Abstract
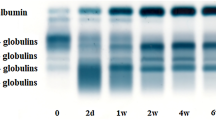
Serum leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) isozymes were compared in four strains of inbred mice during postnatal development, adult life, and pregnancy. In pregnancy, no changes in the maternal serum LAP pattern were observed, in contrast to human studies. One strain, DD/S, differs from the other three in serum LAP. Polymorphism in serum LAP has not been previously described in the mouse. Neonatal DD/S mice exhibit a single band of serum LAP upon starch gel electrophoresis; however, between 14 and 18 days of age, two distinct bands appear, which persist throughout adult life. In the strains C57BL/6J, BALB/cJ, and DBA/2J there is a single band of activity at all stages. Crosses and backcrosses between DD/S and C57BL/6J show that the double-band variant is inherited as an autosomal recessive. The variant is independent of both the supernatant malic enzyme (Mod-1) and the intestinal LAP (Lap-1) loci, which are known to be linked on chromosome 9. The serum LAP variant is linked to an intestinal alkaline phosphatase variant. The presence of a separate structural gene is suggested by the genetic independence of the serum LAP variant from Lap-1. Also, the two serum LAP bands of DD/S are not interconverted by treatment with neuraminidase, β-mercaptoethanol, or heat or by mixing the sera of DD/S and C57BL/6J prior to electrophoresis. The level of serum LAP activity in DD/S is approximately twice that in C57BL/6J. While these observations imply two structurally distinct proteins, the absence of any trace of the second LAP band in the heterozygote strongly suggests that the LAP variant protein is not the result of a separate structural gene. Intestinal LAP in DD/S migrates with the same electrophoretic mobility as the serum LAP variant, implying that the variant might originate in the intestine and its appearance in the serum be modulated by some factor at an unlinked locus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton, G. C. (1963). Polymorphism in the serum post-albumns of cattle. Nature 1981117.
Banks, B. M., Pineda, E. P., Goldberg, J. A., and Rutenburg, A. M. (1960). Clinical value of serum luecine aminopeptidase determinations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2631277.
Bowen, B. S., and Yang, S. Y. (1978). Genetic control of enzyme polymorphisms in the California vole, Microtus californicus. Biochem. Genet. 16455.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 7248.
Dawson, W. D., Huang, L. L., Felder, M. R., and Shaffer, J. B. (1983). Linkage relationships among eleven biochemical loci in Peromyscus. Biochem. Genet. 211101.
Gaines, M. S., and Krebs, C. J. (1971). Genetic changes in fluctuating vole populations. Evolution 25702.
Goldbarg, J. A., and Rutenberg, A. M. (1958). The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer 11283.
Lalley, P. A., and Shows, T. B. (1977). Lysosomal acid phosphatase deficiency: Liver specific variant in the mouse. Genetics 87305.
Mihok, S., and Ewing, D. (1983). Reliability of transferrin and leucine aminopeptidase phenotyping in wild meadows voles (Mictorus pennsylvanicus). Biochem. Genet. 21969.
Moog, F., Birkenmeier, E. H., and Galazier, H. S. (1971). Leucylnaphthylamidase in the small intestine of the mouse: Normal development and influence of cortisone and antibotics. Dev. Biol. 25398.
Paigen, K., Swank, R. T., Tomino, S., and Ganschow, R. E. (1975). The molecular genetics of mammalian glucuronidase. J. Physiol. 85379.
Roderick, T. H., Ruddle, F. H., Chapman, V. M., and Shows, T. B. (1971). Biochemical polymorphism in fetal and inbred mice (Mus musculus). Biochem. Genet. 5157.
Rutenburg, A. M., Banks, B. M., Pineda, E. P., and Goldberg, J. A. (1964). A comparison of serum aminopeptidase and alkaline phosphatase in the detection of hepatobilary disease in anicteric patients. Ann. Intern. Med. 6150.
Scandalios, J. G. (1967). Human serum leucine aminopeptidase. J. Hered. 58153.
Shaw, C. R., and Prasad, R. (1970). Starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes—a compilation of recipes. Biochem. Genet. 4297.
Shows, T. B., and Ruddle, F. H. (1968). Malate dehydrogenase: Evidence for tetrameric structure in Mus musculus. Science 1601356.
Simon, F., Kedinger, M., and Haffen, K. (1977). Intestinal enzymes activities in isolated villus and crypt cells during postnatal development of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 176167.
Wilcox, F. H., Hirschhorn, L., Taylor, B. A., Womack, J. E., and Roderick, T. H. (1969). Genetic variation and alkaline phosphatase of the house mouse (Mus musculus) with emphasis on a manganese requiring isozyme. Biochem. Genet. 171093.
Womack, J. E., Lynes, M. A., and Taylor, B. A. (1975). Genetic variation in intestinal leucine arylaminopeptidase (Lap-1) in the mouse and its location on chromosome 9. Biochem. Genet. 13511.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant RR08117.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finlay, M.F., Huang, L.L. A new variant of serum leucine aminopeptidase in the mouse: Its development and possible regulation. Biochem Genet 23, 169–180 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499121
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499121