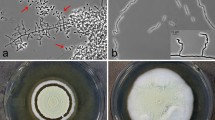
Abstract
Although ‘phycomycosis’ is a common disease of horses in northern Australia little is known about the causative fungi. In this paper the laboratory methods for diagnosis are described. These revealed 38 cases caused by Pythium sp. (Hyphomyces destruens), 6 cases caused by Basidiobolus haptosporus and 2 caused by Conidiobolus coronatus.
Laboratory studies on the chemotactic behaviour of zoospores of Pythium sp. showed that they were strongly attracted to both animal hairs and plant tissue. Because of this behaviour a simple baiting method using human hair was used to trap the fungus from water samples taken from different locations near Townsville, Queensland.
B. haptosporus was isolated by indirect culture from the faeces of 5 bearded dragon lizards (Amphibolurus barbatus) captured near a small creek near Brisbane.
By combining previously published information with data obtained in the present study, ecological life-cycles for Pythium sp., B. haptosporus and C. coronatus are proposed. They include mechanisms whereby horses may become infected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aston, H. I., 1973. Aquatic plants of Australia, Melbourne University Press, Melbourne.
Austwick, P. K. C. & Copland, J. W., 1974. Swamp cancer. Nature, London, 250: 84.
Bridges, C. H. & Emmons, C. W., 1961. A phycomycosis of horses caused by Hyphomyces destruens. J. Am. Vet. Med. Ass. 138: 579–589.
Bridges, C. H., Romane, W. M. & Emmons, C. W., 1962. Phycomycosis of a horse caused by Entomophthora coronata. J. Am. Vet. Med. Ass. 140: 673–677.
Burkitt, D. P., Wilson, A. M. M. & Jelliffe, D. B., 1964. Subcutaneous phycomycosis: a review of 31 cases seen in Uganda. Brit. Med. J. 1: 1669–1672.
Clark, B. M., 1968. The epidemiology of phycomycosis, in Systemic Mycoses, Ciba Foundation Symposium. Wolstenholme, C. E. W. & Porter, R. J. & Churchill, A., London.
Cogger, H. G., 1975. Reptiles and amphibians of Australia, A. H. & A. W. Reed Pty Ltd, Sydney.
Connole, M. D., 1973. Equine phycomycosis. Aust. Vet. J. 49: 214–215.
Coremans-Pelseneer, J., 1972. Epidemiologie de la basidiobolomycose. Ann. Soc. Belge Med. Trop. 52: 315–328.
Coremans-Pelseneer, J., 1973. Isolation of Basidiobolus meristosporus from natural sources. Mycopathologia 49: 173–176.
De Haan, J. & Hoogkamer, L. J., 1903. Hyphomycosis destruens equi. Arch. Wiss. Prakt. Tierheilk., Berlin 29: 395–410.
Drechsler, C., 1955. A southern Basidiobolus forming many sporangia from globose and from elongated adhesive conidia. J. Washington Acad. Sci. 45: 49–56.
Emmons, C. W., Binford, C. H. & Utz, J. P., 1970. Medical mycology, 2nd ed., Lee & Febiger, Philadelphia.
Emmons, C. W. & Bridges, C. H., 1961. Entomophthora coronata, the etiological agent of a phycomycosis of horses. Mycologia 53: 307–312.
Frey, D., 1965. Isolation of keratinophilic and other fungi from soils collected in Australia and New Guinea. Mycologia 57: 202–215.
Fuller, M. S., 1977. The zoospore, hallmark of the aquatic fungi. Mycologia 69: 1–20.
Greer, D. L. & Friedman, L., 1964. Effect of temperature on growth as a differentiating characteristic between human and nonhuman isolates of Basidiobolus species. J. Bacteriol. 88: 812–813.
Gugnani, H. C. & Okafor, J. I., 1980. Mycotic flora of the intestine and other internal organs of certain reptiles and amphibians with special reference to characterization of Basidiobolus isolates. Mykosen 23: 260–268.
Hendrix, F. F. & Campbell, W. A., 1973. Pythiums as plant pathogens. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 11: 77–98.
Hickman, C. J. & Ho, H. H., 1966. Bahaviour of zoospores in plant-pathogenic phycomycetes. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 4: 195–220.
Hutchins, D. R. & Johnston, K. G., 1972. Phycomycosis in the horse. Aust. Vet. J. 48: 269–278.
Ichitani, T. & Amemiya, J., 1980. Pythium gracile isolated from the foci of granular dermatitis in the horse (Equus caballus). Trans. Mycol. Soc. Japan 21: 263–265.
Johnston, K. G. & Henderson, A. W. K., 1974. Phycomycotic granuloma in horses in the Northern Territory. Aust. Vet. J. 50: 105–107.
Johnston, M. J., Soerensen, B., Saliba, A. M., Lacaz, C. de S., Bella Neto, J. & Cruz, J. M., 1967. Phycomycosis in a mule. Isolation of Entomophthora coronata. Arq. Inst. Biol., S. Paulo 34: 51–58.
Kevorkian, A. C., 1935. Studies in the Entomophthoraceae. I. Observations on the genus Conidiobolus. J. Agric. Univ. Puerto Rico 21: 191–220.
King, D. S., 1979. Systemics of fungi causing entomophthoramycosis. Mycologia 71: 731–745.
Krejzova, R., 1977. Enhancement of pathogenicity of the fungus Conidiobolus coronatus by means of multiple precultivation on insect hosts. Vestn. Cesk. Spol. Zool. 41: 105–113.
Miller, R. I., 1980. Studies on equine dermatoses in north Queensland with particular reference to phycomycosis. Ph.D. Thesis. James Cook University of North Queensland.
Miller, R. & Pott, B., 1980. Phycomycosis of the horse caused by Basidiobolus haptosporus. Aust. Vet. J. 56: 224–227.
Mugerwa, J. W., 1976. Subcutaneous phycomycosis in Uganda. J. Dermatol. 94: 539–544.
Porto, E. & Milanez, A. I., 1979. Basidiobolus isolados de repteis e anfibios no Brasil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 21: 237–246.
Restrepo, L. F., Moralles, L. F., Robledo, M., Restrepo, A., Tecnica, C. & Correa, De I., 1973. Rhinophycomycosis from Entomophthora coronata in horses. Information on 15 cases. Antioquia Medica 23: 13–25.
Shipton, W. A., Miller, R. I. & Lea, I. R., 1982. Cell wall, zoospore and morphological characteristics of Australian isolates of a Pythium sp. causing equine phycomycosis. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 79: 15–23.
Van Overeem, C., 1925. Ueber ein merkwuerdiges Vorkommen von Basidiobolus ranarum Eidam. Bull. Jardin Botanique de Buitenzorg 3rd series 7: 423–431.
Waterhouse, G. M., 1962. The zoospore. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 45: 1–20.
Witkamp, J., 1924. Bijdrage tot de kennis van de hyphomycosis destruens. Ned. Ind. Bld. v. Dierg. en Dierenteelt 36: 229–245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, R.I. Investigations into the biology of three ‘phycomycotic’ agents pathogenic for horses in Australia. Mycopathologia 81, 23–28 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443905
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443905