Abstract
By the present investigations the host range of Achlya orion Coker and Couch has been extended to, Puntius sophore, Puntius ticto, Puntius conchonius, Puntius sarana, Chanda ranga, Channa marulius, Channa punctatus, Notopterus notopterus, Labeo rohita, Colisa lalia and Anabas testudineus; 11 freshwater fishes.
The ability of certain Saprolegniaceous fungi to parasitise fish has been reported by several investigators viz., Clinton (2), Tiffney (21, 22), Tiffney & Wolf (23), Gopalakrishnan (3), Vishniac & Nigrelli (24), Scott & O'Bier (7), Bhargava et al (1) and Srivastava & Srivastava (10.20) etc. These fungi are known to attack fish eggs, fry, fingerling and adult fishes and as a general rule the fungal infection starts when the host gets injured either mechanically or as result of infections other than fungal which often result in epidemics causing 100% mortality of the infected hosts (Scott & O'Bier 7).
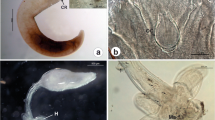
During the course of an investigation on fungi associated with fish diseases, author observed the severe fungal infections of Colisa fasciatus (Bl.) and Anabas testudineus (Bl.) in the waters of Ramgarh Lake, Gorakhpur, causing heavy mortality of the infected hosts. The fungus was identified as Achlya orion Coker Couch and its pathogenicity was also established by conducting laboratory inoculation experiments on the lines of Scott & O'Warren (8); (Srivastava & Srivastava, 14).
In view of the above observations, it seemed desirable to investigate the host range of this mould on accurately identified hosts in order to asses the extent of damage done to such fishes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava, K. S., K. Swarup & C. S. Singh, 1971. Fungi parasitic on certain fresh water fishes of Gorakhpur. Indian Biologists. 3: 65–69.
Clinton, G. P. 1894. Observations on a fungus (Saprolegnia) infesting fish. Bull. U. S. Fish Com. 13: 163–172.
Gopalakrishnan, V. 1963. Controlling pets and diseases of cultured fishes. Indian. Livstk. 1(1): 51–54.
Ibid. 1964. Recent developments in prevention and control of parasites of fishes cultured in Indian water. Proc. of Zool. Soc. India. 17(1): 85–100.
Johnson, T. W. Jr. 1956. The genus Achlya-Morphology and Taxonomy Univ. of Michigan Press. Ann., Arbor. 180 pp.
Jhingran, V. G. 1975. Fish and fisheries of India., Hindustan Publ. House of India, Delhi.
Scott, W. W. & A. H. O'Bier. 1962. Aquatic fungi associated with diseased tropical fish and fish eggs. Prog. Fish. Cult. 24: 3–15.
Scott, W. W. & C. O'Warren, 1964. Studies of the host range and chemical control of fungi associated with diseased tropical fish., Dev. in Indus. Microbiol. 5: 109–123.
Srivastava, G. J. 1968. Fishes of Eastern, U. P., Vishwavidyalaya Praka-shan, Bhairavnath, Varanasi (India).
Srivastava, G. C. & R. C. Srivastava, 1975. Two fungal parasites of the eggs of Channa striatus (Bl). Curr. Sci. 44(22): 817–818.
Ibid., 1976. Ability of Achlya flagellata Coker parasitising-certain fresh water fishes, Geobios, 3: 139–140.
Ibid., 1976. Fungal infection of the eggs of Channa punctatus (Bl) Geobios, 3: 160.
Ibid. 1976. A new host record of Branchiomyces sanguinis Plehn, Curr. Sci. 45(24): 874.
Ibid. 1976. A note on the destruction of the eggs of Cyprinus carpio var. communis by the members of Saprolegniaceae Sci and Cult. 42(12): 612–614.
Ibid. 1977. Host range of Saprolegnia ferax (Gruith) Thuret on certain fresh water teleosts, Curr. sci. 46(3): 87.
Ibid. 1977. Dictyuchus anomalus Nagai, a new pathogen of fresh water teleosts, Curr. Sci. 46(4): 118.
Ibid., 1977., Ability of Saprolegniaceous fungi to parasitise Colisa fasciatus (Bl.& Schn). Geobios., 4(1): 31–32.
1977. Host range of Achlya prolifera Nees De Bary on certain fresh water teleosts., Mycopathologia, 61(1): 61–62.
Ibid. 1977. Isoachlya ansiospora var. indica — a new pathogen of fresh water fishes and fish eggs, Technology, 14(1): (In press).
Srivastava, R. C. and G. C. Srivastava., 1977. Achlya caroliniana Coker as a fish pathogen. Geobios., 4: 156.
Tiffney, W. N. 1939a. The host range of Saprolegnia parasitica Coker. Mycologia, 31: 310–321.
Tiffney, W. N. 1939b. The identity of certain species of Saprolegniaceae parasitic to fish. J. Elisha Mitchell. Sci. Soc. 55: 134–153.
Tiffney, W. N. and F. T. Wolf., 1937. Achlya flagellata — as a fish parasite J. Elisha Mitchell. Sci. Soc. 53: 298–300.
Vishniac, H. S. and R. F. Nigrelli. 1957. The ability of Saprolegnia to parasitise Platyfish. Zoologica., 42: 131–134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, R.C. Host range of Achlya orion Coker & Couch on certain freshwater fishes. Mycopathologia 64, 49–51 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443089
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443089