Summary
Ketotifen is a compound with strong antianaphylactic and anti-histaminic properties both in experimental animals and man. In this paper pharmacological experiments are presented which show that these two activities are independent.
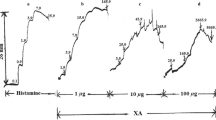
In the rat, the two actions of ketotifen differ markedly in their time course. The ability of ketotifen to prevent a passive cutaneous anaphylactic reaction is of short duration and is already abolished at times when the compound still fully prevents the cutaneous reaction to histamine. Two antihistamines, clemastine and mepyramine, were compared with ketotifen. All three compounds prevented the wheal and flare induced by intracutaneous administration of histamine, but only ketotifen also prevented passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. Accordingly, concomitant administration of the anti-histamine clemastine with ketotifen resulted in enhanced histamine-blocking effects but did not influence the antianaphylactic action of ketotifen. Finally, clemastine and mepyramine differed from ketotifen in their activities in a model of anaphylactically-induced bronchospasm. Ketotifen prevented the bronchospasm, dyspnea and respiratory arrest in dose-dependent fashion, while the two reference antihistamines were virtually inactive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amdur MO, Mead J (1958) Mechanics of respiration in unanesthetized guinea-pigs. Am J Physiol 192 (2):364–368
Craps L, Greenwood C, Radielovic P (1978) Clinical investigations of agents with prophylactic anti-allergic effects in bronchial asthma. Allergy 8:373–382
Dale H (1948) Antihistaminic substances. Br Med J II:281–283
Debelic M, Wüthrich B, Radielovic P (1976) Protektive Medikamentenwirkung bei Antigen-induziertem Bronchialasthma. Pneumologie Suppl 153–159
Ho PhC, Lewis RA, Austen KF, Orange RP (1979) Mediators of immediate hypersensitivity. In: Gupta S, Good RA (eds) Cellular, molecular, and clinical aspects of allergic disorders. New York London, Plenum Medical Book Company, p 179
Karlin JM (1972) The use of antihistamines in asthma. Ann Allergy 30:342–347
Magnussen H, Hartmann V (1977) Allerg Immunopathol Suppl 5:27–32
Martin U, Römer D (1978) The pharmacological properties of a new, orally active antianaphylactic compound: ketotifen, a benzocycloheptathiophene. Arzneim Forsch 28 (I):770–786
Miclous ZE, Gerguson EW, Rosenberg FJ (1974) Effects of anti-anaphylactic drugs upon passive cutaneous anaphylaxis mediated by graded doses of reaginic and non-reaginic antibodies in rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 47:633–649
Mota I (1964) The mechanism of anaphylaxis. I. Production and biological properties of mast cell sensitizing antibody. Immunology 7:681–706
Ney U, Bretz U, Gradwohl P, Martin U (1980) Further characterization of the anti-anaphylactic action of ketotifen (Zaditena). Allergol Immunopathol VIII:479
Pauwels R, Lamont H, van der Straten M (1978) Comparison between ketotifen and DSCG in bronchial challenge. Clin Allergy 8:289–293
Plaut M (1979) Histamine, H1 and H2 antihistamines, and immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 63:371–375
Rocha e Silva M (1966; 1978) Histamine and anti-histaminics. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol XVIII, 1+2. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ross WJ, Harrison RG, Jolley MRJ, Neville MC, Todd A, Venge JP, Dawson W, Sweatman WJF (1979) Antianaphylactic agents. 1. 2-(Acylamino)oxazoles. J Med Chem 22:412–417
Stotland LM, Share NN (1974) Pharmacological studies on active bronchial anaphylaxis in the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 52:1119–1125
Yamatake Y, Sasagawa S, Yanaura S, Kobayashi N (1977) Allergy-induced asthma with ascaris suum administration to dogs. Jpn J Pharmacol 27:285–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, U., Baggiolini, M. Dissociation between the anti-anaphylactic and the anti-histaminic actions of ketotifen. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 316, 186–189 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00505315
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00505315