., Purpura, D. P.: Fine structure of neurons and synapses in the feline hippocampus during postnatal ontogenesis. Exp. Neurol. 22, 394–407 (1968).
Shimada, S., Langman, J.: Cell proliferation, migration and differentiation in the cerebral cortex of the golden hamster. J. comp. Neurol. 139, 227–244 (1970).
Snider, R. S., Del Cerro, M. P.: Drug-induced dendritic sprouts on Purkinje cells in the adult cerebellum. Exp. Neurol. 17, 466–480 (1967).
Stensaas, L. J.: The development of hippocampal and dorsolateral pallial regions of the cerebral hemisphere in fetal rabbits. II. Twenty millimeter stage, neuroblast morphology. J. comp. Neurol. 129, 71–84 (1967a).
Stensaas, L. J.: The development of hippocampal and dorsolateral pallial regions of the cerebral hemisphere in fetal rabbits. III. Twenty-nine millimeter stage, marginal lamina. J. comp. Neurol. 130, 149–162 1967b).
Stensaas, L. J.: The development of hippocampal and dorsolateral pallial regions of the cerebral hemisphere in fetal rabbits. I. Fifteen millimeter stage, spongioblast morphology. J. comp. Neur. 129, 59–70 (1967c).
Stensaas, L. J., Stensaas, S. S.: An electron microscope study of cells in the matrix and intermediate laminae of the cerebral hemisphere of the 45 mm rabbit embryo, Z. Zellforsch. 91, 341–365 (1968).
Tennyson, V. M.: The fine structure of the axon and growth cone of the dorsal root neuroblast of the rabbit embryo. J. Cell Biol. 44, 62–79 (1970).
Voeller, K., Pappas, G. D., Purpura, D. P.: Electron microscope study of development of cat superficial neocortex. Exp. Neurol. 7, 107–130 (1963).
Vogt, C., Vogt, O.: Allgemeinere Ergebnisse unserer Hirnforschung. J. Psychol. u. Neurol. (Lpz.) 25, 273–462 (1919).
Woolsey, T. A., Loos, H., van der: The structural organization of layer IV in the somatosensory region (SI) of mouse cerebral cortex. The description of a cortical field composed of discrete cytoarchitectonic units. Brain Res. 17, 205–242 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stensaas, L.J. An electron microscope study of the organization of the cerebral cortex of the 60 mm rabbit embryo. Z. Anat. Entwickl. Gesch. 137, 335–350 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00519101
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00519101