Summary
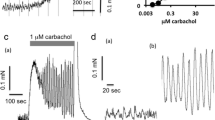
The influence of dopamine was studied on strips of the rat stomach fundus, contracted either by electrical stimulation (1 Hz) or by methacholine.
Dopamine (3 · 10−5 M), like noradrenaline (3 · 10−7 M), inhibited the electrically induced contraction more than the methacholine-induced contraction. The inhibition by dopamine of the response to electrical stimulation was partially antagonized by phentolamine but less so by propranolol; the opposite was true for the inhibition by dopamine of the methacholine-induced contraction. Domperidone and four other dopamine antagonists slightly changed the inhibitory effect of dopamine, but had a similar influence on the inhibition caused by noradrenaline.
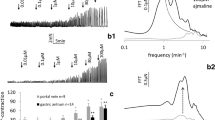
The presence of cocaine as well as reserpine pretreatment reduced markedly the inhibitory effect of dopamine on the response to electrical stimulation. To further characterize the α-receptors on the cholinergic neurons, experiments were performed in the presence of cocaine, hydrocortisone and propranolol. Dopamine, noradrenaline, clonidine and phenylephrine concentration-dependently inhibited the contraction induced by electrical stimulation, clonidine being more potent than phenylephrine. However, the inhibitory effect of dopamine on the response to transmural stimulation was equally blocked by rauwolscine and by prazosin, as were the inhibitions caused by noradrenaline and clonidine.
Our findings indicate that the inhibitory effect of dopamine in the rat stomach fundus can be explained by interaction with prejunctional β-receptors on the smooth muscle cells and prejunctional α-receptors on the intramural cholinergic neurons. No arguments for the existence of specific dopamine receptors were found. The inhibition by dopamine is largely indirect, through uptake in sympathetic nerve endings and liberation of endogenous noradrenaline. The results obtained with α-agonists and-antagonists suggest that the α-receptors on the intramural cholinergic neurons combine the characteristics of both subtypes of α-receptors, or that the receptor population consists of a mixture of α1-and α2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andréjak M, Pommier Y, Mouillé P, Schmitt H (1980) Effects of some α-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 314:83–87
Berkowitz DM, McCallum RW (1980) Interaction of levodopa and metoclopramide on gastric emptying. Clin Pharmacol Ther 27:414–420
Cox B, Ennis C (1980) Mechanism of action of dopamine on the guinea-pig gastro-oesophageal junction in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 71:177–184
De Carle DJ, Christensen J (1976) A dopamine receptor in esophageal smooth muscle of the opossum. Gastroenterology 70:216–219
Del Tacca M, Soldani G, Selli M, Crema A (1970) Action of catecholamines on release of acetylcholine from human taenia coli. Eur J Pharmacol 9:80–84
De Schaepdryver AF, Lefebvre RA, Willems JL (1981) Effect of dopamine on the rat gastric fundus. Abstr. VIIIth Int Congr Pharmacol, Tokyo, July 19–24, p 696
Drew GM (1978) Pharmacological characterization of the presynaptic α-adrenoceptors regulating cholinergic activity in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol 64:293–300
Dubocovich ML, Langer SZ (1980) Dopamine and alpha adrenoceptor agonists inhibit neurotransmission in the cat spleen through different presynaptic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 212:144–152
Ennis C, Janssen PAJ, Schnieden H, Cox B (1979) Characterization of receptors on postganglionic cholinergic neurons in the guinea-pig isolated ileum. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:217–221
Fagbemi SO, Salako LA (1980) The effect of prazosin on the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol 70:395–402
Gershon MD (1967) Effects of tetrodotoxin on innervated smooth muscle preparations. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 29:259–279
Gillespie JS, Khoyi MA (1977) The site and receptors responsible for the inhibition by sympathetic nerves of intestinal smooth muscle and its parasympathetic motor nerves. J Physiol 267:767–789
Görich R, Weihrauch TR, Kilbinger H (1982) The inhibition by dopamine of cholinergic transmission in the isolated guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 318:308–312
Heazell MA (1969) A non-adrenergic component to the inhibitory innervation of the fundus of the rat stomach. Br J Pharmacol 36:186–187 P
Heazell MA (1974) The innervation and receptor population of the rat gastric fundus. Ph D Thesis, University of London
Kamikawa Y, Shimo Y, Uchida K (1982) Inhibitory actions of catecholamines on electrically induced contractions of the submucous plexus-longitudinal muscularis mucosae preparation of the guinea-pig oesophagus. Br J Pharmacol 76:271–277
Kelly KA (1980) Gastric emptying of liquids and solids: roles of proximal and distal stomach. Am J Physiol 239:G71-G76
Kosterlitz HW, Lydon RJ, Watt AJ (1970) The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory α- and β-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol 39:398–413
Laduron PM, Leysen JE (1979) Domperidone, a specific in vitro dopamine antagonist, devoid of in vivo central dopaminergic activity. Biochem Pharmacol 28:2161–2165
Lanfranchi GA, Marzio L, Cortini C, Trento L, Labo C (1978) Effect of dopamine on gastric motility in man: evidence for specific receptors. In: Duthie HL (ed) Gastrointestinal motility in health and disease. MTP Press, Lancaster, England, pp 161–172
Langer SZ (1981) Presynaptic regulation of the release of catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev 32:337–362
Lefebvre RA, Willems JL (1981) Dopamine inhibition of the transmurally stimulated gastric fundus of the rat. Br J Pharmacol 72:537 P
Lefebvre RA, Blanquaert JP, Willems JL, Bogaert MG (1982) The study of the prejunctional α-adrenoceptor involved in the inhibitory effect of dopamine on the rat gastric fundus. Abstr. 1st Eur Symp Gastrointestinal Motility. Bologna, September 7–8, p 41
Luchelli-Fortis MA, Langer SZ (1975) Selective inhibition by hydrocortisone of 3H-normetanephrine formation during 3H-transmitter release elicited by nerve stimulation in the isolated nerve-muscle preparation of the cat nictitating membrane. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 287:261–275
McClelland CM, Sanger GJ (1982) Antagonism by metoclopramide of an inhibitory response to clonidine in rat isolated stomach muscle. Proc Br Pharmacol Soc, Sunderland Polytechnic, September 8–10, C 69
Paton WDM (1975) Transmural and field stimulation of nerve-smooth muscle preparations. In: Daniel EE, Paton DM (eds) Methods in pharmacology, Smooth muscle, vol 3. Plenum Press, New York, pp 313–320
Paton WDM, Vane JR (1963) An analysis of the responses of the isolated stomach to electrical stimulation and to drugs. J Physiol 165: 10–46
Paton WDM, Vizi ES (1969) The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on acetylcholine output by guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle strip. Br J Pharmacol 35:10–28
Randriantsoa A, Heitz C, Stoclet JC (1981) Functional characterization of postjunctional α-adrenoceptors in rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol 75:57–60
Sahyoun HA, Costall B, Naylor RJ (1982a) On the ability of domperidone to selectively inhibit catecholamine-induced relaxation of circular smooth muscle of guinea-pig stomach. J Pharm Pharmacol 34:27–33
Sahyoun HA, Costall B, Naylor RJ (1982b) Catecholamines act at 236-1 to cause contraction of circular smooth muscle of guinea-pig stomach. J Pharm Pharmacol 34:381–385
Seno N, Nakazato Y, Ohga A (1978) Presynaptic inhibitory effects of catecholamines on cholinergic transmission in the smooth muscle of the chick stomach. Eur J Pharmacol 51:229–237
Schuurkes JAJ, Van Nueten JM (1981) Effects of dopamine and its antagonist domperidone cannot be explained by an effect on 236-2 receptors. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 250:324–327
Tanaka T, Weitzell R, Starke K (1978) High selectivity of rauwolscine for presynaptic α-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 52:239–240
Taylor P (1980) Cholinergic agonists. In: Goodman Gilman A, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. McMillan Publishing Co, New York, pp 91–99
Thompson BK, De Carle DJ (1982) The effect of dopamine on human gastric smooth muscle. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 60:123–127
Timmermans PBMWM, Van Zwieten PA (1981) The postsynaptic 236-3. J Auton Pharmacol 1:171–183
Valenzuela JE (1976) Dopamine as a possible neurotransmitter in gastric relaxation. Gastroenterology 71:1019–1022
Valenzuela JE, Eguiguren AL (1976) Effect of l-dopa on human intragastric pressure. Gastroenterology 70:945
Vane JR (1957) A sensitive method for the assay of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol 12:344–349
Van Nueten JM, Janssen PA (1978) Is dopamine an endogenous inhibitor of gastric emptying. In: Duthie HL (ed) Gastrointestinal motility in health and disease. MTP Press, Lancaster, England pp 173–181
Weitzell R, Tanaka T, Starke K (1979) Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 308:127–136
Wikberg J (1977) Localization of adrenergic receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit jejunum to cholinergic neurons and to smooth muscle cells. Acta Physiol Scand 99:190–207
Wikberg J (1978) Differentiation between pre- and postjunctional α-receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit aorta. Acta Physiol Scand 103:225–239
Willems JL (1973) Dopamine-induced inhibition of synaptic transmission in lumbar paravertebral ganglia of the dog. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 279:115–126
Willems JL, Bogaert MG, Buylaert W (1981) Preliminary observations on the interaction of domperidone with peripheral dopamine receptors. Jpn J Pharmacol 31:131–133
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lefebvre, R.A., Blancquaert, J.P., Willems, J.L. et al. In vitro study of the inhibitory effects of dopamine on the rat gastric fundus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 322, 228–236 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500770
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500770