Abstract
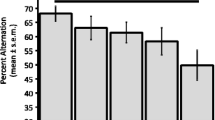
Performance on the radial-arm maze depends on the integrity of both cholinergic and dopaminergic systems. We have previously found that administration of either the nicotinic-cholinergic antagonist, mecamylamine, or the muscarinic-cholinergic antagonist, scopolamine, impairs choice accuracy in the radial-arm maze. Co-administration of the dopaminergic antagonist, haloperidol, ameliorated the performance deficit caused by scopolamine but exacerbated the deficit caused by mecamylamine. Furthermore, antagonism of the effect of scopolamine is due specifically to blockade of D1 receptors. In the present experiment behaviorally subthreshold doses of mecamylamine and the D2 antagonist raclopride impaired maze performance when administered together. No interactive effects were observed between mecamylamine and the D1 antagonist SCH 23390. Although several of the drug treatments studied significantly increased choice latency, an index of motor behavior, there was no perfect relationship between choice accuracy and choice latency. These data indicate that nicotinic-cholinergic and muscarinic-cholinergic systems interact selectively and differentially with D1 and D2 dopaminergic systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beatty WW, Rush JR (1983) Spatial working memory in rats: effects of monoaminergic antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:7–12
Clark D, White FJ (1987) Review: D1 dopamine receptor — the search for a function: a critical evaluation of the D1/D2 dopamine receptor classification and its functional implications. Synapse 1:374–388
Creese I (1987) Biochemical properties of CNS dopamine receptors. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology: the third generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 257–264
Eckerman DA, Gordon WA, Edwards JD, McPhail RC, Gage MJ (1980) Effects of scopolamine, pentobarbital and amphetamine on radial arm maze performance in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:595–602
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–96
Levin ED (1988a) Psychopharmacological effects in the radial-arm maze. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 12:169–175
Levin ED (1988b) Scopolamine interactions with D1 and D2 antagonists on radial-arm maze performance in rats. Behav Neural Biol 50:240–245
Levin ED, Castonguay M, Ellison GD (1987a) Effects of the nicotinic receptor blocker, mecamylamine, on radial arm maze performance in rats. Behav Neural Biol 48:206–212
Levin ED, Galen D, Ellison GD (1987b) Chronic haloperidol effects on radial arm maze performance and oral movements in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:1–6
McGurk SR, Levin ED, Butcher LL (1988) Cholinergic-dopaminergic interactions in radial-arm maze performance. Behav Neural Biol 49:234–239
McGurk SR, Levin ED, Butcher LL (1989) Cholinergic-dopaminergic interactions in radial-arm maze performance: role of nicotinic-cholinergic systems. Behav Neural Biol (in press)
Neter J, Wasserman W, Kutner MH (1985) Applied linear statistical models, 2nd ed. Irwin, Homewood, IL
Olton DS, Samuelson RJ (1976) Remembrance of places passed: spatial memory in rats. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Proc 2:292–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGurk, S.R., Levin, E.D. & Butcher, L.L. Radial-arm maze performance in rats is impaired by a combination of nicotinic-cholinergic and D2 dopaminergic antagonist drugs. Psychopharmacology 99, 371–373 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00445560
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00445560