Summary
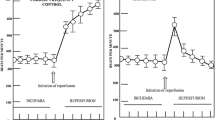
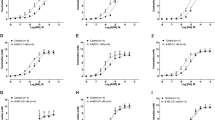
Intraarterial injection of α-latrotoxin (αLTx), the major toxin of the black widow spider (Latrodectus mactans tredecimguttatus) venom, into carotid catheterized rats, induced prompt and marked rises in plasma adrenaline and noradrenaline concentrations, indicating that the toxin stimulates catecholamine release from both the adrenal medulla and sympathetic nerve terminals. Pretreatment with the ganglionic blocker chlorisondamine greatly reduced the plasma adrenaline response to αLTx but had almost no effect on the noradrenaline response, indicating that αLTx-stimulation of sympathetic nerve terminals is direct, whereas catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla is probably mediated by preganglionic release of acetylcholine. In vitro, αLTx induced a dose-dependent release of 3H-noradrenaline from rat irides preincubated with this radioactive amine and this effect was not changed by chlorisondamine plus atropine. By contrast, the toxin had no effect on 3H-noradrenaline release from suspensions of cultured rat chromaffin cells. Specific, high affinity binding of 125I-αLTx in iris and adrenal medulla homogenates was found to be exceedingly low, suggesting that it might be restricted to nerve terminals. No 125I-αLTx binding was seen nor could any effect of the toxin on 14C-5-hydroxytryptamine release be found in rat blood platelet preparations. αLTx binding and its amine releasing effect seem, therefore, to be specific for neurons and absent from other cells, even those, like adrenomedullary cells and blood platelets, which share with neurons their origin and/or other important characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba A, Cooper JR (1980) The action of black widow spider venom on cholinergic mechanisms in synaptosomes. J Neurochem 34:1369–1379
Bolton AE, Hunter WM (1973) The labeling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J 133:529–538
Britos SA, Orsingher OA, Fulginiti S (1978) Effects of venom gland extract of the black widow spider on rat brain and heart levels of noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and acetylcholine. Toxicon 16:393–395
Bühler HU, Da Prada M, Haefely W, Picotti GB (1978) Plasma adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine in man and different animal species. J Physiol (Lond) 276:311–320
Carruba MO, Picotti GB, Miodini P, Lotz W, Da Prada M (1981) Blood sampling by chronic cannulation technique for reliable measurements of catecholamines and other hormones in plasma of conscious rats. J Pharmacol Meth 5:293–303
Coupland RE (1965) Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the rat adrenal medulla. I. The ultrastructure and organization of chromaffin cells in the normal rat adrenal medulla. J Anat 99:231–254
Dahlström A, Haggendal J, Hökfelt T (1966) The noradrenaline content of the varicostities of sympathetic adrenergic terminals in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 67:289–294
Da Prada M, Zürcher G (1976) Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the fentomole range. Life Sci 19:1161–1174
Da Prada M, Picotti GB (1979) Concentration and subcellular localization of catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in human and animal blood platelets: monoamine distribution between platelets and plasma. Br J Pharmacol 65:653–662
Ehinger B, Falk B (1966) Concomitant adrenergic and parasympathetic fibres in the rat iris. Acta Physiol Scand 67:201–207
Frontali N (1972) Catecholamine-depleting effect of black widow spider venom on iris nerve terminals. Brain Res 37:146–148
Frontali N, Granata F, Traina ME, Bellino M (1973) Catecholamine depleting effect of black widow spider venom on fibres innervating different guinea pig tissues. Experientia 29:1525–1526
Frontali N, Ceccarelli B, Gorio A, Mauro A, Siekevitz P, Tzeng MC, Hurlbut WP (1976) Purification from black widow spider venom of a protein factor causing the depletion of synaptic vesicles at neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol 68:462–479
Grasso A (1976) Preparation and properties of a neurotoxin purified from the venom of black widow spider (Latrodectus mactans tredecimguttatus). Biochim Biophys Acta 439:406–412
Grasso A, Senni MI (1979) A toxin purified from the venom of black widow spider affects uptake and release of radioactive ψ-aminobutyrate and N-epinephrine from rat brain synaptosomes. Eur J Biochem 102:337–344
Hurlbut WP, Ceccarelli B (1979) Use of black widow spider venom to study the release of neurotransmitters. In: Ceccarelli B, Clementi F (eds) Neurotoxins tools in neurobiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 87–115
Kilpatrick DL, Ledbetter FH, Carson KA, Kirschner AG, Slepetis R, Kirschner N (1980) Stability of bovine adrenal medulla cells in culture. J Neurochem 35:679–692
Lowry OR, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
Meldolesi J (1982) Studies on α-latrotoxin receptors in rat brain synaptosomes. Correlation between toxin binding and stimulation of transmitter release. J Neurochem 38:1559–1569
Paggi P, Toschi G (1972) Effects of denervation and lack of calcium on the action of latrodectus venom on rat sympathetic ganglion. Life Sci 11:413–417
Picotti GB, Da Prada M, Pletscher A (1976) Uptake and liberation of mepacrine in blood platelets. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 292:127–131
Picotti GB, Carruba MO, Ravazzani C, Cesura AM, Galva MD, Da Prada M (1981) Plasma catecholamines in rats exposed to cold: effects of ganglionic and adrenoreceptor blockade. Eur J Pharmacol 69:321–329
Pletscher A (1978) Platelets as models for monoaminergic neurons. In: Youdim MBH, Lovenberg W, Sharmann DF, Lagnado JR (eds) Essays in neurochemistry and neuropharmacology, vol 3. J. Wiley and Sons, London, pp 49–101
Pumplin DW, McClure WD (1976) The release of acetylcholine elicited by extracts of black widow spider glands: studies using rat superior cervical ganglia and inhibitors of electrically stimulated release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 201:312–319
Sampayo RRL (1944) Pharmacological action of the venom of Latrodectus mactans and other Latrodectus spiders. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 80:309–322
Schneider AS, Herz R, Rosenheck K (1977) Stimulus-secretion coupling in chromaffin cells isolated from bovine adrenal medulla. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5036–5040
Tzeng MC, Siekevitz P (1979) The binding interaction between α-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom and a dog cerebral cortex synaptosomal membrane preparation. J Neurochem 33:263–274
Tzeng MC, Cohen RS, Siekevitz P (1978) Release of neurotransmitters and depletion of synaptic vesicles in cerebral cortex slices by α-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4016–4020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Picotti, G.B., Bondiolotti, G.P. & Meldolesi, J. Peripheral catecholamine release by α-latrotoxin in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 320, 224–229 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510132
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510132