Abstract
39 normal full term infants were fed during the first four months of life with three different diets based on the same formula of heated soy-flour fortified with DL-methionine. Each diet supplied 100 kcal/kg/day and gave about 2.5 (11 infants), 4.0 (19 infants) or 5.5 (9 infants) g/kg/day of soy-protein.
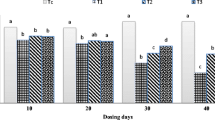
After four months, growth was slightly lower in infants fed 2.5 g/kg/day of protein but was similar in the other two groups. Haematological parameters were in the normal range in all three groups. Serum gammaglobulin and immunoglobulin levels increased with the increase of dietary protein. The highest levels of gammaglobulin (0.51±0.16 mg/100 ml) and IgG (463.13±210.17 mg/100 ml) were observed in infants fed 5.5 g/kg/day of soy-protein and were similar to those previously observed in infants fed 2.5 g/kg/day of cows-milk protein. Morbidity was reduced with the increase of serum gamma-globulin and immunoglobulins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Nutrition: Special diets for infants with inborn errors of metabolism. Pediatrics 57, 783 (1976)
Bates, R. D., Barrett, W. W., Anderson, D. W. Jr., Saperstein, S.: Milk and soy formulas: a comparative growth study. Ann. Allergy 26, 577 (1968)
Cherry, F. F., Cooper, M. D., Stewart, R. A., Platou, R. V.: Cow versus soy formulas. Am. J. Dis. Child. 115, 677 (1968)
Dean, M. E.: A study of normal infants fed a soya protein isolate formula. Med. J. Aust. 1, 1289 (1973)
Fomon, S. J.: Comparative study of human milk and a soya bean formula in promoting growth and nitrogen retention in infants. Pediatrics 24, 577 (1959)
Fomon, S. J., Owen, G. M., Thomas, L. N.: Methionine, valine and isoleucine requirements during infancy: growth and nitrogen balance study with normal fullterm infants receiving soya bean protein. Am. J. Dis. Child. 108, 487 (1964)
Fomon, S. J., Thomas, L. N., Filer, L. J. Jr., Anderson, T. A., Bergman, K. E.: Requirements for protein and essential aminoacids in early infancy. Studies with a soy-isolate formula. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 62, 33 (1973)
Fomon, S. J.: Infant nutrition. Philadelphia: Saunders Co. 1974
Gaull, G. E., Rassin, D. K., Räihä, N. C. R., Heinonen, K.: Milk protein quantity and quality in low-birth-weight infants. III. Effects on sulfur aminoacids in plasma and urine. J. Pediatr. 90, 348 (1977)
Glaser, J., Johnstone, D. E.: Soy bean milk as a substitute for mammalian milk in early infancy. Ann. Allergy 10, 433 (1972)
Graham, G. G., Placko, R. P., Morales, E., Acevedo, G., Cordano, A.: Dietary protein quality in infants and children. VI. Isolated soy protein milk. Am. J. Dis. Child. 120, 419 (1970)
Hansen, A. E., Stewart, R. A. Hughes, G., Söderhjelm, L.: The relation of linoleic acid to infant feeding. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 51, Suppl. 137 (1962)
Hansen, A. E., Wiese, H. F., Boelsche, A. N., Haggard, M. E., Adam, D. J. D., Davis, H.: Role of linoleic acid in infant nutrition. Clinical and chemical study of 428 infants fed on milk mixtures varying in kind and amount of fat. Pediatrics 31, 171 (1963)
Kay, J. L., Daeschwer, C. W., Desmond, M. M.: Evaluation of infants fed soy bean and evaporated milk formulae from birth to three months. Am. J. Dis. Child. 100, 264 (1960)
Leake, R. D., Schroder, K. C., Benton, D. A., Oh, W.: Soy-based formula in the treatment of infantile diarrhoea. Am. J. Dis. Child. 127, 374 (1974)
Omans, W. B., Leuterer, W., Gyorgy, P.: Feeding value of soy milks for premature infants. J. Pediatr. 62, 98 (1963)
Pilgrim, U., Fontanellaz, H. P., Evers, G., Hitzig, W. H.: Normal values of immunoglobulins in premature and in full-term infants, calculated as percentile. Helv. Paediatr. Acta 30, 121 (1975)
Rassin, D. K., Gaull, G. E., Heinonen, K., Räihä, N. C. R.: Milk protein quantity and quality in low-birth-weight infants. II. Effects on selected aliphatic aminoacids in plasma and urine. Pediatrics 59, 407 (1977)
Rassin, D. K., Gaull, G. E., Räihä, N. C. R., Heinonen, K.: Milk protein quantity and quality in low-birth-weight infants. IV. Effects on tyrosine and phenylalanine in plasma and urine. J. Pediatr. 90, 356 (1977)
Scriver, C. R., Rosenberg, L. E.: Aminoacid metabolism and its disorders, p. 42. Philadelphia: Saunders Co. 1973
Zoppi, G., Zamboni, G., Siviero, M., Bellini, P.: Gammaglobulin level and dietary protein intake during first year of life. Pediatrics 62, 1010 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Reported in part at the “International Symposium on Nutritional problems in Childhood”, Modena (Italy, May 5–7, 1978)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zoppi, G., Zamboni, G., Bassani, N. et al. Gammaglobulin level and soy-protein intake in early infancy. Eur J Pediatr 131, 61–69 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442786
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442786