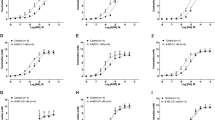
Summary
The contractile effects of dopamine and noradrenaline were compared in the rat isolated vas deferens, in order to obtain evidence for the presence or absence of postsynaptic dopamine receptors in this tissue. Attention was given to the role of several factors known to interfere with receptor characterization.
-
1.
The preparation presented a slight tachyphylaxis for dopamine and a loss of sensitivity to that agonist after treatment with reserpine. These effects were not observed for noradrenaline.
-
2.
Cocaine potentiated the effects of noradrenaline and dopamine by 38.9 and 2.1 times respectively. Metanephrine induced a potentiation of 2.2 times for noradrenaline and did not significantly alter dopamine effects. These results indicate that dopamine is practically not taken up by neuronal or extraneuronal mechanisms. Noradrenaline is only slightly affected by extraneuronal uptake and greatly affected by neuronal uptake as previously shown.
-
3.
The competitive antagonism of haloperidol, analyzed by means of Schild plots, and expressed through pA2 values, was similar for noradrenaline and dopamine when studied after blockade of neuronal uptake by cocaine. In the absence of cocaine, pA2 values for haloperidol were significantly lower when determined against noradrenaline than against dopamine.
-
4.
The α-adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine induced effects which were similar to those of haloperidol.
-
5.
Pimozide and apomorphine induced a non-competitive-like antagonism towards both agonists similar to that induced by papaverine. This antagonism was added to a slight competitive inhibition.
-
6.
It was not possible to differentiate the effects of noradrenaline and dopamine by means of protection experiments against irreversible blockade by phenoxybenzamine.
-
7.
Potentiation of the maximal effects of noradrenaline, previously reported for several α-adrenoceptor antagonists, was also induced by haloperidol and low doses of apomorphine. This phenomenon was never observed when dopamine was used instead of noradrenaline, whichever the antagonist.
-
8.
Our results provide evidence that differences observed among the effects of dopamine and noradrenaline are mostly due to differences on sensitivity towards neuronal uptake and to other minor factors. When the influence of these factors is taken into account, or avoided, the contractile effects for dopamine and noradrenaline are similar, indicating an interaction of both substances with a single type of postsynaptic α-adrenoceptor, in the rat vas deferens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariëns EJ, van Rossum JM (1957) pDx, pAx and pDx' values in the analysis of pharmacodynamics. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 110:275–299
Ferrini R, Miragoli G (1972) Selective antagonism of dopamine by apomorphine. Pharmacol Res Commun 4:347–352
Ferrini R, Miragoli G (1973) Antagonismo dell'effetto della dopamina e della noradrenalina su alcuni organi isolati. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 49:648–652
Furchgott RF (1975) The classification of adrenoceptors (adrenergic receptors). An evaluation from the standpoint of receptor theory. In: Blaschko H, Muscholl E (eds) Catecholamines, Handbuch der experimentellen Pharmakologie, vol XXXIII. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 283–335
Furchgott RF, Jurkiewicz A, Jurkiewicz NH (1973) Antagonism of propranolol to isoproterenol in guinea-pig trachea: some cautionary findings. In: Usdin E, Snyder S (eds) Frontiers in catecholamines research. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 295–299
Jurkiewicz A, Jurkiewicz NH (1976) Dual effect of α-adrenoceptor antagonists in rat isolated vas deferens Br J Pharmacol 56:169–178
Langeloh A, Jurkiewicz A (1978a) Há dois tipos de alfa-adrenoceptores no ducto deferente de rato? Ciência e Cultura (São Paulo) 30:458
Langeloh A, Jurkiewicz A (1978b) Influência da ioimbina, haloperidol, pimozide e cocaina sobre a contração induzida por noradrenalina e dopamina no ducto deferente de rato. Abstracts of the VII Latinamerican Congress of Pharmacology, São Paulo, Brazil, p 221
Nueten JM van, Reneman RS, Janssen PAJ (1977) Specific α-adrenoceptor blocking effect of droperidol on isolated smooth muscles. Eur J Pharmacol 44:1–8
Patil PN, Lapidus JB, Campbell D, Tye A (1967) Steric aspects of adrenergic drugs. II Effects of DL isomers and desoxy derivatives on the reserpine-pretreated vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 155:13–23
Patil PN, Burkman AM, Yamauchi D, Hetey S (1973) Analysis of the effects of apomorphine and bulbocapnine in relation to the proposed dopamine receptor. J Pharm Pharmacol 25:221–228
Quintana A (1978) Effects of pimozide on the response of smooth muscle to non-dopamine agonists and calcium. Eur J Pharmacol 53:113–116
Rossum JM van (1965) Different types of sympathomimetic α-receptor. J Pharm Pharmacol 17:202–216
Rossum JM van, Brink FG van den (1963) Cumulative dose-response curves. I. Introduction to the technique. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 143:240–246
Schild HO (1957) Drug antagonism and pAx. Pharmacol Rev 9:242–246
Simon A, Maanen EF van (1971) Apomorphine and phentolamine antagonism of dopamine and norepinephrine. Fed Proc 30:624
Simon A, Maanen EF van (1976) Dopamine receptors and dopaminergic nerves in the vas deferens of the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 222:4–15
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) Statistical Method (6th edition). Iowa State University Press, Ames
Tayo FM (1979) Occurrence of excitatory dopaminoceptors in the rat and guinea-pig vas deferens. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 6:275–279
Westfall DP (1970) Nonspecific supersensitivity of the guinea-pig vas deferens produced by decentralization and reserpine treatment. Br J Pharmacol 39:110–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langeloh, A., Jurkiewicz, A. Analysis of the effects of dopamine and noradrenaline in relation to the proposed postsynaptic dopamine receptor in rat vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 318, 202–209 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500481
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500481