Abstract
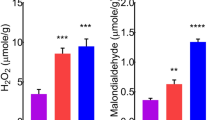
The percent frequency and number of colonies cm−2 leaf area of all the test fungi decreased significantly at the higher doses of cement dust during both pre- and post inoculation treatments. However, the population of some fungi increased at the low dose only. Stimulatory as well as inhibitory effect of cement dust on colony growth of the test fungi were observed at different concentrations of cement dust (500, 1000, 1500, and 2000 μm mL−1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, J. H.: 1986, in N. J. Fokkema and J. Van den Heuvel (eds.), Microbiology of the Phyllosphere, p. 14.
Babich, H. and Stotzky, G.: 1974, Crit. Rev. Environ. Contr. 4, 353.
Bayles, C. J. and Aist, J. R.: 1987, Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 30, 337.
Inoue, H. and Katoh, Y.: 1987, J. Experimental Botany 38, 142.
Malik, C. P. and Srivastava, A. K.: 1982, in Test Book of Plant Physiology, p. 229.
Rai, B. and Pathak, K. K.: 1981, Environ. Pollut. 26, 153.
Singh, A. K.: 1988, J. Indian Bot. Soc. (in press).
Singh, A. K., Solanki, R. S., and Rai, b.: 1989, in: K. S. Bilgrami (ed.) Plant Microbe Interaction, p. 277.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.K., Rai, B. Effect of cement dust treatment on some phylloplane fungi of wheat. Water Air Soil Pollut 49, 349–354 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00507074
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00507074