Abstract
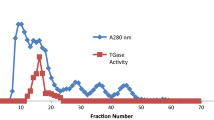
The method of isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel was used to separate HGPRT isoenzymes in crude hemolysates of human and rat erythrocytes. HGPRT from erythrocytes of a normal human male donor consistently revealed three peaks of activity. Their mean isoelectric points, using pH 5–7 range ampholytes, were, peak I, pI 6.00; peak II, pI 5.83; and peak III, pI 5.71. Peak III was wide and tailed. It always had a shoulder with a mean pI of 5.62. HGPRT from rat erythrocytes revealed two peaks of activity, corresponding to isoelectric points of 5.90 and 5.80. The method of isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel is presented as a new way of detecting isoenzyme patterns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, W. J., and Kelley, W. N. (1971). Human hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl-transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2467398.
Atkinson, M. R., and Murray, A. W. (1965). Inhibition of purine phosphoribosyl transferases of Ehrlich ascites cells by 6-mercaptopurine. Biochem. J. 9464.
Awdeh, Z. L., Williamson, A. R., and Askonas, B. A. (1968). Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel and its application to immunoglobulins. Nature 21966.
Bakay, B., and Nyhan, W. L. (1971). The separation of adenine and hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase isozymes by disc gel electrophoresis. Biochem. Genet. 581.
Der Kaloustian, V. M., Byrne, R., Young, W. J., and Childs, B. (1969). An electrophoretic method for detecting hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase variants. Biochem. Genet. 3299.
Der Kaloustian, V. M., Hallal, R. T., and Awdeh, Z. L. A new method of assay of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. In preparation.
Kelley, W. N., Rosenbloom, F. M., Henderson, J. F., and Seegmiller, J. E. (1967). A specific enzyme defect in gout associated with overproduction of uric acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 371735.
Kelley, W. N., Greene, M. L., Rosenbloom, F. M., Henderson, J. F., and Seegmiller, J. E. (1969). Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency in gout. Ann. Int. Med. 70155.
Lesch, M., and Nyhan, W. L. (1964). A familial disorder of uric acid metabolism and central nervous system function. Ann. J. Med. 36561.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by Grant No. 38-5768 from the Lebanese National Council for Scientific Research and Grant No. 18-5240 from the Medical Research Committee, American University of Beirut.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Der Kaloustian, V.M., Awdeh, Z.L., Hallal, R.T. et al. Analysis of human hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase isozymes by isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel. Biochem Genet 9, 91–95 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00485594
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00485594