Summary
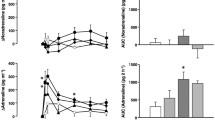
The increase in in vitro adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) activity caused by drugs which produce an increase in preganglionic nerve activity as a result of actions outside the central nervous system was increased by the administration of diazepam. However, other central nervous system depressants such as pentobarbital, phenobarbital and diphenylhydantion were not found to share this property. Adrenal enzyme induction provoked by isoproterenol and 6-hydroxydopamine was increased by diazepam administration, whereas that produced by reserpine or insulin was not altered. The enhanced adrenal TH activity produced by diazepam pretreatment and isoproterenol administration could not be attributed to an increase in intensity or to an altered body temperature. Administration of 5-hydroxytryptophan can antagonize the induction of adrenal TH produced by isoproterenol, however, it did not block the TH induction produced by concurrent administration of diazepam and isoproterenol. The effect of diazepam on adrenal TH induction may be the result of its ability to interfere with central nervous system amine containing nerve functions which modulate preganglionic nerve activity, but the particular neurotransmitter system involved has not been determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anden, N.-E., Carlsson, A., Hillarp, N.-A.: Inhibition by 5-hydroxytryptophan of insulin-induced adrenaline depletion. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.) 21, 183–186 (1964)
Anton, A. H., Sayre, E. D.: A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 138, 360–375 (1962)
Axelrod, J., Mueller, R. A., Thoenen, H.: Neuronal and hormonal control of tyrosine hydroxylase and phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase activity Bayer Symposium II, pp, 212–219. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970
Beer, B., Chasin, M., Clody, D. E., Vogel, J. R., Horovitz, Z. P.: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase in brain: effect of anxiety. Science 176, 428–430 (1972)
Brooks, C. M.: Reflex activation of the sympathetic system in the spinal cat. Amer. J. Physiol. 106, 251–266 (1933)
Chalmers, J. P., Wurtman, R. J.: Participation of central noradrenergic neurons in arterial baroreceptor reflexes in the rabbit. Circulat. Res. 28, 480–491 (1971)
Chase, T. N., Katz, R. I., Kopin, I. J.: Effect of diazepam on fate of intracisternally injected serotonin-C14. Neuropharmacol. 9, 103–108 (1970)
Chen, M. P., Lim, R. K. S., Wang, S. C., Yi, C. L.: On the question of a myelence-phalic sympathetic centre. IV. Experimental location of its descending pathways. Clin. J. Physiol. 11, 385–408 (1937)
Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Lidbrink, P., Olson, L.: Minor tranquilizers, stress and central catecholamine neurons. Brain Res. 29, 1–16 (1971)
DeQuattro, V., Nagatsu, T., Maronde, R., Alexander, N.: Catecholamine synthesis in rabbit with neurogenic hypertension. Circulat. Res. 24, 545–555 (1969)
Goldberg, A. M., Welch, B. L.: Adaptation of the adrenal medulla: sustained increase in choline acetyltransferase by psychosocial stimulation. Science 178, 319–320 (1972)
Gottschalk, L. A., Noble, E. P., Stolzhoff, G. E., Bates, D. E., Cable, C. G., Uliana, R. L., Birchand, H., Fleming, E. W.: Relationships of chlordiazepoxide blood levels to psychological and biochemical responses. Eds.: S. Garattini, E. Mussini, and L. O. Randall. In: The Benzodiazepines. New York: Raven Press 1973
Guidotti, A., Costa, E.: Involvement of adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in the activation of tyrosine hydroxylase elicited by drugs. Science 179, 902–904 (1973)
Hokfelt, B.: Noradrenaline and adrenaline in mammalian tissues. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl. 92, 1–134 (1951)
Ito, A., Schanberg, S. M.: Central nervous system mechanisms responsible for blood pressure elevation induced by p-chlorophenylalanine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 181, 65–74 (1972)
Koe, B. K., Weissman, A.: p-Chlorophenylalanine: a specific depletor of brain serotonin. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 154, 499–516 (1966)
Korner, P. J.: Integrative neural cardiovascular control. Physiol. Rev. 51, 412–367 (1971)
Laverty, R., Sharman, D. F., Vogt, M.: Action of 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylalanine on the storage and release of noradrenaline. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 24, 549–560 (1965)
Levitt, M., Gibb, J. W., Daly, J. W., Lipton, M., Udenfriend, S.: A new class of tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitors and a simple assay of inhibition in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 16, 1313–1321 (1967)
Lim, R. K. S., Wang, S. C., Yi, C. L.: On the question of a myelencephalic sympathetic centre. VII. The depressor area of a sympathoinhibitory centre. Chin. J. Physiol. 12, 61–78 (1938)
Martelli, E. A., Corsico, N.: On the mechanism of lipomobilizing effect of chlordiazepoxide. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 21, 59–65 (1968)
Mueller, R. A., Smith, R. D., Breese, G. R., Copper, B. R.: Modulation of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase induction by serotonin nerve function. Eds.: E. Usdin and S. Snyder. In: Frontiers in catecholamines research. London: Pergamon Press (in Press)
Mueller, R. A., Thoenen, H.: Cardiac catecholamine synthesis. turnover, and metabolism with isoproterenol-induced myocytolysis. Cardiovasc. Res. 5, 364–370 (1971)
Mueller, R. A., Thoenen, H., Axelrod, J.: Increase in tyrosine hydoxylase activity after reserpine administration. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 169, 74–79 (1969)
Nakamura, K., Thoenen, H.: Increased irritability: permanent behavior change induced in the rat by intraventricular administration of 6-hydroxydopamine Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 24, 359–372 (1972)
Oesch, F., Thoenen, H.: Increased activity of the peripheral sympathetic nervous system: induction of choline acetyltranserase in the preganglionic cholinergic neurons. Nature (Lond.) 242, 536–537 (1973)
Patrick, R. L., Kirshner, N.: Effect of stimulation on levels of tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine beta-hydroxylase, and catecholamines in intact and denervated rat adrenal glands. Molec. Pharmacol. 7, 87–96 (1971)
Randall, R. O., Heise, S. A., Schalleck, W., Bagdon, R. F., Banziger, R., Urris, A., Moe, R. A., Abrams, W. B.: Pharmacological and clinical studies on Valium, a new psychotherapeutic agent of the benzodiazepine class. Curr. ther. Res. 3, 405–425 (1961)
Sigg, E. B., Sigg, T. D.: Hypothalamic stimulation of preganglionic autonomic activity and its modification by chlorpromazine, diazepam, and pentobarbital. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 8, 567–572 (1969)
Steele, R. G. D., Torrie, J. H.: Principles and procedures of statistics. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co. 1968
Stein, L., Wise, C. D., Berger, B. D.: Antianxiety action of benzodiazepines: decrease in activity of serotonin neurons in the punishment system. Eds.: S. Garattini, E. Mussini and L. O. Randall. In: The benzodiazepines, pp. 299–326. New York Raven Press 1973
Taylor, K. M., Laverty, R.: The effect of chlordiazepoxide diazepam, and nitrazepam on catecholamine metabolism in regions of the rat brain. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 8, 296–301 (1969)
Thoenen, H.: Neuronally mediated induction in adrenergic neurons and adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 36, 3–15 (1972)
Thoenen, H., Mueller, R. A., Axelrod, J.: Trans-synaptic induction of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. J. Pharmacol. expl Ther. 169, 249–254 (1969)
Wise, C. D., Berger, B. D., Stein, L.: Benzodiazepines: anxiety-reducing activity by reduction of serotonin turnover in the brain. Science 177, 180–183 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, R.D., Breese, G.R. & Mueller, R.A. Potentiation of drug-initiated adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase induction by diazepam. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 284, 195–206 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501122
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501122