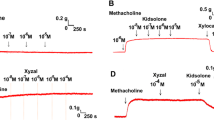
Summary
The deeper airways of patients with asthmatic bronchitis are often infected with Haemophilus influenzae. Vaccination of guinea pigs with H. influenzae resulted in a significant impairment of the isoproterenol induced relaxation of isolated tracheal spirals by approximately 50% 4 days following vaccination. In the present study we further investigated the effects of some drugs affecting catecholamine release on the H. influenzae induced functional desensitization of tracheal spirals. Benserazide, an inhibitor of dopadecarboxylase, completely prevented the reduction in isoproterenol-induced relaxation after H. influenzae vaccination, while no effect on relaxation of tracheal spirals from control animals was detected. On the other hand, inhibiting the re-uptake of catecholamines with desipramine did not influence the relaxation in the H. influenzae vaccinated treacheal spirals. Treatment of control animals with desipramine however resulted in a decreased relaxation of the isolated spirals by 40%. One day following vaccination with H. influenzae the level of norepinephrine in lung tissue was significantly elevated by 71%, and in plasma by 77%, while after 4 days no significant effects were observed. The spontaneous release of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine of tracheal incubates was increased at days 1 and 4 following vaccination. The release of catecholamines from minced lung incubates of H. influenzae pretreated guinea pigs did not differ from that of controls.
On the basis of these results it may be suggested that catecholamine metabolism is changed in lungs from H. influenzae vaccinated animals. Catecholamines, accordingly may play a role in the desensitization of β-adrenoceptors by H. influenzae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson WH, Krzanowski JJ, Polson JB, Szentivanyi A (1979) Characteristics of histamine tachyphylaxis in canine tracheal smooth muscle. Naurnyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 308:117–125
Banerjee SP, Kung LS, Riggi SJ, Chanda SK (1977) Development of beta-adrenergic receptor subsensitivity by antidepressants. Nature 286:455–456
Bartholini G, Pletscher A (1968) Cerebral accumulation and metabolism of C14-dopa after selective inhibition of peripheral decarboxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 161:14–20
Bartholini G, Burkard W, Pletscher A (1967) Increase of cerebral catecholamines caused by 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine after inhibition of peripheral decarboxylase. Nature 215:852–853
Buckner CK, Saini RK (1975) On the use of functional antagonism to estimate dissociation constants for beta-adrenergic receptor agonists in isolated guinea pig trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 194:565–574
Cooper AW, Williamson GM, Zinneman K, Edwards GF, Thornton H (1961) Changes in the bacterial flora of the sputum associated with exacerbations and long-term antibacterial treatment. Br J Dis Chest 55:23–29
Dismukes RK, Daly JW (1974) Norepinephrine-sensitive system generating adenosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate: Increased responses in cerebral cortical slices from reserpine treated rats. Mol Pharmacol 10:933–940
Douglas JS, Lewis AJ, Ridgway P, Brink C, Bouhuys A (1977) Tachyphylaxis to β-adrenoceptor agonists in guinea pig airway smooth muscle in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 42:195–205
Fisher M, Akhtar AJ, Calder MA, Moffat MAJ, Stewart SM, Zeally H, Crofton JW (1969) Pilot study of factors associated with exacerbations in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J 4:187–192
Frazer A, Hess ME, Mendels J, Gable B, Kunkel E, Bender A (1978) Influence of acute and chronic treatment with desmethylimipramine on catecholamines effects in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 206:311–319
Greenberg LH, Weiss B (1979) Ability of aged rats to alter beta-adrenergic receptors of brain in response to repeated administration of reserpine and desmethylimipramine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 211:309–316
Hirschmann JV, Everett ED (1979) Haemophilus influenzae infections in adults: Report of nine cases and a review of the literature. Medicine 58:80–95
Homcy CJ, Strauss HW, Kopiwoda S (1980) Beta receptor occupancy. J Clin Invest 65:1111–1118
Kebabian JW, Zatz M, Romero JA, Axelrod J (1975) Rapid changes in rat pineal β-adrenergic receptor: Alterations in l-(3H)-alprenolol binding and adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:3735–3739
Levitzki A (1980) Catecholamine receptors. In: Schulster D, Levitzki A (eds) Cellular receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester, pp 267–286
Mikey J, Tate R, Lefkowitz RJ (1975) Subsensitivity of adenylate cyclase and decreased β-adrenergic receptor binding after chronic exposure to (-)-isoproterenol in vitro. J Biol Chem 250:5727–5729
Morris HG, De Roch G, Earle M (1972) Urinary excretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine in asthmatic children. J All Clin Immunol 50:138–145
Mukherjee C, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ (1975) Catecholamine-induced subsensitivity of adenylate cyclase associated with loss of β-adrenergic receptor binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1945–1949
Nijkamp FP, Raaijmakers JAM, Schreurs AJM, Terpstra GK (1980) Inhibition of effects of isoprenaline and adrenaline by Haemophilus influenzae vaccination. Br J Pharmacol 68:146P
Ouelette J, Chosey J, Reed CE (1967) Catecholamine excretion after salmonella enteriditis endotoxin in a normal and an asthmatic subject. J All 39:102
Parker CW (1973) Adrenergic responsiveness in asthma. In: Austen KF, Lichtenstein LM (eds) Asthma. Physiology, immunopharmacology and treatment. Academic Press, New York, pp 185–210
Schreurs AJM, Nijkamp FP (1982) Haemophilus influenzae induced loss of lung β-adrenoceptor binding sites and modulation by changes in peripheral catecholaminergic input. Eur J Pharmacol 77:95–102
Schreurs AJM, Terpstra GK, Raaijmakers JAM, Nijkamp FP (1980a) The effects of Haemophilus influenzae vaccination on anaphylactic mediator release and isoprenaline-induced inhibition of mediator release. Eur J Pharmacol 62:261–268
Schreurs AJM, Terpstra GK, Raaijmakers JAM, Nijkamp FP (1980b) Effects of vaccination with Haemophilus influenzae on a drenoceptor function of tracheal and parenchymal strips. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 215:691–696
Strada SJ, Weiss B (1974) Increased response to catecholamines in the cyclic AMP system of rat pineal gland induced by decreased sympathetic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 160:197–204
Su YF, Harden TK, Perkins JP (1979) Isoproterenol induced desensitization of adenylate cyclase in human astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem 254:38–41
Terpstra GK, Raaijmakers JAM, Kreukniet J (1979) Comparison of vaccination of mice and rats with Haemophilus influenzae and Bordetella pertussis as models of atopy. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 6:139–149
U'Prichard DC, Snyder SH (1978) 3H-Catecholamine binding to α-receptors in rat brain: Enhancement by reserpine. Eur J Pharmacol 51:145–155
Van der Gugten J, Palkovits M, Wijnen HLJM, Versteeg DHG (1976) Regional distribution of adrenaline in rat brain. Brain Res 107:171–175
Van der Zwan JC (1976) Bronchial obstructive reactions and Haemophilus influenzae. Thesis, Groningen
Versteeg DHG, Van der Gugten J, De Jong W, Palkovits M (1976) Regional concentrations of noradrenaline and dopamine in rat brain. Brain Res 113:563–574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreurs, A.J.M., Versteeg, D.H.G. & Nijkamp, F.P. Involvement of catecholamines in haemophilus influenzae induced decrease of β-adrenoceptor function. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 320, 235–239 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510134
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510134