Abstract
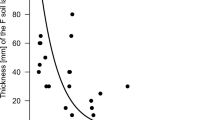
The deposition of strong acids is one of many threats to forest ecosystems and viable forestry. Several counteractions against acidification have been launched, e.g. changes in forestry management and the introduction of chemicals. The inter-institutional programme “Counteractions Against Acidification in Forest Ecosystems” was established in 1993 to evaluate existing knowledge and run experimental and fullscale field experiments. A total of 240 metric tons of coarse dolomite powder was spread by helicopter in September 1994 on 84 ha forest catchment dominated by pine (Pinus sylvestris) and Norway spruce (Picea abies). Potential desirable and undesirable effects after this carbonate application may be less pronounced than recorded at other sites due to the relatively moderate dose (3 tons ha−1). Pre-liming stream water quality (mean values for May 1993-September 1994) was as follows: pH 4.8; Ca 1.13 mg L−1; reactive Al (RAl) 248 μg L−1; inorganic monomeric Al (Al) 72 μg L−1. The reference station was slightly higher in Ca and slightly lower in both RAl and Al. Dolomite application resulted in a significant increase in pH to 5.7 as mean value for the post-liming period (September 1994-April 1995). Both Ca and Mg increased significantly after liming, and both RAl and Al, declined significantly. The rapid detoxification of stream-water may be explained by dissolution of dolomite particles in both streams and catchment, a resulting pH increase and change in Al species composition. Retention of Al in the catchment probably explains the reduction in RAl. No increase in NO3, total N, total P or TOC was recorded the first seven months.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brahmer, G.: 1992, “Project FEELING: Studying the effects of whole-catchment liming”, pp. 23–33. In: Rasmussen, L., Brydges, T. and Mathy, P. (eds.). Experimental manipulations of biota and biogeochemical cycling in ecosystems. Commission of European Communities. Ecosystem report 4.
Driscoll, C.T.: 1984, “A procedure for the fractionation of aqueous aluminum in dilute acidic water”, Inern. J. Environ. Anal. Chem., 16, 267–283.
Hüttl, R.F.: 1991, “Die Nährelementversorgung geschädigter Wälder in Europa und Nordamerika”, Habil. Schrift. Freib. Bodenkdl. Adh., 28, 1–440.
Hüttl, R.F. und Zöttl, H.W.: 1993, “Liming as a mitigating tool to forest decline”, Forest Ecology and Managment, 61, 325–338.
Kreutzer, K.: 1995, “Effects of forest soil liming on soil processes”, Plant and Soil, 168-169, 447–470.
Kroglund, F., Dalziel, T., Rosseland, B.O., Lien, L., Lydersen, E. and Bulger, A.: 1992, “Restoring endangered fish in stressed habitats, ReFish Project 1988–1991”. Acid Rain Research Report 30/1992, NIVA, 43 pp.
Nilsen, P.: 1994, “Proceedings from an international seminar on: Counteractions against acidification in forest ecosystems”, March 3–4 1994, Mastemyr, Norway. Report 14–4, NISK-NLH, 54 pp.
Raddum, G.G. and Fjellheim, A.: 1984, “Acidification and early warning organisms in freshwater in western Norway”, Verh. Int. Verein. LimnoL, 22, 1973–1980.
Rosseland, B.O., Eldhuset, T.D. and Staurnes, M.: 1990, “Environmental effects of aluminium”, Environ. Geochem. Health, 12 (1–2), 17–27.
Traaen, T. S., Frogner, T., Hindar, A., Kleiven, E., Lande, A. and Wright, R.F.: 1994, “Whole-catchment liming at Tjønnstrond, Norway: an 11 year record”, (subm. WASP).
Westling, O. and Skärby, L.: 1993, “Environmental consequences of the Forest Board proposal to a forest soil liming programme (final conclusions)”, IVL (in Swedish).
Wood, C.M. and McDonald, D.G.: 1987, “The physiology of acid/aluminium stress in trout, Annls. Soc. r. zool. Belg., 117 — supplement 1, 399–410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hindar, A., Nilsen, P., Skiple, A. et al. Counteractions Against Acidification in Forests Ecosystems. Effects on stream water quality after dolomite application to forest soil in Gjerstad, Norway. Water Air Soil Pollut 85, 1027–1032 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00476965
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00476965