Abstract
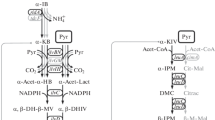
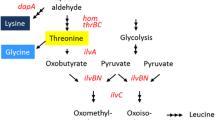
In Arthrobacter strain 23 the allosteric insensitivity of threonin deaminase caused by mutation resulted in derepressed formation of the enzymes of the isoleucine-valine-leucine pathway. Derepression was also observed, when wild type cells were incubated in the presence of α-oxobutyrate. In both cases isoleucine was overproduced and excreted. As growth experiments indicated the excess of α-oxobutyrate in the medium caused endogenous valine and leucine deficiency and a transient inhibition of growth. Derepressed formation of the isoleucinevaline biosynthetic enzymes resulted in relief of growth inhibition.
The transient inhibitory effect of α-oxobutyrate has been traced back to substrate competition at the first enzyme common to the isoleucine and valine pathway, acetohydroxy acid synthase. Due to the low K m of the enzyme for α-oxobutyrate this substrate is preferentially converted. As proven by gaschromatographical measurements of acetoin and acetylethyl carbinol produced in enzyme (acetohydroxy acid synthase) assays with varied substrate concentrations, relatively low concentrations of α-oxobutyrate are able to suppress the formation of α-acetolactate completely. These results explain the transient inhibitory effect of α-oxobutyrate on the growth of bacteria.
Zusammenfassung
In Arthrobacter Stamm 23 führte die durch Mutation verursachte allosterische Unempfindlichkeit der Threonin-Desaminase zur dereprimierten Bildung der Enzyme im Isoleucin-Valin-Leucin-Biosyntheseweg. Derepression erfolgte auch, wenn Wildtypzellen in Gegenwart von α-Ketobuttersäure inkubiert wurden. In beiden Fällen wurde Isoleucin überproduziert und ins Kulturmedium ausgeschieden. Wie aus Wachstumsexperimenten hervorging, verursachte der Überschuß an α-Ketobuttersäure im Medium primär einen Valin- und Leucin-Mangel, der zu einer vorübergehenden Wachstumshemmung führte. Durch die dereprimierte Bildung der Enzyme im Isoleucin-Valin-Biosyntheseweg konnte die Wachstumshemmung überwunden werden.
Der vorübergehende Hemmeffekt der α-Ketobuttersäure ließ sich auf eine Konkurrenz der Substrate am ersten gemeinsamen Enzym im Isoleucin-Valin-Biosyntheseweg, der Acetohydroxysäure-Synthase, zurückführen. Wegen des niedrigen K m-Wertes für α-Ketobuttersäure wird dieses Substrat vom Enzym bevorzugt umgesetzt. Durch gaschromatographische Bestimmungen der Acetoin- und Acetyläthylcarbinol-Bildung in Enzymtests mit variierten Substrat-Konzentrationen konnte nachgewiesen werden, daß relativ geringe Konzentrationen an α-Ketobuttersäure genügen, um die α-Acetolacetat-Bildung vollständig zu unterdrücken. Diese Ergebnisse erklären die durch α-Ketobuttersäure verursachte vorübergehende Wachstumshemmung bei Bakterien.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α-KBS:
-
α-Ketobuttersäure
- FAD:
-
Flavin-adenin-dinucleotid
- AHS:
-
Acetohydroxysäure
- IPM:
-
Isopropylmalat
- TPP:
-
Thiaminpyrophosphat
Literatur
Baumgarten, J.: Die Regulation der Synthese von Isoleucin, Valin und Leucin bei Arthrobacter St. 23. Diss., Universität Göttingen 1969
Baumgarten, J.: Die Bildung von Isoleucin durch Mutanten von Arthrobacter unter variierten Wachstumsbedingungen. Zbl. Bakt. I. Abt. Orig. A 220, 308–315 (1972)
Baumgarten, J., Schlegel, H. G.: Threonin-Desaminase aus Arthrobacter Stamm 23. Arch. Mikrobiol. 75, 312–326 (1971)
Freundlich, M., Burns, R. O., Umbarger, H. E.: Control of isoleucine, valine and leucine biosynthesis. I. Multi-valent repression. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 48, 1804–1808 (1962)
Hill, F. F.: Regulation der Leucinsynthese und Trifluorleucinresistenz bei Hydrogenomonas H 16. Diss., Universität Göttingen 1968
Kisumi, M., Kato, J., Komatsubara, S., Chibata, J.: Increase in isoleucine accumulation by α-aminobutyric acid-resistant mutants of Serratia marcescens. Appl. Microbiol. 21, 569–571 (1971)
Kuwana, H., Caroline, D. F., Harding, R. W., Wagner, R. P.: An acetohydroxy acid synthetase from Neurospora crassa. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 128, 184–193 (1968)
Moyed, M. S.: Induced phenotypic resistance to antimetabolite. Science 131, 1449 (1960)
Schmidt, K., Liaaen-Jensen, S., Schlegel, H. G.: Die Carotinoide der Thiorhodaceae. I. Okenon als Hauptcarotinoid von Chromatium okenii Perty. Arch. Mikrobiol. 46, 117–126 (1963)
Strassman, M., Ceci, L. N.: Enzymatic formation of α-isopropyl malic acid, an intermediate in leucine biosynthesis. J. biol. Chem. 238, 2445–2453 (1963)
Umbarger, H. E., Brown, B.: Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. VIII. The formation of acetolactate. J. biol. Chem. 233, 1156–1160 (1958)
Varga, J. M., Horvath, J.: Role of acetohydroxy acid synthetase in the regulation of valine and isoleucine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta biochem. biophys. Acad. Sci. hung. 2, 357–369 (1967)
Wagner, R. P., Bergquist, A., Barbee, T.: The synthesis in vivo of valine and isoleucine from pyruvate and α-ketobutyrate in Neurospora. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 100, 444–450 (1965)
Westerfeld, W. W.: A colometric determination of blood acetoin. J. biol. Chem. 161, 495–502 (1945)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumgarten, J. Die Bedeutung der “feedback”-Hemmung der Threonin-Desaminase für die Synthese von Valin und Leucin. Arch. Microbiol. 101, 221–232 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00455940
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00455940