Abstract
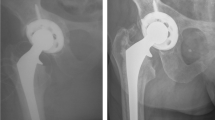
Acetabuloplasty with solid autologous femoral head graft for the treatment of hip dysplasia is an established method which creates the contained cavity needed to accommodate the artificial cup. In order to evaluate the medium- and long-term results of this method using a cementless hemispheric cup, 34 patients (39 hips) operated on between 1979 and 1986 were clinically and radiologically reviewed. The minimal follow-up was 5 years (average 7.6 years). The Harris hip score increased from 36 points preoperatively to 89 points 1 year postoperatively and to 85.1 at the last follow-up. On roentgenographic evaluation, all grafts had been incorporated and appeared to have tolerated the mechanical loading well. Partial resorption of the graft occurred in 22 of the 39 hips, mainly in the lateral non-loaded zone. Twenty-nine of the 39 acetabular components showed migration, on average 4.2 mm cranially and 1.8 mm medially; 92% occurred during the first 2 years, and thereafter it was not progressive. Smaller cups migrated consistently more than larger cups. A significant correlation was found between cup migration and the degree of bone coverage of the cup, and extensive migration occurred in most cases with cup coverage by the host bone of less than 40%–50% of the weight-bearing surface of the cup. Only one acetabular component was altered significantly, and another appears to have become loose. The use of normal-sized cups and cementless fixation medially in the primary acetabulum are thought to have contributed to our favorable mid- to long-term results. The substantial migration rate during the first 2 years was not related to loosening, and it did not continue to progress. Apparently, some migration must be accepted, and this does not necessarily correspond to cup loosening.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brånemark PI, Hansson HA, Adell R, Breine U, Lindström J (1977) Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of edentulous jaw, experience from a 10 year period. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 11 (Suppl) 16):1–28
Brooker AF, Bowermann JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH (1973) Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement: incidence and method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 55:1629–1632
Callaghan JJ, Dysart SH, Savory CG (1988) The uncemented porous-coated anatomic total hip prosthesis: two year results of a prospective consecutive series. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 70:337–342
Carret JP, Bonnin M, Dejour H (1990) Prothèses totales de hanche dans la coxarthrose. Acta Orthop Belg 56:387–393
Carter DR, Vasu R, Harris WH (1982) Stress distribution in the acetabular region II. Effects of cement thickness and metal backing of the total hip acetabular component. J Biomech 15:165–170
Chandler HP, Reineck FT, Wixson RL, McCarthy JC (1981) Total hip replacement in patients younger than thirty years old. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 63:1426–1434
Charnley J, Feagin JA (1973) Low-friction arthroplasty in congenital subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop 91:98–113
Conn RA, Peterson LF, Stauffer RN, Ilstrup DM (1985) Management of acetabular deficiency: long-term results of bone-grafting the acetabulum in total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Trans 9:451–452
Cook SD, Barrack RL, Thomas KA, Haddad RJ (1988) Quantitative analysis of tissue growth into human porous total hip components. J Arthroplasty 3:249–259
Coventry MB (1974) Selection of patients for total hip arthroplasty. In: Calandruccio RA (ed) AAOS Instructional Course Lectures, Vol 23. CV Mosby, St. Louis, pp 136–142
Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS (1979) Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 61:15–23
Davlin LB, Arnstutz HC, Tooke SM, Dorey FJ, Nasser S (1990) Treatment of osteoarthrosis secondary to congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 72:1035–1040
Dorr LD, Takai GK (1983) Total hip arthroplasties in patients less than forty-five years old. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 65:474–479
Dunn HK, Hess WE (1976) Total hip reconstruction in chronically dislocated hips. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 58:838–845
Gerber SD, Harris WH (1985) Femoral head autograft to augment acetabular deficiency in patients requiring total hip replacement; a minimum five year and average seven-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 68:1241–1248
Gross AE, McDermott AG, Lavoie MV, Marks P, Brooks PJ (1987) The use of allograft bone in revision total hip arthroplasty. In: Brand RA (ed) Proceedings of the 14th open scientific meeting of the Hip Society, 1986. CV Mosby, St. Louis, pp 47–54
Hadjari MH, Hollis JM, Hofmann OE, Flahiff CM, Nelson CL (1992) The effect of oversize on cup stability and bone coverage in acetabula with defects. AAOS Meeting, Washington
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 51:737–755
Harris WH (1974) Total hip replacement for congenital of the hip: technique. In: Harris WH (ed) Proceedings of the 2nd open scientific meeting of the Hip Society. CV Mosby, St.Louis, pp 251–265
Harris WH (1978) Total hip replacement for osteoarthritis secondary to congenital dysplasia or congenital dislocation of the hip. Int Orthop 2:127–138
Harris WH (1987) Bone grafting for acetabular deficiency in association with total hip replacement. In: Brand RA (ed) Proceedings of the 14th open scientific meeting of the Hip Society, 1986. CV Mosby, St. Louis, pp 39–46
Harris WH, McGann WA (1986) Loosening of the femoral component after use of the medullary plug cementing technique. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 68:1064–1066
Harris WH, Crothers O, Oh I (1977) Total hip replacement and femoral head bone grafting for severe acetabular deficiency in adults. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 59:752–759
Hedley AK, Gruen TA, Borden LS, Hungerford DS, Haberman E, Kenna RV (1987) Two year follow-up of the PCA noncemented total hip replacement. In: Brand RA (ed) Proceedings of the 14th open scientific meeting of the Hip Society, 1986. CV Mosby, St. Louis, pp 225–229
Jones LC, Hungerford DS (1987) Cement disease. Clin Orthop 225:192–198
Knight JL, Fucjii K, Atwater R, Grothaus L (1993) Bone-grafting for acetabular deficiency during primary and revision total hip arthroplasty. A radiographic and clinical analysis. J Arthroplasty 8:371–382
Kwong LM, Jasty M, Harris WH (1993) High failure rate of bulk femoral had allografts in total hip acetabular reconstructions at 10 years. J Arthroplasty 8:341–346
Lewalle J, Hebrant A (1990) Etude multicentrique belge des résultats des arthroplasties totales pour luxation congénitale invétéré de la hanche. Acta Orthop Belg 56:395–405
Marti R, Schüller HM, Steijn MJA (1994) Superolateral bone grafting for acetabular deficiency in primary total hip replacement and revision. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 76:728–734
Matsuno T, Masuda T, Hasegawa I, Kanno T, Ichioka Y, Matsuno S, Hirai K (1989) A long-term follow-up study of total hip replacement with bone graft: correlations between roentgenographic measurement and hip mobility. Arch Orthp Trauma Surg 108:14–21
McQuerry FG, Johnston RC (1988) Coxarthrosis after congenital dysplasia: treatment by total hip arthroplasty without acetabular bone grafting. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 70:1140–1144
Mendes DG (1981) Total hip arthroplasty in congenital dislocated hips. Clin Orthop 161:163–169
Morscher E (1983) Cementless total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 181:76–91
Morscher E (1991) Hydroxyapatite coating of prostheses. Editorial. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 73:705–706
Morscher E (1992) Current status of acetabular fixation in primary total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 274:172–193
Morscher E, Masar Z (1988) Development and first experience with an uncemented press-fit cup. Clin Orthop 232:96–103
Morscher E, Schmassmann A (1983) Failures of total hip arthroplasty and probable incidence of revision surgery in the future. Arch Orthp Trauma Surg 101:137–149
Morscher E, Dick W, Kernen V (1982) Cementless fixation of polyethylene acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 99:223–232
Morscher E, Bereiter H, Lampert C (1989) Cementless press-fit cup: principles, experimental data and three year follow-up study. Clin Orthop 249:12–20
Mulroy RD, Harris WH (1990) Failure of acetabular autogenous grafts in total hip arthroplasty: increasing incidence: a follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 72:1536–1540
Mulroy RD, Harris WH (1990) The effect of improving cementing technique on component loosening in total hip replacement. An eleven year radiographic review. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 72:1536–1540
Otto KB, Baars GW, Nieder E (1989) Alloarthroplastische Therapie der kongenitalen Hüftgelenksdysplasie. Orthopäde 18:470–477
Philipps TW, Rao DR (1990) Bateman bipolar hips with autologous bone graft reinforcement for dysplastic acetabula. Clin Orthop 251:104–112
Ritter MA, Trancick TM (1985) Lateral acetabular bone graft in total hip arthroplasty: a three to eight year follow-up study without internal fixation. Clin Orthop 193:156–159
Sanzen L, Fredin HO, Johnsson K, Nosslin B (1988) Fate of bone grafts in acetabular roof reconstructions assessed by roentgenography and scintigraphy. Clin Orthop 231:103–109
Schüller HM, Dalstra M, Huiskes R, Marti R (1993) Total hip reconstruction in acetabular dysplasia. A finite element study. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 75:468–474
Sharp IK (1971) Acetabular dysplasia: the acetabular angle. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 43:268–272
Shigenori I, Ejh G, Mifumi A (1994) Total hip replacement using femoral neck bone to graft the dysplastic acetabulum. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 76:735–739
Silber DA, Engh CA (1990) Cementless total hip arthroplasty with femoral head bone grafting for hip dysplasia. J Arthroplasty 5:231–240
Sutherland CJ, Wilde AH, Borden LS, Marks KE (1982) A ten year follow-up of one hundred consecutive Müller curved-stem total hip replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 64:970–982
Trancick TM, Stulberg BN, Wilde AH, Feiglin D (1985) Allografting of deficient acetabulae in revision total hip arthroplasty. Read at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Las Vegas
Vasu R, Carter DR, Harris WH (1982) Stress distributions in the acetabular region. I. Before and after total joint replacement. J Biomech 15:155–164
Wiberg G (1939) Studies on dysplastic acetabular and congenital subluxation of the hip joint. Acta Chir Scand 83 (Suppl 58):1–22
Wilson MG, Nikpoor N, Aliabadi P, Poss R, Weissman BN (1989) The fate of acetabular allografts after bipolar revision arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 71:1469–1476
Wilson-MacDonald J, Morscher E, Masar Z (1990) Cementless uncoated polyethylene acetabular components in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 72:423–430
Wolfgang GL (1990) Femoral head autografting with total hip arthroplasty for lateral acetabular dysplasia: a twelve year experience. Clin Orthop 255:173–185
Woolson ST, Harris WH (1983) Complex total hip replacement for dysplasia or hypoplasia hips using miniature or microminiature components. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 65:1099–1108
Zlatic M, Radojevic B, Lazovic C (1990) Reconstruction of the hypoplastic acetabulum in Cementless arthroplasty of the hip. Int. Orthop 14:371–375
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hintermann, B., Morscher, E.W. Total hip replacement with solid autologous femoral head graft for hip dysplasia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 114, 137–144 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443387
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443387