Summary
-
1.
Capsaicin treated rats, in which the function of substance P-containing primary sensory neurons was impaired, were used to investigate the function of afferent fibers within the splanchnic nerve. The effects of electrical stimulation of the splanchnic nerve either distal or proximal to the site of its transsection on blood pressure and heart rate were investigated.
-
2.
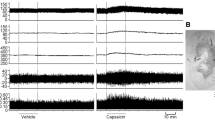
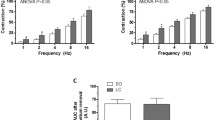
Distal splanchnic nerve stimulation evoked an equal rise in blood pressure in capsaicin treated rats and in their controls. Distal splanchnic nerve stimulation did not cause plasma extravasation in the adrenal medulla, an effect which is produced by antidromic stimulation of cutaneous sensory nerves. Peripheral effects of stimulation of primary afferent fibers within the splanchnic nerve cannot be assumed from these experiments.
-
3.
Proximal stimulation of the splanchnic nerve evoked a reflex fall in blood pressure but no bradycardia. The fall in blood pressure was absent in capsaicin treated rats, which indicates that this effect is mediated by primary afferent fibers. Since the reflex fall in blood pressure was abolished by adrenergic blockade with guanethidine, it can be explained by vasodilatation resulting from reduction of sympathetic vasoconstrictor tone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brasch H, Zetler G (1982) Caerulein and morphine in a model of visceral pain. Effects on the hypotensive response to renal pelvis distension in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 319:161–167
Cervero F, McRitchie A (1982) Neonatal capsaicin does not affect unmyelinated efferent fibers of the autonomic nervous system: functional evidence. Brain Res 239:283–288
Dalsgaard CJ, Hökfelt T, Elfvin LG, Skirboll L, Emson P (1982) Substance P-containing primary sensory neurons projecting to the inferior mesenteric ganglion: evidence from combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience 7:647–654
Donnerer J, Lembeck F (1982) Analysis of the effects of intravenously injected capsaicin in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 320:54–57
Dun NJ, Minota S (1981) Effects of substance P on neurones of the inferior mesenteric ganglia of the guinea-pig. J Physiol 321:259–271
Frumin UJ, Ngai SH, Wang SC (1953) Evaluation of vasodilator mechanisms in the canine hind leg; question of dorsal root participation. Am J Physiol 173:428–436
Furness JB, Elliott JM, Murphy R, Costa M, Chalmers JP (1982) Baroreceptor reflexes in conscious guinea-pigs are unaffected by depletion of cardiovascular substance P nerves. Neuroscience Letters 32:285–290
Gamse R, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1980) Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmac 68:207–213
Gamse R, Wax A, Zigmond RE, Leeman SE (1981a) Immunoreactive substance P in sympathetic ganglia: distribution and sensitivity towards capsaicin. Neuroscience 6:437–441
Gamse R, Leeman SE, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1981b) Differential effects of capsaicin on the content of somatostatin, substance P, and neurotensin in the nervous system of the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:140–148
Häusler G, Osterwalder R (1980) Evidence suggesting a transmitter or neuromodulatory role for substance P at the first synapse of the baroreceptor reflex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 314:111–121
Hökfelt T, Elfvin L-G, Schultzberg M, Goldstein M, Nilsson G (1977) On the occurrence of substance P-containing fibers in sympathetic ganglia: immunohistochemical evidence. Brain Res 132:29–41
Holzer P, Bucsics A, Lembeck F (1982) Distribution of capsaicin-sensitive nerve fibers containing immunoreactive substance P in cutaneous and visceral tissues of the rat. Neurosci Lett 31:253–257
Jiang ZG, Dun NJ, Karczmar AG (1982) Substance P: A putative sensory transmitter in mammalian autonomic ganglia. Science 217:739–741
Konishi S, Tsunoo A, Yanaihara N, Otsuka M (1980) Peptidergic excitatory and inhibitory synapses in mammalian sympathetic ganglia: roles of substance P and enkephalin. Biomed Res 1:528–536
Lembeck F, Holzer P (1979) Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 310:175–183
Lembeck F, Skofitsch G (1982) Visceral pain reflex after pretreatment with capsaicin and morphine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:116–122
Lorez HP, Häusler G, Aeppli L (1981) The capsaicin treated rat: a suitable model to study the role of substance P in baroreceptor reflex function? Neuroscience Suppl 7:208
Maley B, Elde R (1982) Immunohistochemical localization of putative neurotransmitter within the feline nucleus tractus solitarii. Neuroscience 7:2469–2490
Matthews MR, Cuello C (1982) Substance P-immunoreactive peripheral branches of sensory neurons innervate guinea pig sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79:1668–1672
Niijima A, Winter DL (1968) Baroreceptor in the adrenal gland. Science 159:434–435
Pernow P (1953) Studies on substance P. Purification, occurrence and biological actions. Acta Physiol Scand 29 (Suppl 105):1–90
Role LW, Leeman SE, Perlman RL (1981) Somatostatin and substance P inhibit catecholamine secretion from isolated cells of guinea-pig adrenal medulla. Neuroscience 6:1813–1821
Sejnowski TJ (1982) Peptidergic synaptic transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Fed Proc 41:2923–2928
Tsunoo A, Konishi S, Otsuka M (1982) Substance P as an excitatory transmitter of primary afferent neurons in guinea-pig sympathetic ganglia. Neuroscience 7:2025–2037
Willems JL, Bogart MG (1978) Neurogenic vasodilatation. Gen Pharmacol 9:223–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lembeck, F., Donnerer, J. Reflex fall in blood pressure mediated by capsaicin-sensitive afferent fibers of the rat splanchnic nerve. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 322, 286–289 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508344
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508344