Abstract
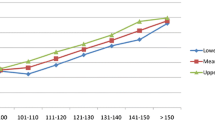
Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) and standing height (Ht) were measured in 522 healthy Greek children aged 7–16 years. The regression equation of PEFR on height in centimetres was PEFR=5.34 Ht-380.8. This demonstrated markedly higher values for PEFR in Greek children compared to previously published data from other countries. A sample of 339 British children was examined similarly. The regression equation of PEFR on height in centimetres was PEFR=5.64 Ht-472.5. This was similar to previously published data. No cause for this discrepancy was found after close examination of population sampling, measurement error or calibration error in the Greek study. It is therefore concluded that Greek children appear to have an unexpectedly high PEFR for height.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binder RE, Mitchell CA, Schoenberg JB, Bouhuys A (1976) Lung function among black and white children. Am Rev Respir Dis 114:955–959
Burr ML, Eldridge BA, Boysieuricz LK (1974) Peak expiratory flow rates before and after exercise in school children. Arch Dis Child 49:923–926
Chang ST, Han TS (1965) Peak flow rate in relation to age, sex and anthropometric measurements. Acta Paediatr Scand 54: 439–445
Eveleth PB, Tanner JM (1976) Worldwide variation in human growth. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 21–31
G.A.P. Conference committee of the C.F. foundation recomendations (1980) Standardisation of lung function testing in children. J Pediatr 97:668–676
Godfrey S, Kamburoff PL, Nairn JN (1970) Spirometry lung volumes and airway resistance in normal children aged 5 to 18 years. Br J Dis Chest 64:15–24
Gupta CK, Mathur N (1982) Statistical models relating peak expiratory flow rates to age, height and weight in men and women. J Epidemiol Community Health 36:64–67
Hsu KHK, Jenkins DE, Hsi BP, Bourhofer E, Thompson V, Hsu FCF, Jacob SC (1979) Ventilatory function of normal children and young adults—Mexican-American, white and black. II Wright Peak Flow Meter. J Pediatr 95:192–196
Juhl B (1970) Pulmonary function investigations on 1011 school children using Wright's Peak Flow Meter. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 25:355–361
König P, Godfrey S (1973) Prevalence of exercise-induced bronchial lability in families of children with asthma. Arch Dis Child 48:513–538
Murray AB, Cooke CD (1963) Measurement of peak expiratory flow rates in 220 normal children from 4.5 to 18.5 years of age. J Pediatr 62:439–445
Nairn JR, Bennet AJ, Andrew JD, Macarthur P (1961) A study of respiratory function in normal school children. The peak flow rate. Arch Dis Child 36:253–258
Polgar G, Promadhat V (1971) Pulmonary function testing in children: techniques and standards. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 188–194
Weng T-R, Levison H (1969) Standards of pulmonary function in children. Am Rev Respir Dis 99:879–894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsanakas, J.N., Primhak, R.A., Milner, R.D.G. et al. Unexpectedly high peak expiratory flow rates in normal Greek children. Eur J Pediatr 141, 46–49 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00445668
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00445668