Summary
Nine guinea pigs, anaesthetized and fully curarized, were used in the present experiments. A compound action pptential of the left cochlear nerve was evoked by electrical stimulation of a small section of the homolateral spiral lamina. This compound action potential was recorded for many hours.
-
1.
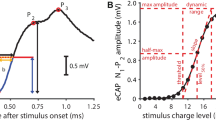
The auditory nerve when stimulated electrically generates three peaks (N1, N2, N3). The appearance of N2 and N3 depends on the stimulating energy, N1 having the lowest threshold, N2 a higher and N3 the highest threshold.
-
2.
The intensity function of the N1− or N2−- or N3 amplitude is a continuous but non-linear function with only one point of Inflexion.
-
3.
Latencies get shorter as the stimulating energy increases.
-
4.
The time needed for the three peaks to run through the cochlea differs by 0.1 msec. A peripheral coding of loudness generated by the auditory nerve fibres seems to exist.
Zusammenfassung
An 9 narkotisierten und curaresierten Meerschweinchen wurde das Summenaktionspotential des linken Hörnerven mit einer großen Drahtelektrode abgeleitet. Das Potential wurde durch elektrischen punktförmigen Reiz an der linken Lamina spiralis erzeugt. Die experimentellen Bedingungen ließen sich über mehrere Stunden konstant halten.
Das Summenaktionspotential des Hörnerven hat 3 negative Gipfel, genannt N1, N2 und N3. Dabei tritt N1 bei den geringsten elektrischen Reizstärken auf, bei etwas größeren Stärken erscheint N2, und bei noch größeren Reizstärken schließlich N3.
Die Größe von N1, N2 und N3 ist eine im ganzen kontinuierliche, S-förmige Funktion der elektrischen Reizstärke, solange die Reizdauer konstant gehalten bleibt.
Die Latenzen von N1, N2 und N3 werden mit zunehmender elektrischer Reizstärke kürzer.
Die Laufzeit durch die Schnecke ist für N1, N2 und N3 fast identisch, sie differiert nur um 0,1 msec. Dieser Befund stützt die alte Annahme, daß die Verschlüsselung der Lautstärke zum Teil schon auf der Höhe der primären, auditorischen Neurone durchgeführt wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis, H.: Peripheral coding of auditory information. In: Sensory Communication. W. A. Rosenblith, edit., vol. 16, pp. 119–141. M.I.T. Press, Cambridge 39, Mass. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1961
Davis, H., Gernant, B. E., Riesco-Mc Clure, J. S.: Threshold of action potentials in ear of guinea pig. J. Neurophysiol. 13, 73 (1950)
Firbas, W., Wicke, W., Volavsek, Ch.: Über Zahl und Anordnung der Ganglienzellen im Ganglion spirale des Meerschweinchens. Mschr. Ohrenheilk. 104, 6 (1970)
Frischkopf, L. S.: A probability approach to certain neuroelectric phenomena. Research Lab. of Electron. Technical Report. 307 Cambridge Mass. (1956)
Gacek, R., Rasmussen, G. L.: Fiber analyses of the state acousticus nerve of guinea pig, cat and monkey. Anat. Rec. 139, 455 (1961)
Kayser, D., Legouix, J. P.: Tonotopic projections on the auditory cortex of the guinea pig. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 157, 2161 (1964)
Keidel, W. D.: Physiologie des Hörens. Klin. Wschr. 37, 1205 (1959)
Pfalz, R., Pirsig, W.: Compound afferent action potential of the cochlear nucleus evoked electrically. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis) 75, 1077 (1966)
Woolsey, C. N. a., Walzl, E. M.: Topical projection of nerve fibers from local regions of the cochlea to the cerebral cortex of the cat. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 71, 315 (1942)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagel, D. Compound action potential of the cochlear nerve evoked electrically. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 206, 293–298 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00460282
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00460282