Summary
-
1.
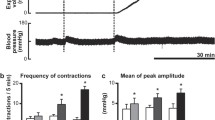
Distension of the proximal jejunum by increasing the intraluminal pressure for short time periods causes a reflex response in blood pressure of anaesthetized rats which correlates with the magnitude of distension. The blood pressure response consists of a short initial rise followed by a marked decrease for the time of distension.
-
2.
The absence of the depressor response in capsaicin desensitized rats indicates its mediation by C fibre afferents. These afferents are located within the periarterial mesenteric nerves. The depressor response was also elicited by stimulation of these nerves and abolished by local application of percain or capsaicin onto the mesenteric stalk. Vagal afferents were not involved in this depressor response as shown by bilateral vagotomy or by afferent vagus stimulation.
-
3.
The depressor response is absent in spinal rats. Therefore, the location of the reflex centre is assumed to be supraspinal. Because it is augmented by naloxone and abolished by morphine in a naloxone reversible way it is regarded as a nociceptive reflex response.
-
4.
The efferent side of the depressor response is unknown; cholinergic and α-adrenergic activation were excluded.
-
5.
The initial pressor response to intestinal distension or to afferent periaterial mesenteric nerve stimulation persists in capsaicin desensitized rats excluding the involvement of C fibre afferents and in spinal rats indicating that the reflex centre is within the spinal cord. It is not diminished by morphine and therefore not a nociceptive response. Its inhibition by phentolamine suggests an α-adrenergic spinal response to intestinal distension. In control rats the pressor response is greatly overlapped by the much more pronounced depressor response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth A, Hall P, Wall PD, Allt G, MacKenzie ML, Gibson S, Polak JM (1981) Effects of capsaicin applied locally to adult peripheral nerve. II. Anatomy and enzyme and peptide chemistry of peripheral nerve and spinal cord. Pain 11:379–388
Andrews CJH, Andrews WHH, Orbach J (1972) A sympathetic reflex elicited by distension of the mesenteric venous bed J Physiol 226:119–132
Bessou P, Perl ER (1966) A movement receptor of the small intestine. J Physiol 182:404–426
Brasch H, Zetler G (1982) Caerulein and morphine in a model of visceral pain: effects on the hypotensive response to renal pelvis distension in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 319:161–167
Cervero F, McRitchie HA (1981) Neonatal capsaicin and thermal nociception: a paradox. Brain Res 215:414–418
Cervero F, McRitchie HA (1982) Effects of neonatal administration of capsaicin on several nociceptive systems of the rat. Adv Pain Res Ther 4:1–15
Clarke GD, Davison JS (1974) Tension receptors in the oesophagus and stomach of the rat. J Physiol 239:41P-42P
Donnerer J, Lembeck F (1982) Analysis of the effects of intravenously injected capsaicin in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (in press)
Downman CBB, McSwiney BA (1946) Reflexes elicited by visceral stimulation in the acute spinal animal. J Physiol 105:80–94
Downman CBB, McSwiney BA, Vass CCN (1948) Sensitivity of the small intestine. J Physiol 107:97–106
Duggan AW (1982) Brain stem control of the responses of spinal neurones to painful skin stimuli. Trends Neurosci 5:127–130
Floyd K, Hick VE, Morrison JFB (1976) Mechanosensitive afferent units in the hypogastric nerve of the cat. J Physiol 259:457–471
Furness JB, Papka RE, Della NG, Costa M, Eskay RL (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerves associated with the vascular system of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 7:447–459
Gamse R (1982) Capsaicin and nociception in the rat and mouse. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 320:205–216
Gamse R, Lembeck F, Cuello AC (1979) Substance P in the vagus nerve. Immunochemical and immunohistochemical evidence for axoplasmic transport. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 306:37–44
Gamse R, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1980) Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol 68:207–213
Gamse R, Petsche U, Lembeck F, Gábor Jancsó A (1982) Capsaicin applied to peripheral nerve inhibits axoplasmic transport of substance P and somatostatin. Brain Res 239:447–462
Gernandt B, Zotterman Y (1946) Intestinal pain: an electrophysiological investigation on mesenteric nerves. Acta Physiol Scand 12:56–72
Holzer P, Gamse R, Lembeck F (1980) Distribution of substance P in the rat gastrointestinal tract — lack of effect of capsaicin pretreatment. Eur J Pharmacol 61:303–307
Iggo A (1955) Tension receptors in the stomach and the urinary bladder. J Physiol, 128:593–607
Iggo A (1957) Gastrointestinal tension receptors with unmyelinated afferent fibres in the vagus of the cat. Q J Exp Physiol 42:130–143
Iggo A (1958) The electrophysiological identification of single nerve fibres, with particular reference to the slowest-conducting vagal afferent fibres in the cat. J Physiol 142:110–126
Jancsó G, Király E (1981) Sensory neurotoxins: chemically induced selective destruction of primary sensory neurons. Brain Res 210:83–89
Jancsó G, Király E, Jancsó-Gábor A (1977) Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurons. Nature 270:741–743
Jancsó G, Király E, Jancsó-Gábor A (1980) Chemosensitive pain fibres and inflammation. Int J Tiss React II:57–66
Jancsó G, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM, Király E, Halász N, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Rehfeld J, Steinbusch H, Verhofstad A, Elde R, Said S, Brown M (1981) Immunohistochemical studies on the effect of capsaicin on peptide and monoamine neurons using antisera to substance P, gastrin/CCK, somatostatin, VIP, enkephalin, neurotensin and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Neurocytol 10:963–980
Juan H (1982) Nicotinic nociceptors on perivascular sensory nerve endings. Pain 12:259–264
Kelly DD (1981) Somatic sensory system IV: central representations of pain and anlgesia. In: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH (eds) Principles of Neural Science. Elsevier North Holland, Inc, New York, pp 199–204
Khayutin VM, Lukoshkova EV, Gailans YB (1977) Sympathetic reflex responses presumably specific for nociceptive stimulation. J Physiol 73:305–318
Lim RKS, Guzman F, Rodgers DW, Goto K, Braun C, Dickerson G, Engle RJ (1964) Site of action of narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics determined by blocking bradykinin-evoked visceral pain. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 152:25–58
Leek BF (1977) Abdominal and pelvic visceral receptors. Br Med Bull 33:163–168
Lembeck F (1957) Untersuchungen über die Auslösung afferenter Impulse. Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 230:447–459
Lennander KG (1901) Lakttagelser öfver känseln i bukhalan. Hygica LXIII:217–250
Lewis T, Kellgren (1939) Observations relating to referred pain, visceromotor reflexes and other associated phenomena. Clin Sci 4:47–71
Longhurst JC, Spilker HL, Ordway GA (1981) Cardiovascular reflexes elicited by passive gastric distension in anaesthetized cats. Am J Physiol 240:H539-H545
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Kewenter J, Petterson G, Ahlman H, Edin R, Dahlström A, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Uvnäs-Wallensten K, Said S (1979) Substance P-, VIP-, and enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the human vagus nerve. Gastroenterology 77:468–471
Meyer AW (1919) Expermentelle Untersuchungen über die Sensibilität von Magen und Darm. Dtsch Z Chir 151:153–163
Moore RM, Galveston T (19838) Some experimental observations relating to visceral pain. Surgery 3:534–555
Morrison JFB (1972) Mechanoreceptors in the region of the mesentery with A-delta and C-fibres in the splanchnic nerves of cats. J Physiol 226:100–101
Morrison JFB (1973) Splanchic slowly adapting mechanoreceptors with puntate receptive fields in the mesentery and gastrointestinal tract of the cat. J Physiol 233:349–361
Nagy JI, Hunt SP, Iversen LL, Emson PC (1981) Biochemical and anatomical observations on the degeneration of peptide-containing primary afferent neurons after neonatal capsaicin. Neuroscience 6:1923–1934
Petsche U, Fleischer E, Lembeck F, Handwerker HO (1982) Selective blockade of impulse conduction in unmyelinated afferent fibres by axonal application of capsaicin. Neurosci Lett Suppl 10:S384-S385
Petty MA, Reid JL (1982) The effect of opiates on arterial baroreceptor reflex function in the rabbit. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (in press)
Potter GD, Guzman F, Lim RKS (1962) Visceral pain evoked by intraarterial injection of substance P. Nature 193:983–984
Procacci P, Zoppi M, Maresca M (1979) Experimental pain in man. Pain 6:123–140
Scadding JW (1980) The permanent anatomical effects of neonatal capsaicin on somatosensory nerves. J Anat 131:473–484
Shipley RE, Tilden JN (1959) A pithed rat preparation suitable for assaying pressor substances. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 64:453
Wood JD, Mayer CJ (1979) Intracellular study of tonic-type enteric neurons in guinea-pig small intestine. J Neurophysiol 42:569–581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lembeck, F., Skofitsch, G. Visceral pain reflex after pretreatment with capsaicin and morphine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 321, 116–122 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518478
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518478