Summary
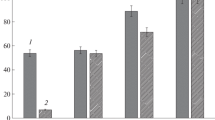
Phallolysin from Amanita phalloides (Vaill. ex Fr.) Secr., rubescenslysin from Amanita rubescens (Pers. ex Fr.) Gray, and fascicularelysin from Hypholoma fasciculare (Huds. ex Fr.) Kummer, in vitro caused disruption of mast cells in rat mesentery. The mast-cell-degranulating potency of rubenscenslysin and fascicularelysin roughly corresponded to their haemolytic potency; the dose-response curves were extremely steep and the cells were either completely destroyed or remained intact. The action of rubescenslysin and fascicularelysin was very fast: at 37° C 95 resp. 90% of the cells were disrupted within 5 min. —Phallolysin degranulated mast cells only at 10–50-fold heamolytic concentrations; the concentration-response curve was flatter, and the effect less radical: a high percentage of the cells underwent only incomplete degranulation. 75% of the cells were degranulated within 5 min. — Fascicularelysin released marker molecules from both, lecithin and sphingomyelin liposomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferguson TFM, Prottey C (1976) The effect of surfactants upon mammalian cells in vitro. Food Cosmet Toxicol 14:431–434
Freeman SE, Turner RJ (1969) A pharmacological study of the toxin of a cnidarian, Chironex fleckeri Southcott. Br J Pharmacol 35:510–520
Habermann E (1960) Zur Toxikologie und Pharmakologie des Gasbrandgiftes (Clostridium Welchii Typ A) und seiner Komponenten. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Path Pharmak 238:502–524
Habermann E (1968) Biochemie, Pharmakologie und Toxikologie der Inhaltsstoffe von Hymenopterengiften. Ergeb Physiol 60:220–325
Högberg B, Uvnäs B (1957) The mechanism of the disruption of mast cells produced by compound 48/80. Acta Physiol Scand 41:345–369
Ito Y, Kurita H, Yamaguchi T, Sato M, Okuda T (1967) Naematolin, a new biologically active substance produced by Naematoloma fasciculare (Fr.) Karst. Chem Pharm Bull 15:2009–2010
Jeljaszewicz J, Szmigielski S, Hryniewicz W (1978) Biological effects of staphylococcal and streptococcal toxins. In: Jeljaszewicz J, Wadström T (eds) Bacterial toxins and cell membranes. Academic Press, London New York San Francisco, pp 185–227
Lin J-Y, Wu H-L, Shi G-Y (1975) Toxicity of the cardiotoxic protein, flammutoxin, isolated from the edible mushroom Flammulina velutipes. Toxicon 13:323–331
Lowry OW, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–273
Odenthal KP, Seeger R, Vogel G (1975) Toxic effects of phallolysin from Amanita phalloides. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 290:133–143
Odenthal KP, Mengs U, Seeger R (1976) Acute toxic effects of the haemolysin from Amanita rubescens after i.v. injection in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 294:R24
Richards MH, Gardner CR (1978) Effects of bile salts on the structural integrity of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 543:508–522
Seeger R (1970) Degranulation von Rattenmastzellen als Ausdruck der Histaminfreisetzung durch verschiedene Muskelrelaxantien. Z Prakt Anästh Wiederbel 5:116–122
Seeger R (1975) Demonstration and isolation of phallolysin, a haemolytic toxin from Amanita phalloides. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 287:277–287
Seeger R (1976) Purification and some properties of the haemolysin from Amanita rubescens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 294:R25
Seeger R (1980a) Studies on rubescenslysin haemolysis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 311:95–103
Seeger R (1980b) Cytolytic toxins of basidiomycetes. In: Eaker D, Wadström T (eds) Natural toxins. Invited papers and workshops from the 6th international symposium on animal, plant and microbial toxins, Uppsala, August 1979. Pergamon Press, Oxford New York Paris Frankfurt
Seeger R, Burkhardt M (1976) The haemolytic effect of phallolysin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 293:163–170
Seeger R, Wachter B (1980) Damage to phospholipid cholesterol liposomes by rubescenslysin and phallolysin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 311:R26
Seeger R, Wiedmann R (1972) Zum Vorkommen von Hämolysinen und Agglutininen in höheren Pilzen. Arch Toxikol 29:189–217
Sessa G, Freer JH, Colacicco G, Weissmann G (1969) Interaction of a lytic polypeptide, mellitin, with the lipid membrane systems. J Biol Chem 244:3575–3582
Strandberg K, Westerberg S (1976) Composition of phospholipids and phospholipid fatty acids in rat mast cells. Mol Cell Biochem 11:103–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seeger, R., Bunsen, E. Degranulation of rat mast cells in vitro by the fungal cytolysins phallolysin, rubescenslysin and fascicularelysin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 315, 163–166 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499259
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499259