Summary
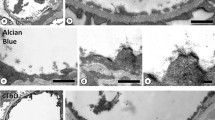
When ruthenium red (RR) is combined with OsO4, an electronopaque complex forms which readily binds to the cell surface coat. However, the RR-OsO4 complex is often excluded from intercellular spaces in many cell types, and thus is not dependable as a tracer of regions continuous with the extracellular space. Postfixation of erythrocytes agglutinated by the lectin helix (Helix promatia) and intact carotid artery endothelium with a freshly prepared mixture of 1% OsO4 containing 0.1% ruthenium red (RR) resulted in a dense surface deposit of these cells, but intercellular regions were penetrated to a minimal degree by the stain. When a similar mixture of RR-OsO4 was allowed to stand 3 h before use, RR is oxidized by OsO4 to yield a ruthenium compound that has a spectrophotometric absorbance maximum at 365 nm. This RR molecule has a reduced number of cationic sites due to binding with osmium dioxide OsO =2 . Postfixation of agglutinated RBCs and carotid artery endothelium with this oxidized ruthenium-OsO4 mixture resulted in a 50–80% decrease in surface deposition but markedly enhanced penetration into intercellular regions. The enhanced penetration is attributed to decreased binding affinity of the oxidized ruthenium for anionic surface membrane components, permitting effective stain penetration into regions of cell-to-cell contact rather than extensive surface deposition. These studies indicate that the ruthenium compound formed by OsO4 oxidation of ruthenium red may be a useful tracer for ultrastructural visualization of intercellular spaces and junctions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babai F (1978) An ultrastructural method for the study of cell viability using ruthenium red. In: Sturgess JM (ed) Proc 9th Int Congr Electron Microsc, Toronto, 1978, vol I. Microscopical Soc Canada, pp. 304–305
Baldwin KM (1977) The fine structure of healing over in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol 9:956–966
Beaudoin AR, Paquet MR, Lord A, Dionne L (1978) Exocytosis in mammalian cells. II. Topography of ferritin concanavalin A conjugate and ruthenium red binding sites on the luminal surface of pancreatic acinar cells. J Ultrastruct Res 63:170–177
Blanquet PR (1976a) Ultrahistochemical study on the ruthenium red surface staining. I. Processes which give rise to electron-dense marker. Histochemistry 47:63–78
Blanquet PR (1976b) Ultrahistochemical study on the ruthenium red surface staining. II. Nature and affinity of the electron dense marker. Histochemistry 47:175–189
Collin R, Griffith WP, Phillips FL, Skapski AC (1974) Staining and fixation of unsaturated membrane lipids by osmium tetroxide. Biochim Biophys Acta 354:152–154
Dierichs R (1979) Ruthenium red as a stain for electron microscopy. Some new aspects of its application and modification. Histochemistry 64:171–188
Dierichs R, Lindner E (1979) Ultrahistochemical investigations of dog lung surfactant with ruthenium red and iodoplatinate reactions. Histochemistry 60:335–346
Fletcher JM, Greenfield BF, Hardy CJ, Scargill D, Woodhead JL (1961) Ruthenium red. J Chem Soc 2000–2006
Forbes MS, Sperelakis N (1979) Ruthenium red staining of skeletal and cardiac muscles. Cell Tissue Res 200:367–382
Handley DA, Olsen B (1979) Butvar B-98 as a thin support film. Ultramicroscopy 4:479–480
Haugen A (1979) Ruthenium red binding to cell coat in neoplastic neurogenic cell lines in culture. Virchows Arch B 29:245–252
Hewson WD, Hager LP (1979) Oxidation of horseradish peroxidase compound II to compound I. J Biol Chem 10:3182–3186
Huttner I, Boutet M, More RH (1973) Studies on protein passage through arterial endothelium. I. Structural correlates of permeability in rat arterial endothelium. Lab Invest 28:672–677
Huttner I, Peters HL (1978) Heterogeneity of cell junctions in rat endothelium: a freeze-fracture study. J Ultrastruct Res 64:303–308
Lee MLL, Chien S (1979) Morphological effects of pressure changes on canine carotid artery endothelium as observed by scanning electron microscopy. Anat Rec 194:1–14
Luft JH (1971a) Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec 171:347–368
Luft JH (1971b) Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec 171:369–416
Luft JH (1976) The structure and properties of the cell surface coat. Int Rev Cytol 45:291–382
Morel FMM, Baker RF, Wayland H (1971) Quantitation of human red blood cell fixation by glutaraldehyde. J Cell Biol 48:91–100
Nielson AJ, Griffith WP (1978) Tissue fixation and staining with osmium tetroxide: the role of phenolic compounds. J Histochem Cytochem 26:138–140
Nielson AJ, Griffith WP (1979) Tissue fixation by osmium tetroxide. J Histochem Cytochem 27:997–999
O'Hare KH (1974) Fine structural observations of ruthenium red binding in developing and adult rat lung. Anat Rec 178:267–288
Pouchelet M, Anteunis A (1979) Nuclear fibrillar centre and oxidized diaminobenzidine staining. Biol Cellulaire 35:133–136
Riemersma JV (1970) Chemical effects of fixation in biological systems. In: Parsons DF (ed) Some biological techniques in electron microscopy. Academic Press, New York, pp 69–91
Simionescu M, Simionescu N, Palade GE (1976) Segmental differentiations of cell junctions in the vascular endothelium. Arteries and viens. J Cell Biol 68:705–723
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
White DL, Andrews SB, Faller, JW, Barrnett RJ (1976) The chemical nature of osmium tetroxide fixation and staining of membranes by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 436:577–592
Yee JP, Mel HC (1978) Kinetics of glutaraldehyde fixation of erythrocytes, size, deformability, form, osmotic and hemolytic properties. Blood Cells 4:485–497
Zingsheim HP, Plattner H (1976) Electron microscopic methods in membrane biology. In: Korn ED (ed) Methods in membrane biology, vol 7. Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Handley, D.A., Chien, S. Oxidation of ruthenium red for use as an intercellular tracer. Histochemistry 71, 249–258 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00507828
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00507828