Summary
-
1.
In experiments involving injection of tetanus toxin into the rat diaphragm it was shown that the toxin, by acting on the presynaptic apparatus, disturbs the neuromuscular transmission.
-
2.
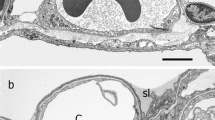
Electron microscopic investigation does not reveal any visible ultrastructural changes in neuromuscular and axosomatic synapses of spinal motoneurons in tetanus intoxication. However, synaptic vesicles accumulate in the axon terminals.
-
3.
Neuraminidase splits off the sialic acid and liberates the toxin from the protagon-tetanus toxin complex.
-
4.
Toxin neutralized by antitoxin is still able to react with protagon.
-
5.
Toxin bound to protagon can be neutralized by antitoxin; when neutralized, the toxin is retained in complex with protagon. Partial neutralization of the toxicity of the protagon-toxin complex is effected by small amounts of antitoxin; complete neutralization of residual toxicity requires comparatively greater amounts of antitoxin.
-
6.
Fragments of antitoxin [F(ab′)2 and Fab′] are more effective for complete neutralization of toxin bound on protagon than the initial JgG-antitoxin.
-
7.
Injections of antitoxin into the cisterna magna during the incubation period and at earlier stages of experimental tetanus ascendens and descendens are more effective than intramuscular, intravenous or intracarotid injections. At later stages of intoxication all ways of antitoxin injection used are ineffective.
-
8.
The tetanus toxin molecule has at least three groupings; one of them is responsible for the binding on its receptor in brain substance, the other for the interaction with antitoxin and the third for tis specific toxic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bondartchuk, N. G., Kirilenko, O. A., Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Rozanov, A. Ja.: Protagon binding of tetanus toxin neutralized by Antitoxin. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 10, 71–74 (1971).
Bowsher, D. R.: Pathways of absorption of protein from the cerebrospinal fluid: an autoradiographic study in the cat. Anat. Rec. 128, 23–39 (1957).
Brightman, M. W.: The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebrospinal fluid compartments II Parenchymal distribution. Amer. J. Anat. 117, 193–219 (1965).
Brightman, M. W.: The intracerebral movement of proteins injected into blood and cerebrospinal fluid of mice. Progr. Brain. Res. 29, 19 (1968).
Brooks, V. B., Curtis, D. R., Eccles, J. C.: The action of tetanus toxin on the inhibition of motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 135, 655–672 (1957).
Curtis, D. R., De Groat, W. C.: Tetanus toxin and spinal inhibition. Brain Res. 10, 208–212 (1968).
Dekirmenjian, H., Brunngraber, E. G.: Distribution of protein-bound N-acetyl-neuraminic acid in subcellular particulate fractions prepared from rat whole brain. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 177, 1–10 (1969).
Del Castillo, J., Katz, B.: Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 124, 560–573 (1954a).
Del Castillo, J., Katz, B.: Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 124, 574–585 (1954b).
Eccles, J. C.: The physiology of synapses. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1964.
Fedinec, A. A.: Studies on the mode of the spread of tetanus toxin in experimental animals. In: Recent advances in the pharmacology of toxins, pp. 125–138. Ed. H. W. Raudonat. Oxford-Praha: Pergamon Press, Czechoslovak Medical Press, 1965.
Fedinec, A. A.: Absorption and distribution of tetanus toxin in experimental animals. In: Principles on tetanus, pp. 169–175. Ed. L. Eckmann. Bern-Stuttgart: H. Huber 1967.
Friedemann, U., Hollander, A., Tarlov, J. M.: Investigations on the pathogenesis of the tetanus. III. J. Immunol. 40, 325–364 (1941).
Fulthorpe, A. J.: Adsorption of tetanus toxin by brain tissue. J. Hyg. (Lond.) 54, 315–327 (1956).
Geinismann, Ju. Ja., Dyakonova, M. V., Kryzhanovsky, G. N.: Morphofunctional characteristics of spinal motoneurone synapses in tetanus intoxication. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 11, 71–75 (1967).
Gray, E. G.: Electron microscopy of presynaptic organelles of the spinal cord. J. Anat. (Lond.) 97, 101–106 (1963).
Guschin, J. S., Kozhechkin, S. N., Sverdlov, Ju. S.: On the presynaptic nature of the suppression of postsynaptic inhibition by tetanic toxin. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSR 3, 685–688 (1969).
Guschin, J. S., Kozhechkin, S. N., Sverdlov, Ju. S.: The hyperpolarizing effect of glycine on “tetanus” motoneurones. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 8, 29–32 (1970).
Habermann, E.: Pharmakokinetische Besonderheiten des Tetanustoxin und ihre Beziehungen zur Pathogenese des lokalen bzw. generalisierten Tetanus. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 267, 1–19 (1970).
Habermann, E.: Some general rules governing fate and action of polypeptide and protein drugs, as derived from investigations with staphylococcal-α-toxin, tetanus toxin, and socalled crotoxin. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 269, 124–135 (1971).
Habermann, E.: Distribution of 125J-tetanus toxin and 125J-toxoid in rats with local tetanus, as influenced by antitoxin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 272, 75–88 (1972).
Hochwald, G. M., Wallenstein, M. S.: Exchange of γ-globuline between blood cerebrospinal fluid and brain in the cat. Exp. Neurol. (Chic.) 19, 115 (1967).
Kirilenko, O. A., Minervin, S. M., Rozanov, A. Ja.: The fate of labelled tetanus toxin in the animal organism. Zh. Mikrobiol. (Mosk.) 9, 123–129 (1964).
Kirilenko, O. A., Minervin, S. M., Rozanov, A. Ja.: Tetanus Toxin-131J absorption from the muscles and distribution in the organism. Zh. Mikrobiol. (Mosk.) No. 10, 105–111 (1965).
Klatzo, J., Miquel, J., Ferris, P. J., Prokop, J. D., Smith, D. E.: Observations on the passage of the fluorescein labelled serum proteins. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 23, 18–35 (1964).
Kozhechkin, S. N.: Observation of disappearance of post-synpatic inhibition. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 4, 38–42 (1969).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N.: On the action of tetanus toxin as a neurotropic agent. In: Recent advances in the pharmacology of toxins, pp. 105–111. Ed. H. W. Raudonat. Oxford-Praha: Pergamon Press-Czechoslovak. Medical Press 1965.
Kryzhanovsky, G. N.: Tetanus. State Publish. House “Medicine”, Moscow 1966 (in Russian).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N.: The neural pathway of toxin: its transport ot the central nervous system and the state of the spinal reflex apparatus in tetanus intoxication. In: Principles on tetanus, pp. 155–168. Ed. L. Eckmann. Bern-Stuttgart: H. Huber 1967.
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Alexeev, L. P., Kulberg, A. Ja., Tarkhanova, J. A.: Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 8, 66–69 (1972).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Alexeev, L. P., Rozanov, A. Ja.: Antitoxin neutralization of tetanus toxin bound with the cerebral substance. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. 9, 63–65 (1970).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Dyakonova, M. V.: A change of the throughout capacity of the spinal cord efferent output in tetanus intoxication. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 9, 12–17 (1964).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Kasymov, A. Kh.: The effect of tetanus toxin on neuromuscular transmission. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. 10, 65–70 (1964).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Krasnova, N. M.: Intracisternal introduction of tetanus antitoxin in experimental tetanus intoxication. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 5, 38–42 (1971).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Pevnitsky, L. A., Grafova, V. N., Polgar, A. A.: Routes of tetanus toxin entrance into the central nervous system and some problems of pathogenesis of experimental tetanus. Reports I, II, III, IV. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 3, 42–49; No. 8, 31–37; No. 11, 35–43; No. 12, 30–37 (1961).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Pozdynakov, O. M., Dyakonova, M. V., Polgar, A. A., Smiznova, V. S.: Disturbance of the neurosecretion in neuromuscular junctions of tetanus toxin poisoned muscle. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 12, 27–31 (1971).
Kryzhanovsky, G. N., Sakharova, O. P.: The effect of neuraminidase on the protagon-tetanus toxin complex. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 5, 38–42 (1971).
Lapetina, E. C., Soto, E. F., de Robertis, E.: Gangliosides and acetylcholinesterase in isolated membranes of the rat brain cortex. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 135, 33–43 (1967).
Lee, J. C., Olszewski, J.: Penetration of radioactive bovine albumin from cerebrospinal fluid into brain tissue. Neurology (Minneap.) 10, 814–822 (1960).
Liley, A. W., North, K. A. K.: An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J. Neurophysiol. 16, 509–527 (1953).
Marie, A., Morax, V.: Recherches sur l'absorption de la toxine tetanique. Ann. Inst. Pasteur 116, 818–832 (1902).
Mellanby, J., van Heyningen, W. E.: The role of ganglioside in the mode of action of tetanus toxin. In: Recent advances in the pharmacology of toxins, pp. 121–123. Ed. H. W. Raudonat. Oxford-Praha: Pergamon Press, Czechosl. Medical Press 1965.
Mellanby, J., van Heyningen, W. E.: Biochemical research on the mode of action of Tetanus toxin. In: Principles on Tetanus, pp. 177–187. Ed. L. Eckmann Bern-Stuttgart: H. Huber 1967.
Mellanby, J., van Heyningen, W. E., Whittaker, V. P.: Fixation of tetanus toxin by subcellular fractions on brain. J. Neurochem. 12, 77–79 (1965).
Mellanby, J., Pope, D., Ambache, N.: The effect of treatment of crude tetanus toxin with ganglioside cerebroside complex on sphincter paralysis in rabbit's eye. J. gen. Microbiol. 50, 479–486 (1968).
Meyer, H., Ransom, F.: Untersuchungen über den Tetanus. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 49, 369–416 (1903).
Nisonoff, A., Wissler, F. C., Lipman, L. N., Woernley, D. L.: Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch. Biochem. 89, 230–244 (1960).
Peracchia, C.: Ultrastructure of the spinal cord and the sciatic nerve of rats with tetanus toxin poisoning. Lab. Invest. 15, 479–491 (1966).
Peracchia, C.: Modifications ultrastructurelles de la moelle epinière motrice dans l'intoxication tétanique expérimentale. Path. et Biol. 15, 132–140 (1967).
Pillemer, Z., Grossbery, D. B., Wittler, R. G.: The immunochemistry of toxin and toxoid. II. The preparation and immunological evaluation of purified tetanol toxoid. J. Immunol. 54, 213–224 (1946).
Polgar, A. A., Smirnova, V. S., Kryzhanovsky, G. N.: Activation of synaptic processes in a tetanus toxin poisoned neuromuscular junction by rhythmic stimulation of the nerve. Byull. éksp. Biol. Med. No. 5, 22–26 (1972).
Sverdlov, Ju. S.: The spinal cord reflex activity under local tetanus (electrophysiological study). Fiziol. Zh. SSSR 46, 941–947 (1960).
Sverdlov, Yu. S.: Potentials of spinal motoneurones in cats with experimental tetanus. Neurophysiol. (Kiev) 1, 25–34 (1969).
Tomita, J. T., Feigen, G. A.: Serological identification and physical chemical properties of the non-spasmogenic principle (NSP) in tetanus toxin. Immunochemistry 6, 421–435 (1969).
Uchizono, K.: Ref.: Structure and function of inhibitory neuronal mechanisms, p. 121. Oxford: 1968.
Uchizono, K., Sakai, T.: Synaptic organization of neurosecretory cells. Microscopic élécronique III. Biol. Grenoble, p. 703–704 (1970).
Van Heyningen, W. E.: The fixation of tetanus toxin by nervous tissue. J. gen. Microbiol. 20, 291, 300 (1959a).
Van Heyningen, W. E.: Chemical assay of the tetanus toxin receptor in nervous tissue. J. gen. Microbiol. 20, 301–309 (1959b).
Van Heyningen, W. E.: Tentative identification of the tetanus toxin receptor in nervous tissue. J. gen. Microbiol. 20, 310–320 (1959c).
Van Heyningen, W. E., Miller, P. M.: The fixation of tetanus toxin by ganglioside J. gen. Microbiol. 24, 107–119 (1961).
Warren, J. J.: The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J. biol. Chem. 234, 1971–1975 (1959).
Wilson, R. A., Cramer, W.: On protagon: its chemical composition and physical constants, its behavior towards alcohol and its individuality. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 1, 97 (1908).
Wright, G. P.: The neurotoxins of clostridium botulinum and clostridium tetani. Pharmacol. Rev. 7, 413–465 (1955).
Wright, E. A., Morgan, R. S., Wright, G. P.: The movements of toxin in the nervous system in experimental tetanus in rabbits. Brit. J. exp. Path. 32, 169–182 (1951).
Yates, J. C., Yates, R. D.: An electron microscopic study of the effects of tetanus toxin on motoneurones of the rat spinal cord. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 16, 382–394 (1966).
Zacks, S. J., Sheff, M. F.: Tetanus toxin: fine structure localization of binding sites in striated muscle. Science 159, 643–644 (1967).
Zacks, S. J., Sheff, M. F.: Biochemical and physiological aspects of tetanus intoxication. In: Neuropoisons: Their pathophysiological actions, vol. 1, pp. 225–262. Plenum Press 1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kryzhanovsky, G.N. The mechanism of action of tetanus toxin: Effect on synaptic processes and some particular features of toxin binding by the nervous tissue. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 276, 247–270 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499880
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499880