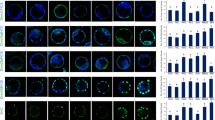
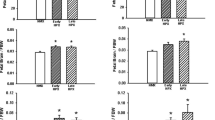
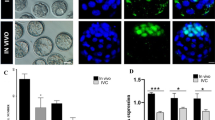
Summary
Inhibition of mitochondrial protein synthesis in rat embryos during late organogenesis leads to impaired embryonic development.
-
1.
Thiamphenicol (TAP), similar to chloramphenicol, inhibits in vivo the synthesis of cytochrome oxidase (cytox), which is partially synthesized by the mitochondrion. Subsequently, DNA synthesis and embryonic growth are affected.
-
2.
Embryos on day 10 and 11, in contrast to embryos on day 9 of gestation, show a high sensitivity of mitochondrial protein synthesis, measured as cytox activity. From day 10 onwards, such an inhibition leads to pronounced impairment of DNA synthesis. The rat hemochorial placenta starts functioning on day 12 of gestation. Larger doses of TAP are required to inhibit cytox and DNA synthesis for treatment after placentation rather than before placentation.
-
3.
Dose-response relationships differ depending on the date and duration of treatment. Application of TAP for 1 day requires 10–30 mg/kg TAP to inhibit cytox synthesis and 60–100 mg/kg to impair embryonic growth. Prolongation of treatment to 4 days (day 10–13) lowers the dose required for inhibition of DNA synthesis to 10 mg TAP/kg/day. This is lower than the human therapeutic dose. Larger doses lead to embryolethality.
-
4.
The extent of inhibition of DNA synthesis provoked by inhibition of mitochondrial protein synthesis depends on a number of factors which include: different growth rates during organogenesis, the number of mitochondria present prior to treatment, availability of extramitochondrial ATP sources and placental permeability barrier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvin, J., Dixit, B. N.: Pharmacologic implications of alterations in the metabolism of chloramphenicol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23, 139–151 (1974)
Bass, R.: Significance of mitochondrial function for embryonic development: Proposal of a mechanism for the induction of embryolethal effects. In: New approaches to the evaluation of abnormal embryonic development (Neubert and Merker, eds.), pp. 524–541. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1975
Bass, R., Merker, H. J. Jäger, E.: Inhibition of mammalian mitochondrial protein synthesis reactions (in vivo and in vitro) by large doses of Rifampicin. FEBS-Meeting Budapest f9d4 (1974)
Brunaud, H., Stoliaroff, M., Laplassotte, J., Navarro, J.: Toxicité aigué du chloramphénicol et du thiophénicol chez le rat adulte et nouveau-né. Thérapie 17, 36–41 (1962)
Courtney, K. D., Valerio, D. A.: Teratology in the macaca mulatta. Teratology 1, 163–172 (1969)
Deutsches Ärzteblatt Nr. 4 (1969) p. 185, Zur Therapie mit Chloramphenicol
Ferrari, V., Della Bella D.: Comparison of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol metabolism. Postgrad. Med. 50, (Suppl. 5), 17–22 (1974)
Fritz, H., Hess, R.: The effect of chloramphenicol on the prenatal development of rats, mice and rabbits. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 19, 667–674 (1971)
Jäger, E., Bass, R.: Chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol and cycloheximide as tools for the measurement of mitochondrial protein synthesis in vitro during organogenesis of rat embyros. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 290, 161–173 (1975)
Köhler, E., Merker, H. J., Ehmke, W., Wojnorowicz, F.: Growth kinetics of mammalian embryos during the stage of differentiation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 272, 169–181 (1972)
Mackler, B., Grace, R., Tippit, D. F., Lemire, R. J., Shepard, T. H., Kelley, V. C.: Studies on the development of congenital anomalies in rats: III. Effects of inhibition of mitochondrial energy systems on embryonic development. Teratology 12, 291–296 (1975)
McChesney, E. W., Koss, R. F., Shekosky, J. M., Deitz, W. H.: Metabolism of dextrosulphenidol in several animal species. J. Amer. pharm. Ass. 49, 762–766 (1960)
Merker, H. J.: Beobachtungen an den DNS Fäden der Mitochondrien. Verh. Anat. Ges. 125 (Suppl.), 229–236 (1969)
Neubert, D., Oberdisse, E., Bass, R.: Biosynthesis and degradation of mammalian mitochondrial DNA. In: Biochemical aspects of the biogenesis of mitochondria (E. C. Slater, J. M. Tager, S. Papa, and E. Quagliariello, eds.), pp. 103–128. Bari: Adriatica Editrice 1968
Neubert, D., Peters, H., Teske, S., Köhler, E., Barrach, H. J.: Studies on the problem of “Aerobic Glycolysis” occurring in mammalian embryos. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 268, 235–241 (1971)
Nijhof, W., Kroon, A. M.: The interference of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol with the biogenesis of mitochondria in animal tissues. A possible clue to the toxic action. Postgrad. Med. 50 (Suppl. 5), 53–59 (1974)
Oerter, D., Bass, R.: Effect of chloramphenicol infusion on the rate of synthesis of cytochrome oxidase in mammalian embryonic tissue. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 272, 239–242 (1972)
Oerter, D., Bass, R.: Embryonic development and mitochondrial function: 1. Effects of chloramphenicol infusion on the synthesis of cytochrome oxidase and DNA in rat embryos during late organogenesis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 290, 175–189 (1975)
Oerter, D., Kirstaedter, H. J., Bass, R., Merker, H. J.: Effect of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol on mitochondrial components and the possible relationship to drug toxicity. Postgrad. Med. 50 (Suppl.) 65–68 (1974)
Piko, L., Chase, D. G.: The role of the mitochondrial genome during early development in mice: Effects of ethidium bromide and chloramphenicol. J. Cell Biol. 58, 357–378 (1973)
Schatz, G., Mason, T. L.: The biosynthesis of mitochondrial proteins. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 43, 51–87 (1974)
Schnaitman, D., Erwin, V. G., Greenawalt, J. W.: The submitochondrial localization of monoamine oxidase. An enzymatic marker for the outer membrane of rat liver mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 32, 719–735 (1967)
Silva, N. O. G., Andrade, A. T. L.: The effects of thiamphenicol upon the rat conceptus. Fertil. and Steril. 21, 431–433 (1970)
Uehlin, M., Bass, R.: Evaluation of a possible action of chloramphenicol/thiamphenicol on microsomal/ribosomal protein synthesis from rat embryos. In: New approaches to the evaluation of abnormal embryonic development (Neubert and Merker, eds.), pp. 542–549. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1975
Walter, A. M., Heilmeyer, L.: Antibiotika-Fibel, pp. 450–472. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bass, R., Oerter, D. Embryonic development and mitochondrial function. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 296, 191–197 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498685
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498685