Summary
The site and mode of action of capsaicin were analysed on the guinea-pig isolated ileum.
-
1.
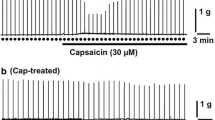
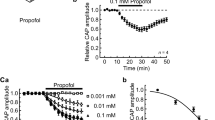
Capsaicin produced longitudinal contraction (EC50 4.2×10−8 g/ml) followed by a specific, rapid and irreversible tachyphylaxis (IC50 2.8×10−7 g/ml).
-
2.
Capsaicin was ineffective in the presence of tetrodotoxin (2×10−7 g/ml) or on ilea kept for 24–48 h at 4°C, without an oxygen supply.
-
3.
On ileal segments, the perivascular mesenteric nerves of which were transsected 5–8 days before the experiment, practically no response to capsaicin was obtained. Chronic abdominal bilateral vagotomy was without any effect.
-
4.
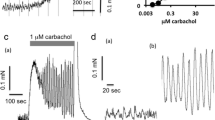
Hyoscine (1×10−8–1×10−6 g/ml) or morphine (2×10−6 g/ml) strongly inhibited contractions produced by capsaicin. Neither mecamylamine (1×10−5 g/ml), nor nicotine (5×10−5 g/ml) and dimethylphenylpiperazinium (5×10−6 g/ml) caused any change, while an increased response to capsaicin was obtained in the presence of hexamethonium (1×10−4 g/ml).
-
5.
Unaltered contractions were produced by capsaicin on ileal segments made tachyphylactic to 5-HT, bradykinin or substance P. Histamine antagonists at H1 and H2 receptors (chloropyramine, burimamide), the prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor indomethacin, pretreatment with the adrenergic neuron blocking agent guanethidine, as well as in vivo reserpine pretreatment were also ineffective in this respect.
-
6.
It is concluded that in the guinea-pig ileum capsaicin causes predominantly cholinergic contraction by stimulating terminals of extrinsic, non-parasympathetic nerves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baraz, L. A., Khayutin, V. M., Molnár, J.: Effects of capsaicin upon the stimulatory action of potassium chloride in the visceral branches of spinal afferents of the cat. Acta Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 33, 237–246 (1968)
Bell, C.: Differential effects of tetrodotoxin on sympathomimetic actions of nicotine and tyramine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 32, 96–103 (1968)
Brownlee, G., Johnson, E. S.: The site of the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor on the intramural nervous plexus of the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 21, 306–322 (1963)
Burn, J. H.: Release of noradrenaline from sympathetic endings. Nature 231, 237–240 (1971)
Burn, J. H.: Evidence that acetylcholine releases noradrenaline in the sympathetic fibre. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 29, 325–329 (1977)
Coleridge, H., Coleridge, J.: Cardiovascular receptors. In: Modern trends in physiology (C. B. B. Downman, ed.), pp. 245–267. London: Butterworths 1972
Ehrenpreis, S., Sato, T., Takayanagi, I., Comaty, J. E., Takagi, K.: Mechanism of morphine block of electrical activity in ganglia of Auerbach's plexus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 40, 303–309 (1976)
Garcia Leme, J., Hamamura, L.: Formation of a factor increasing vascular permeability during electrical stimulation of the saphenous nerve in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 51, 383–389 (1974)
Högyes, A.: Beiträge zur physiologischen Wirkung der Bestandteile des Capsicum annuum. Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmak. 9, 119–130 (1878)
Jancsó, N., Jancsó-Gábor, A.: Dauerausschaltung der chemischen Schmerzempfindlichkeit durch Capsaicin. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmak. 236, 142–145 (1959)
Jancsó-Gábor, A., Szolcsányi, J.: Neurogenic inflammatory responses. J. Dental Res. 51, 264–269 (1972)
Jancsó, N., Jancsó-Gábor, A., Szolcsányi, J.: Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 31, 138–151 (1967)
Jancsó, N., Jancsó-Gábor, A., Szolcsányi, J.: The role of sensory nerve endings in neurogenic inflammation induced in human skin and in the eye and paw of the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 33, 32–41 (1968)
Kao, C. Y.: Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol. Rev. 18, 997–1049 (1966)
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: Tetrodotoxin and neuromuscular transmission. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. [Biol.] 167, 8–22 (1967)
Kosterlitz, H. W., Lees, G. M.: Pharmacological analysis of intrinsic intestinal reflexes. Pharmacol. Rev. 16, 301–339 (1964)
Krauss, K. R., Carpenter, D. O., Kopin, I. J.: Acetylcholine-induced release of norepinephrine in the presence of tetrodotoxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 173, 416–421 (1970)
Lembeck, F., Fischer, G.: Gekreuzte Tachyphylaxie von Peptiden. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. Exp. Path. 258, 452–456 (1967)
Molnár, J., György, L., Unyi, G., Kenyeres, J.: Effect of capsaicin on the isolated ileum and auricle of the guinea-pig. Acta Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 35, 369–374 (1969)
Paton, W. D. M.: The response of the guinea-pig ileum to electrical stimulation by coaxial electrodes. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 127, 40–41P (1955)
Paton, W. D. M.: The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 12, 119–127 (1957)
Rocha e Silva, M., Valle, J. R., Picarelli, Z. P.: A pharmacological analysis of the mode of action of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamin) upon the guinea-pig ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 8, 378–388 (1953)
Schaumann, W.: Inhibition by morphine of the release of acetylcholine from the intestine of the guinea-pig. Br. J. Pharmacol. 12, 115–118 (1957)
Szolcsányi, J.: A pharmacological approach to elucidation of the role of different nerve fibres and receptor endings in mediation of pain. J. Physiol. (Paris) 73, 251–259 (1977)
Szolcsányi, J., Barthó, L.: New type of nerve-mediated cholinergic contraction of the guinea-pig small intestine and its selective blockade by capsaicin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 305, 83–90 (1978)
Szolcsányi, J., Jánossy, T.: Mechanism of the circulatory and respiratory reflexes evoked by pungent agents. Acta Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 39, 260–261 (1971)
Szolcsányi, J., Jancsó-Gábor, A., Joó, F.: Functional and fine structural characteristics of the sensory neuron blocking effect of capsaicin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 287, 157–169 (1975)
Toh, C. C., Lee, T. S., Kiang, A. K.: The pharmacological actions of capsaicin and analogues. Br. J. Pharmacol. 10, 175–182 (1955)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barthó, L., Szolcsányi, J. The site of action of capsaicin on the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 305, 75–81 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00497008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00497008