Summary
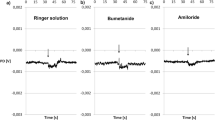
The path of the transepithelial Na transport through the frog skin was investigated by the use of compartment analysis. Therefore tracer wash-out kinetics from the preloaded epithelium to both sides of the skin and time course of tracer uptake at the epithelial side were measured under control conditions and after alteration of transport parameter by amiloride, ouabain and incubation at 0°C. In all experiments the skins were short-circuited throughout and the SCC registered.
The results indicate that the major part of the Na involved in transport is already transported and located in an extracellular compartment, possibly the intercellular space between the epithelial cells. The decisive step of the transepithelial transport seems to be located at the outer epithelial border of the cell layer since entrance of Na into the skin is similarly altered by all inhibitors of transport.
Two additional compartments which are labelled from the epithelial side are detectable. The Na content of the compartment with the lowest exchange rate is increased by ouabain and 0° C but remains unchanged after amiloride. It might be located intracellularly but is not responsible for transepithelial transport. The actual transport pool must be very small.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceves, J., Erlij, D.: Sodium transport across the isolated epithelium of the frog skin. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 212, 195–210 (1971)
Bently, P. J.: Amiloride: A potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 195, 317–330 (1968)
Biber, T. U. L., Cruz, L., Curran, P. F.: Sodium influx at the outer surface of the frog skin. J. Membrane Biol. 7, 365–376 (1972)
Biber, T. U. L., Curran, P. F.: Direct measurement of uptake of sodium at the outer surface of frog skin. J. gen. Physiol. 56, 83–99 (1970)
Cereijido, M., Reisin, I., Rotunno, C. A.: The effect of sodium concentration on the content and distribution of sodium in the frog skin. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 196, 237–253 (1968)
Cereijido, M., Rotunno, C. A.: Transport and distribution of sodium across the frog skin. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 190, 481–497 (1967)
Curran, P. F., Herrera, F. C., Flanigan, W. J.: The effect of Ca and antidiuretic hormone on Na transport across frog skin. II. Sites and mechanisms of action. J. gen. Physiol. 46, 1011–1027 (1962)
Cuthbert, A. W.: Neurohypophysal hormones and sodium transport. Phil. Trans. B 262, 103–110 (1971)
Diamond, J. M., Bossert, W. H.: Standing gradient osmotic flow. A mechanism for coupling of water a and solute transport in epithelia. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 2061–2083 (1967)
Dörge, A., Nagel, W.: Effect of amiloride on sodium transport in the frog skin: II. Sodium transport pool and unidirectional fluxes. Europ. J. Physiol. 321, 91–101 (1970)
Dörge, A., Nagel, W.: Washout kinetics of Na from the transport pool to the epithelial and corium side of the frog skin. Pflügers Arch. 337, 285–297 (1972)
Ehrlich, E. N., Crabbe, J.: The mechanism of action of amipramizide. Pflügers Arch. 302, 79–96 (1968)
Eigler, J.: Der Einfluß von Aldosteron auf Natriumtransport und transepithelialen Wasserfluß durch isolierte Bauchhaut von Rana temporaria. Pflügers Arch. 317, 236–251 (1970)
Erlij, D.: Salt transport across isolated frog skin. Phil. Trans. B 262, 153–162 (1971)
Erlij, D., Smith, M. W.: Sodium uptake by frog skin and its modification by inhibitors of transepithelial sodium transport. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 228, 221–239 (1973)
Gehring, K., Dörge, A., Nagel, W., Thurau, K.: The use of the scanning electron microscope in connection with a solid state detector for analysis and localization of electrolytes in biological tissue. In: Modern techniques in physiological sciences, edit. by J. F. Gross, R. Kaufmann, and E. Wetterer. London-New York: Academic Press 1973
Herrera, F.: Bioelectric properties and ionic content in toad bladder. J. gen. Physiol. 51, 261s-270s (1968)
Hoshiko, T., Lindley, B. D., Edwards, Ch.: Diffusion delay in frog skin connective tissue: a source of error in tracer investigations. Nature (Lond.) 201, 932–933 (1964)
Hoshiko, T., Ussing, H. H.: The kinetics of Na24 flux across amphibian skin and bladder. Acta physiol. scand. 49, 74–81 (1960)
Imamura, A., Takeda, H., Sasaki, N.: The accumulation of sodium and calcium in a specific layer of frog skin. J. cell. comp. Physiol. 66, 221–226 (1965)
Leaf, A.: Transepithelial transport and its hormonal control in toad bladder. Ergebn. Physiol. 56, 216–263 (1965)
Moreno, J. H., Reisin, I. L., Rodriguez Boulan, E., Rotunno, C. A., Cereijido, M.: Barriers to sodium movement across frog skin. J. Membrane Biol. 11, 99–115 (1973)
Motais, R., Garcia-Romeu, F.: Transport mechanisms in the teleostean gill and amphibian skin. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 34, 141–176 (1972)
Nagel, W., Dörge, A.: Effect of amiloride on sodium transport of frog skin. I. Action on intracellular sodium content. Pflügers Arch. 317, 84–92 (1970)
Nagel, W., Dörge, A.: A study of the different sodium compartments and the transepithelial sodium fluxes of the frog skin with the use of ouabain. Pflügers Arch. 324, 267–278 (1971)
Nielsen, R.: The effect of aldosterone in vitro on the active sodium transport and moulting of the frog skin. Acta physiol. scand. 77, 85–94 (1969)
Parson, P. H., Hoshiko, T.: Separation of epithelium from frog skin and rapid washout of 22-Na. J. gen. Physiol. 57, 254–255 (1971)
Rotunno, C. A., Vilallonga, F. A., Fernandez, M., Cereijido, M.: The penetration of sodium into the epithelium of the frog skin. J. gen. Physiol. 55, 716–735 (1970)
Schoffeniels, E.: An isolated single electroplax preparation. II. Improved preparation for studying ion flux. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 26, 585–596 (1957)
Schwartz, T. L., Snell, F. M.: Non-steady-state three compartment tracer kinetics. I. Theory. Biophys. J. 8, 805–817 (1968)
Ussing, H. H.: The active ion transport through the isolated frog skin in the light of tracer studies. Acta physiol. scand. 17, 1–37 (1948a)
Ussing, H. H.: The distinction by means of tracer between active transport and diffusion. Acta physiol. scand. 19, 43–56 (1950)
Ussing, H. H.: The alkali metal ions in biology. In: Handbuch der experimentellen Pharmakologie. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960
Ussing, H. H., Zerahn, K.: Active transport of sodium as the source of electric current in the short-circuited isolated frog skin. Acta physiol. scand. 23, 110–127 (1951)
Zerahn, K.: Nature and localisation of the sodium pool during active transport in the isolated frog skin. Acta physiol. scand. 77, 272–281 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagel, W., Dörge, A., Moshagen, D. et al. Analysis of sodium compartments and fluxes in frog skin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 281, 281–294 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500597
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500597