Abstract
Aspergillus microcysticus Sappa TÜ 502 produces a formerly unknown antibiotic named asposterol. Extractions of culture filtrates from fermentations with ethyl acetate and subsequent column chromatography of the extracts on silica gel using benzene/ethyl acetate for the elution yielded up to 35 mg/l of practically pure preparations of the antibiotic.
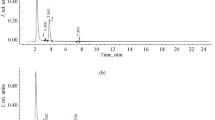
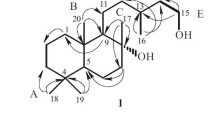
Asposterol is lipophilic and instable. The elemental composition was determined as C24H33NO4, molecular weight 399. The antibiotic exists in two isomeric forms. A steran skeleton is attributed to the compound. There is no evidence for other similarities with known steroid antibiotics.
Asposterol inhibits both bacteria and fungi. The minimal inhibitory concentrations are 0.3 μg/ml for Bacillus subtilis and 1.2 μg/ml for Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
The inhibitory effect of asposterol is compensated by α-tocopherol. It is assumed that the cytoplasmic membrane is the site of the primary antibiotic action. Linolenic acid, undecylenic acid and other unsaturated fatty acids show similarities with respect to the type of their antimicrobial effects.
Zusammenfassung
Aspergillus microcysticus Sappa, Stamm TÜ 502, bildet ein bisher unbekanntes Antibioticum, das Asposterol genannt wird. Es läßt sich aus dem Filtrat von Submerskulturen des Pilzes mit Äthylacetat extrahieren und nach anschließender Säulenchromatographie an Kieselgel durch Elution mit Benzol/Äthylacetat in Ausbeuten bis zu 35 mg/l in praktisch reiner Form darstellen.
Asposterol ist lipophil und instabil. Ihm kommt die Summenformel C24H33NO4, MG 399, zu. Die Verbindung liegt in zwei isomeren Formen vor und besitzt vermutlich ein Steran-Grundgerüst.
Asposterol hemmt das Wachstum von Bakterien und Pilzen. Die minimale Hemmkonzentration liegt für Bacillus subtilis bei 0,3 μg/ml, für Schizosaccharomyces pombe bei 1,2 μg/ml.
Die Hemmwirkung des Asposterols wird durch α-Tocopherol aufgehoben. Als primärer Wirkort des Antibioticums wird die Cytoplasma-Membran angesehen. Linolensäure, Undecen(10)säure und andere ungesättigte Fettsäuren ähneln dem Asposterol in der Art ihrer antimikrobiellen Wirkung.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bergmeyer, H. U.: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Band II. Weinheim (Bergstr.): Verlag Chemie 1970
Bishop, D. G.: Lipid metabolism. In: Biochemistry and methodology of lipids, A. R. Johnson, J. B. Davenport, (eds.). New York-London-Sydney-Toronto: Wiley 1971
Bishop, D. G., Rutberg, L., Samuelsson, B.: The chemical composition of the cytoplasmic membrane of Bacillus subtilis. Europ. J. Biochem. 2, 448–453 (1967)
Bonifas, V.: Détermination de l'association synergique binaire d'antibiotes et de sulfonamides: Experientia (Basel) 8, 234–235 (1952)
Carrasco, L., Vazquez, D: Ribosomal sites involved in binding of aminoacyl-t RNA and EF 2. Mode of action of fusidic acid. FEBS Letters 32, 152–156 (1973)
Davis, B. D., Mingioli, E. S.: Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J. Bact. 60, 17–28 (1950)
DeLuca, H. F., Suttie, J. W.: The fat-soluble vitamins. Madison-Milwaukee-London: The University of Wisconsin Press 1970
Drews, G.: Mikrobiologisches Praktikum für Naturwissenschaftler. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1968
Evans, R. J., Waterworth, P. M.: Naturally-occuring fusidic acid resistance in staphylococci and its linkage to other resistances. J. clin. Path. 19, 555–560 (1966)
Fales, H. M., Luukkainen, T.: O-Methyloximes as carbonyl derivatives in gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance. Analyt. Chem. 37, 955–957 (1965)
Fieser, L. F., Fieser, M.: Organische Chemie. Weinheim (Bergstr.): Verlag Chemie 1968
Fischer, B., Keller-Schierlein, W., Kneifel, H., König, W. A., Loeffler, W., Müller, A., Muntwyler, R., Zähner, H.: Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 118. Mitteilung. δ-N-Hydroxy-l-arginin, ein Aminosäure-Antagonist aus Nannizzia gypsea. Arch. Mikrobiol. 91, 203–220 (1973)
Gamage, P. T., Mori, T., Matsushita, S.: Effects of linoleic acid hydroperoxides and their secondary products on the growth of Escherichia coli. Agr. Biol. Chem. 35 33–39 (1971)
Gaunt, J. K., Stowe, B. B.: Analysis and distribution of tocopherols and quinones in the pea plant. Plant Physiol. 42, 851–858 (1967)
Gottlieb, D., Shaw, P. D.: Antibiotics I. Mechanism of action. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1967
Green, J.: Vitamin E and the biological antioxidant theory. In: The fat-soluble vitamins, H. F. DeLuca, J. W. Suttie, Eds. Madison-Milwaukee-London: The University of Wisconsin Press 1970
Haller, B., Loeffler, W.: Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 71. Mitteilung. Fusidinsäure aus Dermatophyten und anderen Pilzen. Arch. Mikrobiol. 65, 181–194 (1969)
Hamilton-Miller, J. M. T.: Polyene-resistance in yeasts: a consideration of physiological and biochemical mechanisms. Microbios 8, 209–213 (1973)
Heberle, W.: Asposterol, ein Antibiotikum aus Aspergillus microcysticus. Untersuchungen zur Isolierung, Charakterisierung und Wirkungsweise. Dissertation Universität Tübingen 1974
Hesse, G.: Chromatographisches Praktikum. In: Methoden der Analyse in der Chemie, Band 6, F. Hecht, R. Kaiser, H. Kriegsmann, W. Simon, Eds. Frankfurt a. Main: Akad. Verlagsges. 1968
Hüttlin, H.: Isolierung und Charakterisierung eines membranophilen Antibiotikums aus Streptomyces violaceoniger. Diplomarbeit, Universität Tübingen 1972
Kage, M. P.: Visualisierung des Unsichtbaren. Bild Wiss. 10, 502–511 (1973)
König, W. A., Kneifel, H., Bayer, E., Müller, H., Zähner, H.: Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 116. Mitteilung. O-(l-Norvalyl-5)Isourea, a new arginine antagonist. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 26, 44–50 (1973)
Kunze, B.: Lipomycin, ein polyenartiges, antibakteriell wirkendes Antibiotikum. Untersuchungen zur biologischen Wirkung. Diplomarbeit, Universität Tübingen 1972
Kunze, B., Schabacher, K., Zähner, H., Zeeck, A.: Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 111. Mitteilung. Lipomycine. I. Isolierung, Charakterisierung und erste Untersuchungen zur Konstitution und Wirkungsweise. Arch. Mikrobiol. 86, 147–174 (1972)
Laidman, D. L., Hall, G. S.: Adsorption column chromatography of tocopherols. In: Methods in enzymology, Vol. XVIII, part c, S. P. Colowick, N. O. Kaplan, Eds. New York-London: Academic Press 1971
Loeffler, W.: Ein einfaches Verfahren zum Erkennen von Dermatophyten. In: Diagnostik und Therapie der Pilzkrankheiten und neuere Erkenntnisse in der Biochemie der pathogenen Pilze, H. Götz, H. Rieth, Eds. Berlin: Grosse 1970
Mandels, G. R.: Kinetics of fungal growth. In: The fungi, Vol. I, G. C. Ainsworth, A. S. Sussman, Eds. New York-London: Academic Press 1965
Mitchison, J. M.: Physiological and cytological methods for Schizosaccharomyces pombe. In: Methods in cell physiology, Vol. 4, D. M. Prescott, Ed. New York-London: Academic Press 1970
Nair, P. P., Kayden, H. J.: International conference on vitamin E and its role in cellular metabolism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 203, 1–53 (1972)
Pache, W.: Zur Wirkungsweise des Boromycins. Dissertation, Universität Tübingen 1969
Pache, W., Chapman, D.: Interaction of antibiotics with membranes: Chlorothricin. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 255, 348–357 (1972)
Pache, W., Zähner, H.: Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 76. Mitteilung. Bindung von Antibiotica an Lipoprotein. Arch. Mikrobiol. 66, 281–288 (1969)
Poralla, K.: Zur Wirkungsweise des makrolidartigen Antibiotikums Borrelidin und typischer Makrolid-Antibiotika. Dissertation, Universität Tübingen 1967
Raper, K. B., Fennell, D. I.: The genus Aspergillus. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins 1965
Recknagel, R. O., Ghoshal, A. K.: No accelerated mobilization of peripheral lipid in CCl4 hepatotoxicity. Gastroenterology 48, 509–510 (1965)
Stahl, E.: Dünnschicht-Chromatographie. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1967
Theise, H.: Lipide. In: Molekulare Biologie der Zelle, H. Bielka, Ed. Stuttgart: Fischer 1973
Turner, W. B.: Fungal metabolites, London-New York: Academic Press 1971
Weibull, C.: The isolation of protoplasts from Bacillus megaterium by controlled treatment with lysozyme. J. Bact. 66, 688–695 (1953)
Williams, D. H., Fleming, I.: Spektroskopische Methoden in der organischen Chemie. Stuttgart: Thieme 1968
Zähner, H.: Biologie der Antibiotica. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1965
Zähner, H., Maas W. K.: Biology of antibiotics. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
135. Mitteilung: Ernst, J., Winkelmann, G.: Iron transport properties of semisynthetic coprogen derivatives in Neurospora crassa. Arch. Microbiol. (in press, 1974).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heberle, W., Loeffler, W. & König, W.A. Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. Arch. Microbiol. 100, 73–95 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446308
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446308