Summary
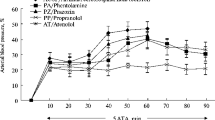
We have found bulbocapnine to be an effective, apparently competitive inhibitor of dopamine depressor responses in the anesthetized, phenoxybenzamine-treated cat. The duration of action of the compound as a dopaminergic antagonist exceeded 3 hrs after an intravenous dose of 8 mg/kg. In the same preparation, however, bulbocapnine did not at all inhibit the depressor responses to acetylcholine, histamine and isoproterenol, indicating a selectivity of action. Although administration of a high dose of propranolol (2 mg/kg, i.v.) did not alter the response of the alpha-receptor blocked cat to dopamine, the subsequent infusion of bulbocapnine remained effective. These results suggest that dopamine is acting as a blood pressure depressor agent via a unique receptor mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariens, E. J.: In Molecular Pharmacology, vol. 1, pp. 148–156. New York: Academic Press (1964a)
Ariens, E. J.: In Molecular Pharmacology, vol. 1, p. 292. New York: Academic Press 1964b
Black, J. W., Duncan, W. A. M., Durant, C. J., Ganellin, C. R., Parsons, E. M.: Definition and antagonism of histamine H2-receptors. Nature (Lond.) 256, 385–390 (1972)
Dhasmana, K. M., Dixit, J. S., Dhawan, K. N., Gupta, G. P.: Blockade of depressor response of dopamine. Jap. J. Pharmacol. 19, 168–169 (1969)
Janssen, P. A. J., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Schellekens, K. H. L.: Is it possible to predict the clinical effects of neuroleptic drugs (major tranquillizers) from animal data? Arzneimittel-Forsch. 15, 104–117 (1965)
McDonald, R. H., Goldberg, L. I.: Analysis of the cardiovascular effects of dopamine in the dog. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 140, 60–66 (1963)
Ross, G., Brown, W. A.: Cardiovascular effects of dopamine in the anesthetized cat. Amer. J. Physiol. 212, 823–828 (1967)
Samson, R. G., Scroop, G. C., Louis, W. J.: Cardiovascular effects of dopamine in the anesthetized dog. Clin. exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1, 3–12 (1974)
Setler, P. E., Pendleton, R. G., Finlay, E.: The cardiovascular actions of dopamine and the effects of central and peripheral catecholaminergic receptor blocking drugs. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 192, 702–712 (1975)
Tseng, L. F., Walaszek, E. J.: Blockade of the dopamine depressor response by bullbocapnine. Fed. Proc. 29, 741 (1970)
van Praag, H. M.: Neuroleptics as a guideline to biological research in psychotic disorders. Comprehens. Psychiat. 16, 7–22 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pendleton, R.G., Finlay, E. & Sherman, S. Effect of bulbocapnine as a peripheral dopamine receptor antagonists in the anesthetized cat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 289, 171–178 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501304
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501304