Abstract
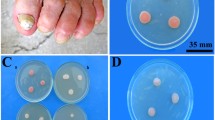
Hormiscium dermatitidis Kano is a well known etiological agent of cutaneous and generalized chromomycosis. However, the generic designation of this fungus has long been a much debated question. The results of the present study of the type culture ATCC 28869 indicate that the fungus is polymorphic, producing a Phialophora state in media containing glucose or maltose and a Cladosporium state in media containing galactose or melibiose. Morphologically and developmentally this chromomycotic agent is closely related to Fonsecaea pedrosoi (Brumpt) Negroni and should be classified as Fonsecaea dermatitidis (Kano) Carrión.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Doory, Y. 1972. Chromomycosis. Mountain Press Publishing Co., Missoula, Montana, 203 p.
Binford, C. H., G. Hess & C. W. Emmons. 1944. Chromoblastomycosis. Report of a case from continental United States and discussion of the classification of the causative fungus. Arch. Dermatol. Syph. 49: 1–5.
Carrión, A. L. 1950. Yeastlike dematiaceous fungi infecting the human skin. Arch. Dermatol. Syph. 61: 996–1008.
Carrión, A. L. & M. Silva-Hutner. 1971. Taxonomic criteria for the fungi of Chromoblastomycosis with reference to Fonsecaea pedrosoi. Int. J. Dermatol. 10: 35–43.
Cole, G. T. & W. B. Kendrick. 1973. Taxonomic studies of Phialophora. Mycologia 65: 661–688.
Conant, N. F., D. T. Smith, R. D. Baker, J. L. Callaway & S. A. Martin. 1953. Manual of clinical mycology, 2nd ed. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 465 p.
Ellis, M. B. 1971. Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, England, 608 p.
Emmons, C. W., C. H. Binford & J. P. Utz. 1963. Medical mycology, 1st ed. Lea and Febinger, Philadelphia, 380 p.
Emmons, C. W., C. H. Binford & J. P. Utz. 1970. Medical mycology, 2nd ed. Lea and Febinger, Philadelphia, 508 p.
Jotisankasa, V., H. S. Nielsen, Jr. & N. F. Conant. 1970. Phialophora dermatitidis; Its morphology and biology. Sabouraudia 8: 98–107.
Kano, K. 1937. Über die Chromoblastomykose durch einen noch nicht als pathogen beschriebenen Pilz. Hormiscium dermatitidis n. sp. Arch. Dermatol. Syph. (Berlin) 176: 282–294.
Kendrick, W. B. & J. W. Carmichael. 1973. Hyphomycetes, p. 323–509. In G. C. Ainsworth et al. [ed.], The fungi. Vol. IVA. Academic Press, New York.
Negroni, P. 1936. Estudio micologico del primer caso argentino de cromomicosis, Fonsecaea (n.g.) pedrosoi (Brumpt 1921). Rev. Inst. Bact. del Depto. Nacional de Higiene. B Aires 7: 419–426.
Oujezdsky, K. B. & P. J. Szaniszlo. 1974. Conidial ontogeny in Phialophora dermatitidis. Mycologia 66: 537–542.
Rippon, J. W. 1974. Medical mycology. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 587 p.
Schol-Schwarz, M. B. 1968. Rhinocladiella, its synonym Fonsecaea and its relation to Phialophora. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Ned. Tijdschr. Hyg. 34: 119–152.
Thom, C. J. 1940. Naming molds. J. Washington Acad. Sci. 30: 49–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butterfield, W., Jong, S.C. Effect of carbon source on conidiogenesis in fonsecaea dermatitidis, agent of chromomycosis. Mycopathologia 58, 59–62 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00493594
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00493594